A supernova in a nearby galaxy resulted in a compact massive object, providing a link between supernovae, black holes, and neutron stars.



The Dark Energy Survey took an entire decade to produce a value for the cosmological constant—and it’s smaller than you might think! There were other stories as well, including one about primeval black holes, and because I am inescapably drawn by the relentless gravity of black hole news, it’s included below, along with two other stories related in one way or another to heads.
Dogs’ primary sense is olfactory, and if their visual perception flags something interesting in the environment, the first thing they do is stick their cute little noses in it. But the opposite is true for humans; we are able to perceive millions of colors, but only a fraction of the olfactory stimuli dogs are usually way too engaged with.
If you smell natural gas in your house, you go looking for the source with your cute little retinas and their super-dense constellation of photoreceptive cells to determine that one of the gas knobs on the stove is open. Researchers at Johns Hopkins University grew retinal organoids in a lab to determine how human visual perception develops.

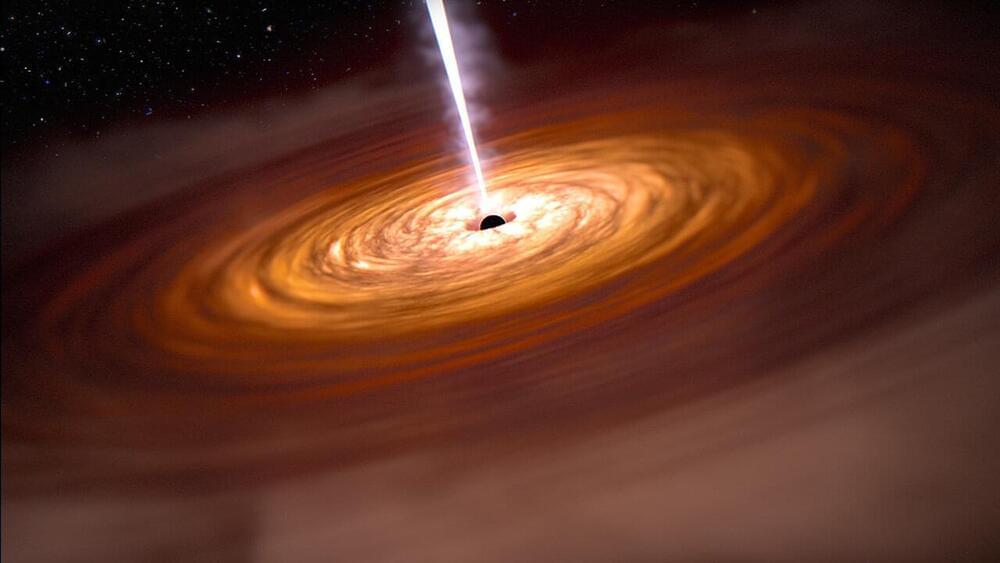
Black holes are very important for galactic formation.
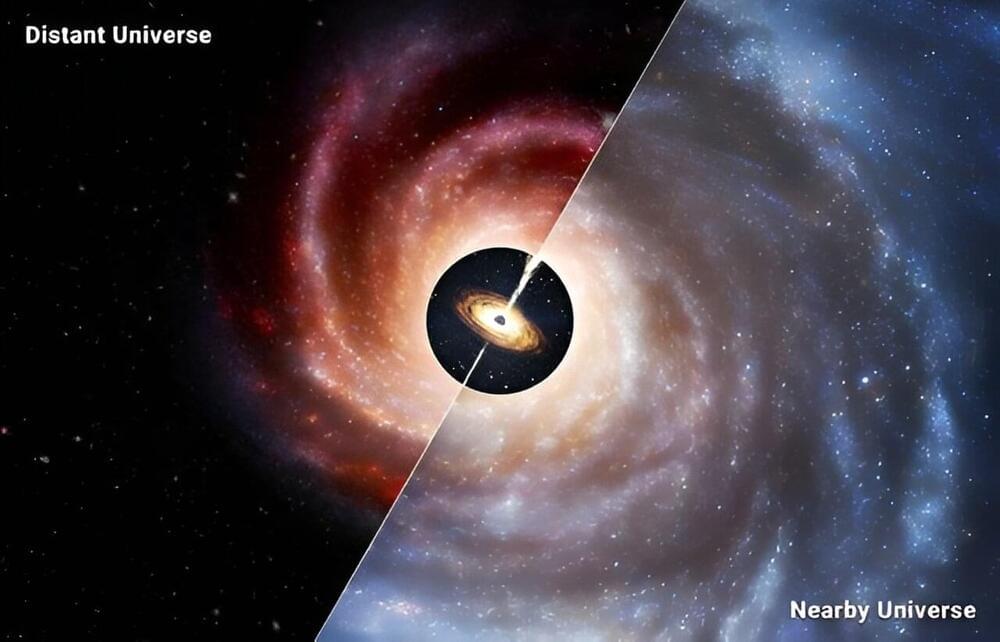
Astronomers have discovered that the supermassive black holes in the centers of early galaxies are much more massive than expected. These surprisingly hefty black holes offer new insights into the origins of all supermassive black holes, as well as the earliest stages of their host galaxy’s lives.
In nearby, mature galaxies like our Milky Way, the total mass of stars vastly outweighs the mass of the big black hole found at the galaxy’s center by about 1,000 to 1. In the newfound distant galaxies, however, that mass difference drops to 100 or 10 to 1, and even to 1 to 1, meaning the black hole can equal the combined mass of its host galaxy’s stars.
This picture of unexpectedly massive black holes in fledgling galaxies comes from the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST), NASA’s latest flagship observatory. Until JWST, which launched in late 2021, astronomers were generally limited in their studies of distant black holes to stupendously bright quasars, composed of monster, matter-devouring black holes that completely outshine the stars in their host galaxies.
