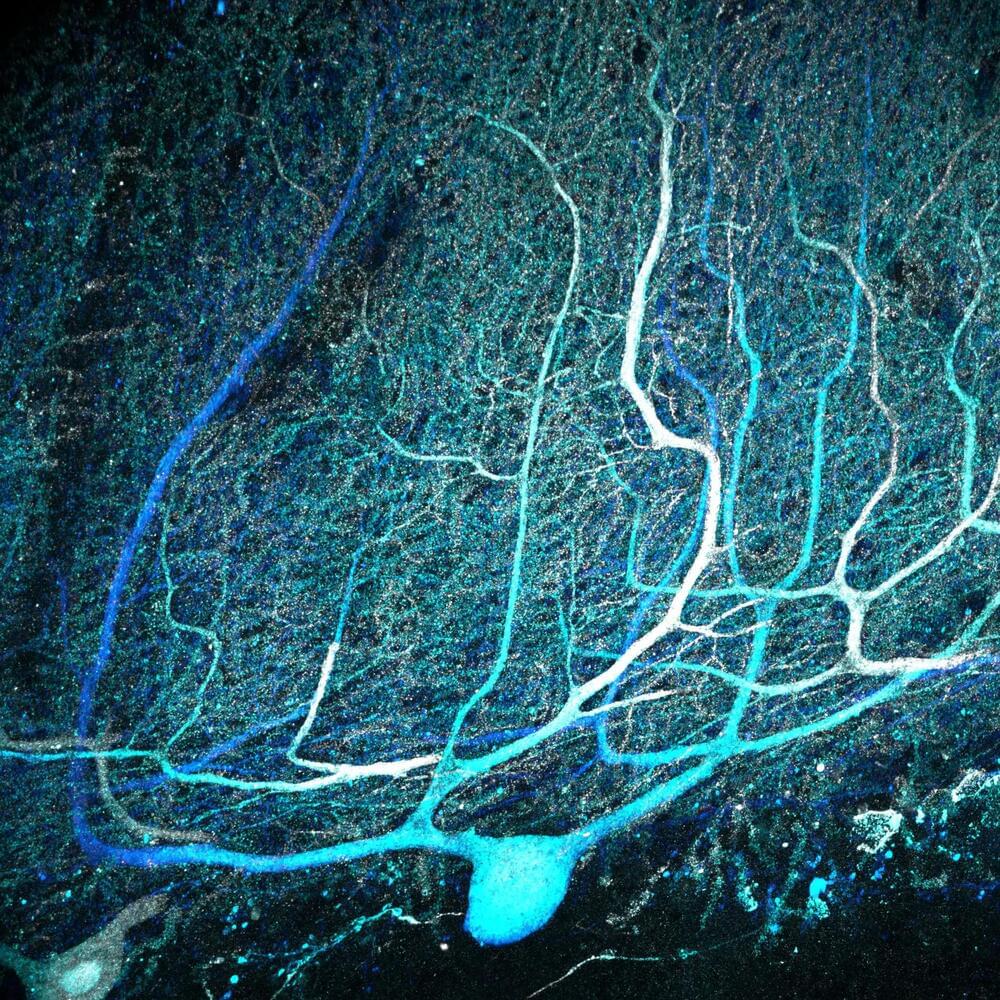
Images of thousands of Purkinje cells reveal that almost all human cells have multiple primary dendrites. These structures, when observed in mice, facilitate connections with multiple climbing fibers originating from the brain stem.
In 1906, the Spanish researcher Santiago Ramón y Cajal received the Nobel Prize for his trailblazing exploration of the microscopic structures of the brain. His renowned illustrations of Purkinje cells within the cerebellum depict a forest of neuron structures, with multiple large branches sprouting from the cell body and splitting into beautiful, leaf-like patterns.
Despite these early portrayals showing multiple dendrites branching out from the cell body, the enduring consensus among neuroscientists is that Purkinje cells possess only a single main dendrite that forms a connection with a lone climbing fiber originating from the brain stem. However, a recent study from the University of Chicago, recently published in the journal Science, reveals that Cajal’s sketches were indeed accurate — practically all Purkinje cells in the human cerebellum have multiple primary dendrites.