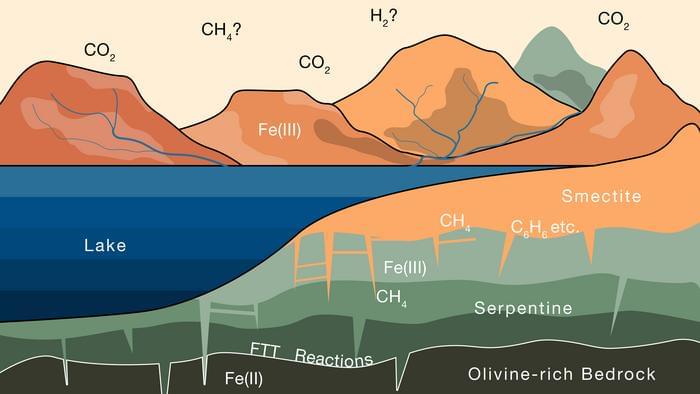
Billions of years ago, Mars is hypothesized to have been a much warmer and wetter planet featuring active volcanoes and vast liquid water oceans. However, something happened that caused the Red Planet to become the cold and dry world we see and explore today, but where did its atmosphere go? This is what a recent study published in Science Advances hopes to address as a team of researchers from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT) investigated how the large amounts of carbon that once existed in Mars’ atmosphere could now exist in the clay across the planet’s surface. This study holds the potential to help scientists better understand the formation and evolution of Mars and what that means in the search for life on the Red Planet, and beyond Earth.
For the study, the researchers calculated the amount of carbon storage within clays that potentially existed during what’s known as the Noachian Period on Mars, or between approximately 3.6 to 4 billion years ago. Their hypothesis is that when liquid water existed on the Red Planet, this water could have seeped its way into rocks, resulting in carbon dioxide being removed from the atmosphere and being converted into methane. In the end, the researchers calculated that the clays on Mars could potentially be housing up to 1.7 bar of carbon dioxide, or just over one standard atmosphere’s worth of carbon dioxide and approximately 80 percent of Mars’ ancient atmosphere.
“Based on our findings on Earth, we show that similar processes likely operated on Mars, and that copious amounts of atmospheric CO2 could have transformed to methane and been sequestered in clays,” said Dr. Oliver Jagoutz, who is a professor of geology in MIT’s Department of Earth, Atmospheric and Planetary Sciences (EAPS) and the sole co-author on the study. “This methane could still be present and maybe even used as an energy source on Mars in the future.”