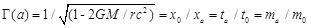To achieve interstellar travel, the Kline Directive instructs us to be bold, to explore what others have not, to seek what others will not, to change what others dare not. To extend the boundaries of our knowledge, to advocate new methods, techniques and research, to sponsor change not status quo, on 5 fronts, Legal Standing, Safety Awareness, Economic Viability, Theoretical-Empirical Relationships, and Technological Feasibility.
There is one last mistake in physics that needs to be addressed. This is the baking bread model. To quote from the NASA page,
“The expanding raisin bread model at left illustrates why this proportion law is important. If every portion of the bread expands by the same amount in a given interval of time, then the raisins would recede from each other with exactly a Hubble type expansion law. In a given time interval, a nearby raisin would move relatively little, but a distant raisin would move relatively farther — and the same behavior would be seen from any raisin in the loaf. In other words, the Hubble law is just what one would expect for a homogeneous expanding universe, as predicted by the Big Bang theory. Moreover no raisin, or galaxy, occupies a special place in this universe — unless you get too close to the edge of the loaf where the analogy breaks down.”
Notice the two qualifications the obvious one is “unless you get too close to the edge of the loaf where the analogy breaks down”. The second is that this description is only correct from the perspective of velocity. But there is a problem with this.
Look up in the night sky, and you can see the band of stars called the Milky Way. It helps if you are up in the Rocky Mountains above 7,000 ft. (2,133 m) away from the city lights. Dan Duriscoe produced one of the best pictures of our Milky Way from Death Valley, California that I have seen.
What do you notice?
I saw a very beautiful band of stars rising above the horizon, and one of my friends pointed to it and said “That is the Milky Way”. Wow! We could actually see our own galaxy from within.
Hint. The Earth is half way between the center of the Milky Way and the outer edge.
What do you notice?
We are not at the edge of the Milky Way, we are half way inside it. So “unless you get too close to the edge of the loaf where the analogy breaks down” should not happen. Right?
Wrong. We are only half way in and we see the Milky Way severely constrained to a narrow band of stars. That is if the baking bread model is to be correct we have to be far from the center of the Milky Way. This is not the case.
The Universe is on the order of 103 to 106 times larger. Using our Milky Way as an example the Universe should look like a large smudge on one side and a small smudge on the other side if we are even half way out. We should see two equally sized smudges if we are at the center of the Universe! And more importantly by the size of the smudges we could calculate our position with respect to the center of the Universe! But the Hubble pictures show us that this is not the case! We do not see directional smudges, but a random and even distribution of galaxies across the sky in any direction we look.
Therefore the baking bread model is an incorrect model of the Universe and necessarily any theoretical model that is dependent on the baking bread structure of the Universe is incorrect.
We know that we are not at the center of the Universe. The Universe is not geocentric. Neither is it heliocentric. The Universe is such that anywhere we are in the Universe, the distribution of galaxies across the sky must be the same.
Einstein (TV series Cosmic Journey, Episode 11, Is the Universe Infinite?) once described an infinite Universe being the surface of a finite sphere. If the Universe was a 4-dimensional surface of a 4-dimensional sphere, then all the galaxies would be expanding away from each other, from any perspective or from any position on this surface. And, more importantly, unlike the baking bread model one could not have a ‘center’ reference point on this surface. That is the Universe would be ‘isoacentric’ and both the velocity property and the center property would hold simultaneously.
Previous post in the Kline Directive series.
Next post in the Kline Directive series.
—————————————————————————————————
Benjamin T Solomon is the author & principal investigator of the 12-year study into the theoretical & technological feasibility of gravitation modification, titled An Introduction to Gravity Modification, to achieve interstellar travel in our lifetimes. For more information visit iSETI LLC, Interstellar Space Exploration Technology Initiative.
Solomon is inviting all serious participants to his LinkedIn Group Interstellar Travel & Gravity Modification.