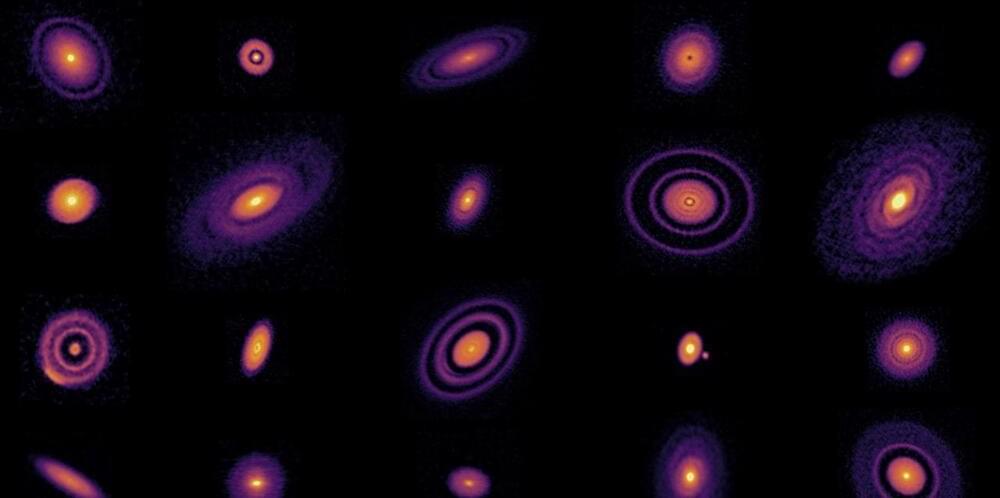
Now look out past the sun, way beyond. Most of the stars harbor planets of their own. Astronomers have spotted thousands of these distant star-and-planet systems. But strangely, they have so far found none that remotely resemble ours. So the puzzle has grown harder: Why these, and why those?
The swelling catalog of extrasolar planets, along with observations of distant, dusty planet nurseries and even new data from our own solar system, no longer matches classic theories about how planets are made. Planetary scientists, forced to abandon decades-old models, now realize there may not be a grand unified theory of world-making—no single story that explains every planet around every star, or even the wildly divergent orbs orbiting our sun. “The laws of physics are the same everywhere, but the process of building planets is sufficiently complicated that the system becomes chaotic,” said Alessandro Morbidelli, a leading figure in planetary formation and migration theories and an astronomer at the Côte d’Azur Observatory in Nice, France.
Still, the findings are animating new research. Amid the chaos of world-building, patterns have emerged, leading astronomers toward powerful new ideas. Teams of researchers are working out the rules of dust and pebble assembly and how planets move once they coalesce. Fierce debate rages over the timing of each step, and over which factors determine a budding planet’s destiny. At the nexus of these debates are some of the oldest questions humans have asked ourselves: How did we get here? Is there anywhere else like here?