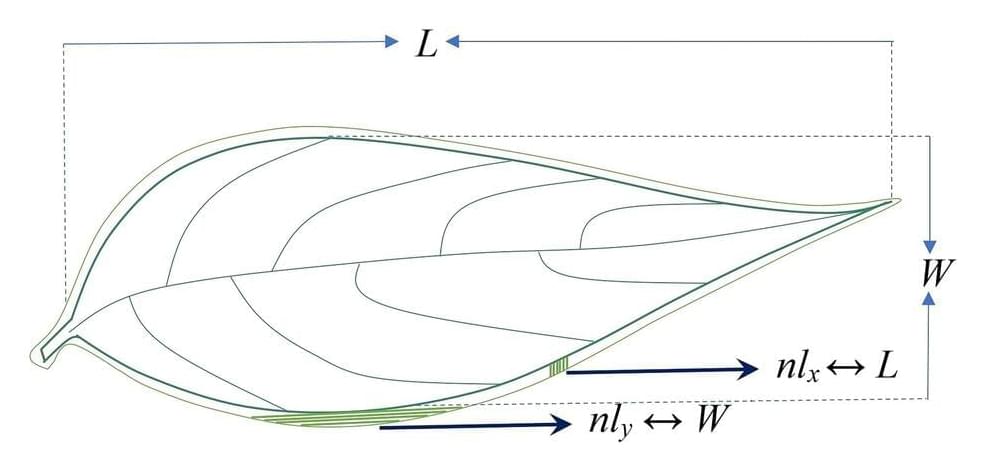
Complexity of biological forms has fascinated humankind over the years. Different species of plants have different leaf shapes. Have you ever wondered why it is so? Why does this shape diversity exist? Plants can change their leaf shapes over time and space. But how?
Does the distinct shape of leaf forms play a significant role in energy optimization? In fact, the shape of leaves has a lot to do with adapting to their surrounding environment. How is the unfolding of shape related to the evolutionary process of nature? These intriguing questions have led us to focus on quantitative approaches to the complexity of plant leaves.
Quantifying leaf shapes using Euclidean shapes, such as circles, triangles, etc., are appropriate to only a few plant species. Therefore, various quantitative measures of leaf shapes have been developed with varying accuracy. But Is the shape of an object really its actual shape? Visual perception of definite shape or geometry of physical objects is only an abstraction.
NASA scientists have identified unexpectedly massive clouds of cold gas within the spiral galaxy NGC 4,945, located 13 million light-years away.
As per the release, the revelation of this cold gas serves as the discovery of a “galactic fossil.”
The observations suggest that the gas likely rushed through this galaxy following the outburst from its supermassive black hole some five million years ago.
The key to understanding our universe lies in two theories—one of the generally-very-big and one of the generally-very-small. Albert Einstein’s Theory of General Relativity explains things like gravity and time, while Quantum Field Theory explores the subatomic world. However, one celestial object frustrates astrophysicists and quantum theorists in equal measure: black holes.
Because black holes release Hawking radiation (named for famous physicist Stephen Hawking), they eventually evaporate, which seemingly destroys the information that fell into the black hole. However, quantum field theory states that information cannot be destroyed. Result? Paradox.

