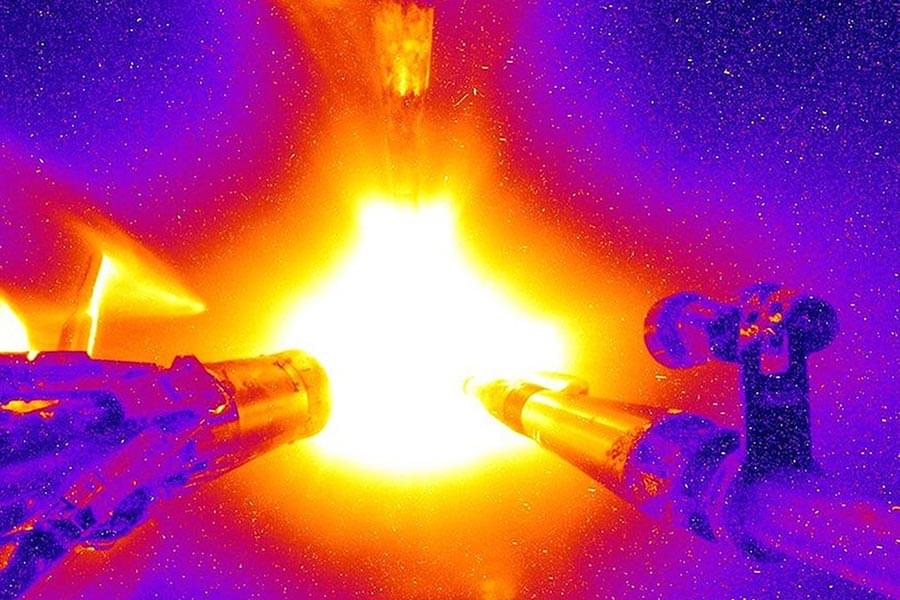
MIT students are part of the large team that achieved fusion ignition for the first time in a laboratory. Researchers around the world have been engaged in attempts to achieve fusion ignition in a laboratory for more than half a century. It is a grand challenge of the 21st century. An approach called inertial confinement fusion (ICF), which uses lasers to implode a pellet of fuel in a quest for ignition, has been the focus of the High-Energy-Density Physics (HEDP) group at MIT’s Plasma Science and Fusion Center. This group, including nine former and current MIT students, was crucial to a historic ICF ignition experiment performed in 2021. The results were published this year on the anniversary of that success.