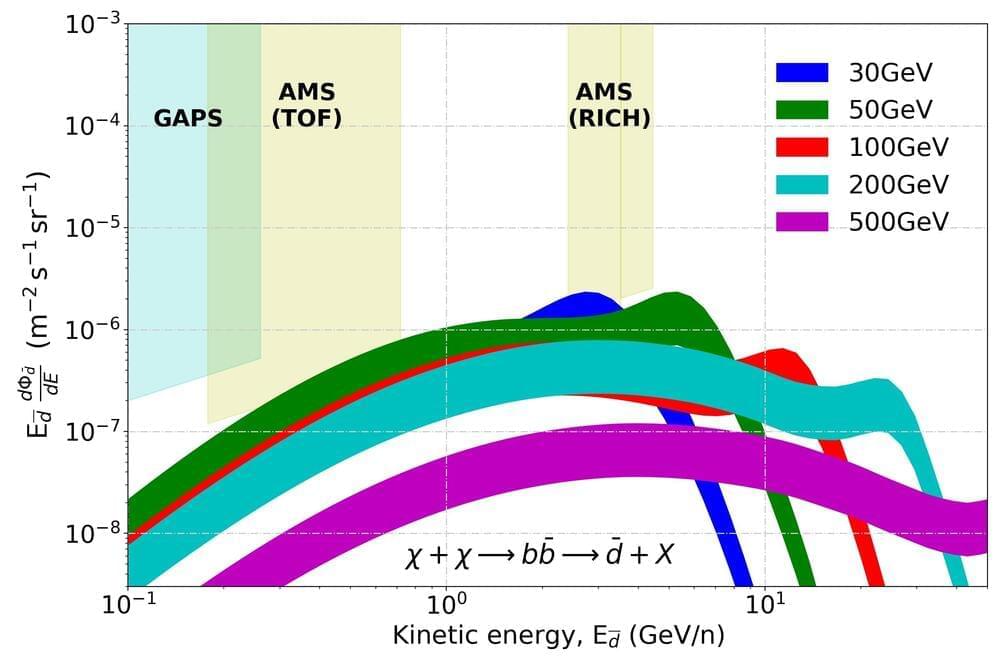
I think Stephen hawking was right about the Einstein physics of our universe but at the quantum mechanical realm it breaks all the rules with infinite energy.
The usual theory of inflation breaks down in eternal inflation. We derive a dual description of eternal inflation in terms of a deformed Euclidean CFT located at the threshold of eternal inflation. The partition function gives the amplitude of different geometries of the threshold surface in the no-boundary state. Its local and global behavior in dual toy models shows that the amplitude is low for surfaces which are not nearly conformal to the round three-sphere and essentially zero for surfaces with negative curvature. Based on this we conjecture that the exit from eternal inflation does not produce an infinite fractal-like multiverse, but is finite and reasonably smooth.