It ‘flies’ in a figure-of-8 pattern against the tidal flow.
The World Economic Forum’s Clean Power, Grids and Electrification initiative is focused on delivering a rapid and responsible energy transition.


The attempt began on the evening of March 20, and GWR officials were present at the test site. Engineers from Stadler drove the train in shifts over the night and the following day. When the train stopped at 5:23 pm on March 22, it had traveled 1,741.7 miles (2,803 km) over 46 hours, all on a single fuel tank.
This is six times the distance of FLIRT H2’s advertised range – 285 miles (460 km). However, it is unlikely to be replicated in real-life scenarios since the train did not stop and start multiple times during the record attempt, nor did it travel on different inclines. Nevertheless, it showcased the ability of hydrogen fuel as a potential power source for trains.
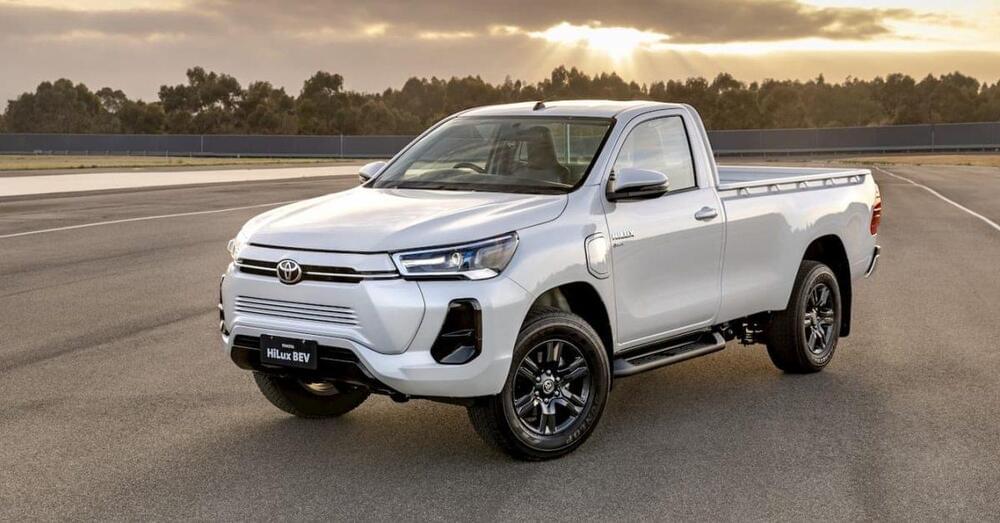

An all-electric Toyota pickup may be closer than expected. According to the company’s Thailand president, Toyota will launch an electric Hilux pickup by the end of 2025. The move comes after Japanese rival Isuzu is set to reveal its first 100% electric truck later this month.
Toyota’s Hilux is one of the top-selling pickup trucks globally, so it would make sense for an all-electric version.
The Toyota Hilux is built in six nations with sales across 180 countries and regions. Despite releasing its first “electrified” Hilux Hybrid 48V in December, it still featured a 2.8L diesel engine. The update provided a modest 5% improvement in fuel efficiency.

Researchers at Osaka University have discovered that considering sustainability issues through the lens of “imaginary future generations” provides valuable perspectives on technological advancements and trends in society.
The world stands on the brink of a crucial environmental threshold; the choices we make today about energy, resources, and the environment will have profound consequences for the future. Despite this, most sustainable thought tends to be limited to the viewpoint of current generations.
In a study published in Technological Forecasting and Social Change, researchers from Osaka University have revealed that adopting the perspective of “imaginary future generations” (IFGs) can yield fascinating insights into long-term social and technological trends.

Anyone who wants to produce medication, plastics or fertilizer using conventional methods needs heat for chemical reactions – but not so with photochemistry, where light provides the energy. The process to achieve the desired product also often takes fewer intermediate steps.
Researchers from the University of Basel are now going one step further and are demonstrating how the energy efficiency of photochemical reactions can be increased tenfold. More sustainable and cost-effective applications are now tantalizingly close.
Industrial chemical reactions usually occur in several stages across various interim products. Photochemistry enables shortcuts, meaning fewer intermediate steps are required. Photochemistry also allows you to work with less hazardous substances than in conventional chemistry, as light produces a reaction in substances which do not react well under heat. However, to this point there have not been many industrial applications for photochemistry, partly because supplying energy with light is often inefficient or creates unwanted by-products.
A system designed at MIT could allow sensors to operate in remote settings, without batteries.
MIT researchers have developed a battery-free, self-powered sensor that can harvest energy from its environment.
Because it requires no battery that must be recharged or replaced, and because it requires no special wiring, such a sensor could be embedded in a hard-to-reach place, like inside the inner workings of a ship’s engine. There, it could automatically gather data on the machine’s power consumption and operations for long periods of time.
Tesla continues to make progress on its upcoming diner, drive-in theater and Supercharger in Los Angeles, with recent drone footage showing new water runoff infrastructure, preparations for stucco installation on the first-floor walls, and seemingly, materials for the start of some interior construction.
In a drone video update shared by YouTube channel 247Tesla on Sunday, you can see new stacks of sheetrock both inside and outside of entrances to the Tesla diner building, as construction prepares to begin focus on interiors. The video also shows a new rectangular area dug roughly five feet deep into the ground, which the video’s host says will likely be used to control water runoff.
In addition, you can see shots of the site’s power shed, though it doesn’t include transformers or batteries as of yet. The diner building’s walls surrounding the first-floor structure have also now been covered with a waterproofing sealer, the host notes, which is usually installed prior to stucco being applied.