UMass Amherst physicists believe such an explosion could occur within the next decade, potentially “revolutionizing physics and rewriting the history of the universe.” Physicists have long thought that black holes end their lives in rare explosions that occur, at most, once every 100,000 years. N
Category: cosmology – Page 28

Ringing black hole confirms Einstein and Hawking’s predictions
A decade ago, scientists first detected ripples in the fabric of space-time, called gravitational waves, from the collision of two black holes. Now, thanks to improved technology and a bit of luck, a newly detected black hole merger is providing the clearest evidence yet of how black holes work—and, in the process, offering long-sought confirmation of fundamental predictions by Albert Einstein and Stephen Hawking.
The new measurements were made by the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-Wave Observatory (LIGO), with analyses led by astrophysicists Maximiliano Isi and Will Farr of the Flatiron Institute’s Center for Computational Astrophysics in New York City. The results reveal insights into the properties of black holes and the fundamental nature of space-time, hinting at how quantum physics and Einstein’s general relativity fit together.
“This is the clearest view yet of the nature of black holes,” says Isi, who is also an assistant professor at Columbia University. “We’ve found some of the strongest evidence yet that astrophysical black holes are the black holes predicted from Albert Einstein’s theory of general relativity.”
An exploding black hole could reveal the foundations of the universe
Physicists have long believed that black holes explode at the end of their lives, and that such explosions happen—at most—only once every 100,000 years. But new research published in Physical Review Letters by physicists at the University of Massachusetts Amherst has found a more than 90% probability that one of these black-hole explosions might be seen within the decade, and that, if we are prepared, our current fleet of space and earthbound telescopes could witness the event.
Such an explosion would be strong evidence of a theorized but never observed kind of black hole, called a “primordial black hole,” that could have formed less than a second after the Big Bang occurred, 13.8 billion years ago.
Furthermore, the explosion would give us a definitive catalog of all the subatomic particles in existence, including the ones we have observed, such as electrons, quarks and Higgs bosons, the ones that we have only hypothesized, like dark matter particles, as well as everything else that is, so far, entirely unknown to science. This catalog would finally answer one of humankind’s oldest questions: from where did everything in existence come?

