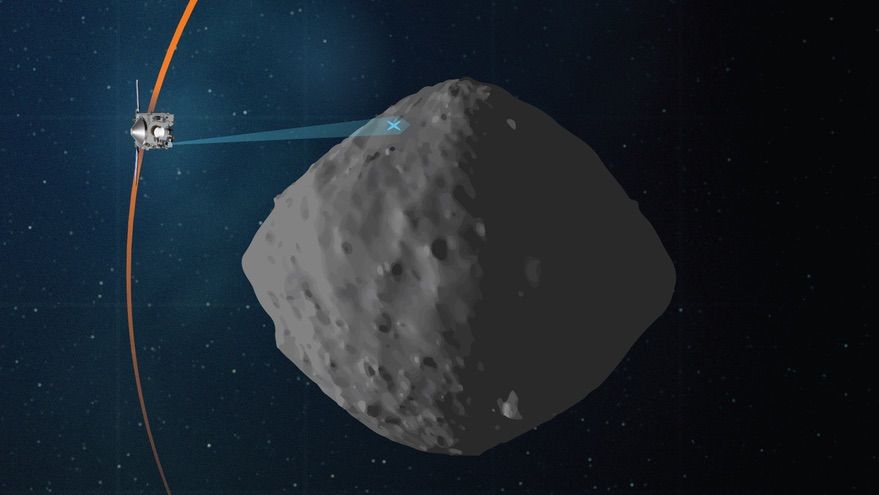
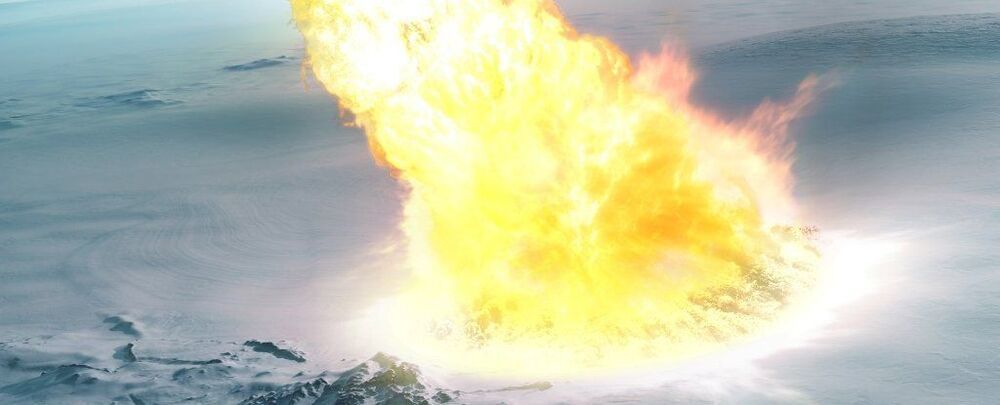
Each day this week, we will be providing updates on a fictional impact scenario playing out at the International Planetary Science Conference in College Park, Maryland. This scenario is designed to help key decision makers practice for a real asteroid impact. Currently, there is no known asteroid with a significant probability of impacting Earth in the next century. Day 5: What Was This Exercise All About? This week at the 2019 Planetary Defense Conference, conference participants were tasked with responding to a hypothetical asteroid impact scenario in which they have eight years to stop an asteroid on a collision course with Earth. Every day, the audience heard updates — at one point, they weren’t sure whether the 140–260-meter-wide (500−850 feet) asteroid was actually going to hit Earth. Once they found out it was on a certain collision, NASA and space agencies around the world decided to send a fleet of kinetic impactors to deflect the asteroid. The kinetic impactors hit the asteroid…but ended up splitting off a chunk, which, on Day 4 (four years from impact), again was headed towards Earth.
While headlines routinely report on “close shaves” and “near-misses” when near-Earth objects (NEOs) such as asteroids or comets pass relatively close to Earth, the real work of preparing for the possibility of a NEO impact with Earth goes on mostly out of the public eye.