Researchers can print cells and biomaterials that make up human tissues, but there’s still a long way to go before fully functional organs can be made to order.

What can 3D printing do for medicine? The “sky is the limit,” says Northwell Health researcher Dr. Todd Goldstein.

Swarming 3D printed smarticles unlock new method of robot locomotion and may be able to form load-bearing structures
An accidental discovery about construction staples led to the development of the swarming robots. Nick Gravish, a doctoral student at Georgia Tech working on a project with the Army Research Laboratory, found that if these heavy duty staples were poured into a box with removable sides, they would self-assemble into tower structures that will stay standing even if the box was disassembled. This, he realised, meant that entangling simple structures could lead to the formation of a composite structure with mechanical properties well beyond those of the original structures.
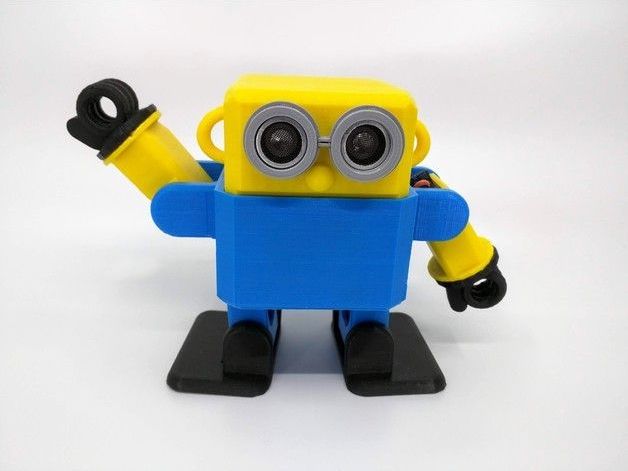

Brings children and people closer to technology : learn the logical connection between code and action, and by assembling it they understand how its components, and electronics work.
Buy a Otto DIY Kit robot you will be able to build your own custom robot in as little as one hour with your kids!
Otto DIY is more than a robot: you will learn how robots works, you will build and code your own Otto and his personality!The robot is completely open source, Arduino compatible, 3D printable, and with a social impact mission to create an inclusive environment for all kids.
Otto DIY brings children and people closer to technology : learn the logical connection between code and action, and by assembling it they understand how its components, and electronics work.

The future of bioprinting looks promising from a technical and scientific perspective, but it’s far from clear how it will be regulated.

Choice is the one thing our creators gave us. Me, personally I prefer hemp, and not just because I smoke the female version for medicinal reasons, but because scientifically it makes sense, and can help unscrew #AmericanFarmers…Yes we need more forests, not less. However, we don’t need to use trees, when we have hemp. Pembient can 3D Print ivory, thus making animal Ivory obsolete, yet people still kill for Ivory. We can make wood products from hemp, yet we still fell trees. #HowDumbAreWe
Eco-Friendly Our hemp is grown using sustainable methods, which helps eliminate deforestation.
Made in the USA All hemp growth and material production is conducted in the United States of America.
Multiple Uses HempWood can.

Many of you are way ahead of me on this topic. I design 3D printed parts for aircraft, but I didn’t think that functional, transplantable 3D printed human organs were this advanced. This article is about a heart, but it is currently only the size of a rabbit heart. Sizing it up to human size and testing are next, but this is much farther along than I expected.
Rapid creation of replacement organs, using the patient’s own cells to circumvent the body rejecting the transplant, is a direct contributor to superlongevity.
Researchers from Tel Aviv University have created the world’s first 3D printed heart, using cellular materials from the patient.