Hawking and Kerr black hole theories confirmed by gravitational wave
Scientists have confirmed two long-standing theories relating to black holes—thanks to the detection of the most clearly recorded gravitational wave signal to date.
Ten years after detecting the first gravitational wave, the LIGO-Virgo-KAGRA Collaboration has (10 Sep) announced the detection of GW250114—a ripple in spacetime which offers unprecedented insights into the nature of black holes and the fundamental laws of physics.
The study confirms Professor Stephen Hawking’s 1971 prediction that when black holes collide, the total event horizon area of the resulting black hole is bigger than the sum of individual black holes—it cannot shrink.
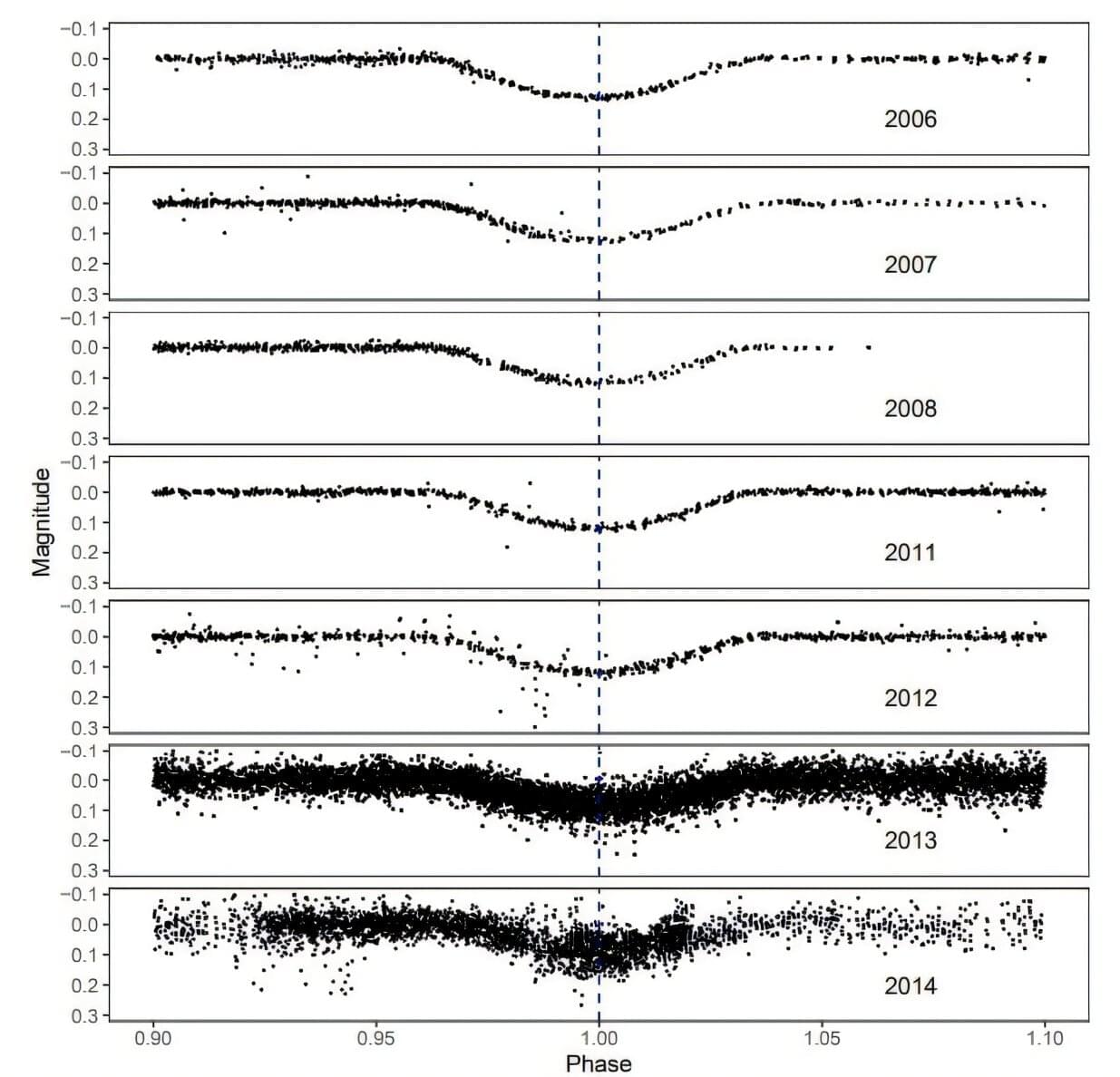
Discovery of young eclipsing binary system offers insight into early stellar evolution
An international team of astronomers reports the discovery of a new pre-main-sequence eclipsing binary system. The newfound binary, designated MML 48, consists of two young low-mass stars. The finding will be published in the upcoming issue of the Astronomy & Astrophysics journal.
Stellar systems showing regular light variations due to one of the stars passing directly in front of its companion are known as eclipsing binaries (EBs). In these systems, the orbit plane of the two stars lies so nearly in the line of sight of the observer that the components undergo mutual eclipses. EBs can provide direct accurate measurement of the mass, radius and effective temperature of stars; therefore, they are essential for testing and calibrating theoretical stellar-evolution models.
Astronomers are especially interested in finding new young EBs. This is due to the fact that such binaries constrain pre-main-sequence (PMS) stellar evolution models in the regime when the temperatures, luminosities, and radii of stars are changing rapidly as they settle onto the main sequence (MS).


First-ever complete measurement of a black-hole recoil achieved thanks to gravitational waves
A team of researchers led by the Instituto Galego de Física de Altas Enerxías (IGFAE) from the University of Santiago de Compostela (Spain) has measured for the first time the speed and direction of the recoil of a newborn black hole formed through the merger of two others. The result, published today in the journal Nature Astronomy, offers new insights into some of the most extreme events in the universe.
Gravitational waves (GWs) are ripples in the fabric of spacetime that travel away from their sources at the speed of light, encoding information about them. They provide a completely novel information channel that allows us to observe astrophysical phenomena that do not emit light—such as black hole mergers—and obtain new information about processes that do—such as supernovae or neutron-star mergers.
While Einstein predicted the existence of GWs in 1916, they are so weak that detecting them requires incredibly sensitive detectors and extremely violent astrophysical events such as black-hole mergers, supernovae or the Big Bang itself.


An American Collider Is Finally Ready to Recreate Matter from the Beginning of Time
Today, the absolute heart of particle physics is located in Geneva, Switzerland at CERN’s Large Hadron Collider. This instrument’s unmatched size, power, and precision make it the ultimate tool for exploring high-energy particle physics. However, one tool can’t do everything, and even immensely useful ones like the LHC sometimes need a helping hand.
That’s where Brookhaven National Laboratory’s (BNL) Relativistic Heavy Ion Collider (RHIC) comes in. In 2015, the U.S. Department of Energy approved an upgrade to the Pioneering High Energy Nuclear Interaction eXperiment (PHENIX)—an instrument originally designed to explore the components of the quark-gluon plasma (QGP) that formed one millionth of a second after the Big Bang. According to Edward O’Brien (a physicist from BNL), the idea behind this super PHENIX, or sPHENIX, was to “provide physics results which focused on jets and heavy flavor [of quarks] that complemented and overlapped with the Heavy Ion physics results being generated by the experiments at the CERN Large Hadron Collider.”