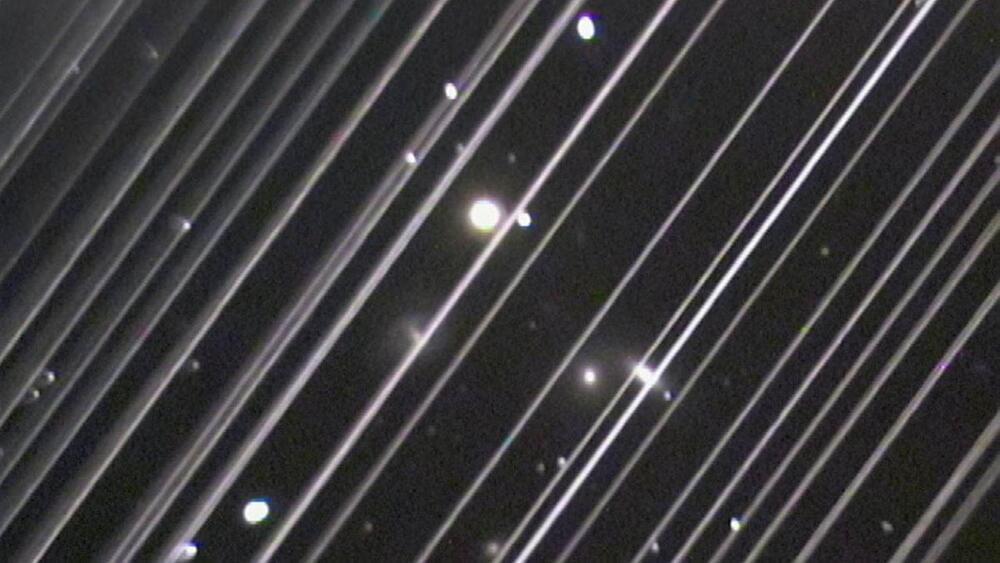
Even if we can dodge a disaster in orbit by responsibly de-orbiting derelict satellites, many scientists are concerned that the number of objects circling our planet could still do harm: When they deorbit, they could deposit a significant flux of metals that could alter the chemical makeup of Earth’s atmosphere.
“Effects on astronomy are just the tip of the iceberg,” said Barentine, who says we may be fast approaching a turning point where tragedy becomes imminent, either in space due to a collision or on the ground from falling debris. “Space policy-making moves far too slowly to effectively deal with all of this.”
“Right now, there’s not a lot to look forward to that is positive,” he added. “If the New Space Age goes badly in the end, history will not look favorably on it.”