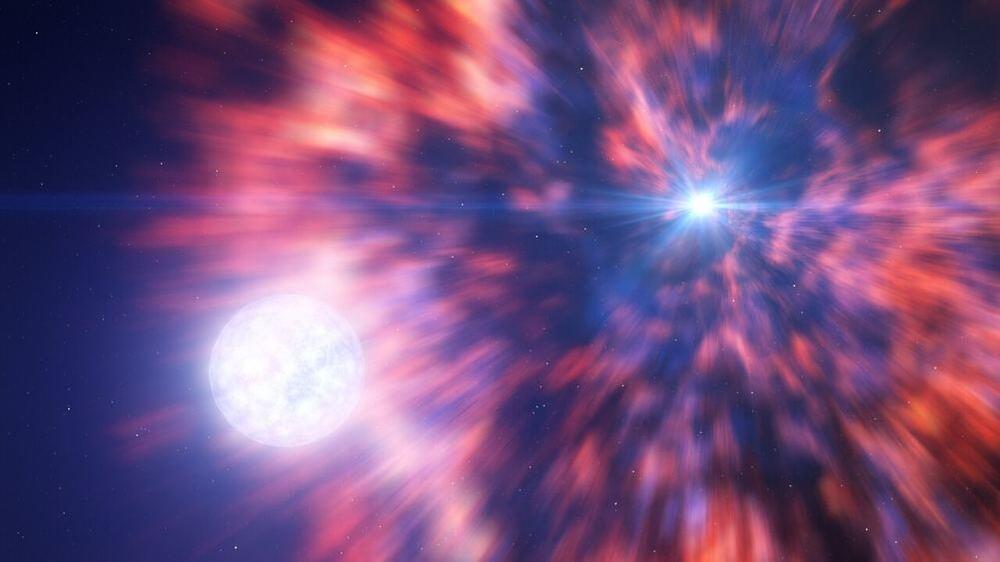
Scientists have found a star unlike any other one recorded—which may change our understanding of how stars die.
This unusual star, 13,000 light-years away, has an elemental makeup that suggests it was formed in the aftermath of a more massive star exploding in a way that no existing theory seems to explain. According to everything else we know, the original star should have turned into a black hole instead.
The discovery may rearrange our picture of how stars explode and how some of the heavier elements are made. It also helps us better understand what the first generation of stars in the universe may have looked like.

How is a black hole formed? In the simplest language, a black hole is born when a star dies. Now, astronomers have claimed that they might have just witnessed the birth of such a black hole in a major first. This is huge for the scientific community worldwide as it directly links the death of a star to the formation of a black hole-like compact object.
“Our research is like solving a puzzle by gathering all possible evidence,” Ping Chen, a researcher at the Weizmann Institute of Science in Israel, and lead author of a study published in Nature, was quoted as saying by Cosomos Magazine.
It started with the discovery of a super bright object in space, called SN 2022jli. The object, located some 76 million years away, was discovered by a South African amateur astronomer, Berto Monard. Soon it was confirmed that they had their eyes set on a supernova. A supernova occurs just as a star is breathing its last, or when a black hole is about to form.

Over ten years ago, the Dark Energy Survey (DES) began mapping the Universe to find evidence that could help us understand the nature of the mysterious phenomenon known as dark energy.
I’m one of more than 100 contributing scientists that have helped produce the final DES measurement, which has just been released at the 243rd American Astronomical Society meeting in New Orleans.
Dark energy is estimated to make up nearly 70 percent of the observable Universe, yet we still don’t understand what it is. While its nature remains mysterious, the impact of dark energy is felt on grand scales. Its primary effect is to drive the accelerating expansion of the Universe.