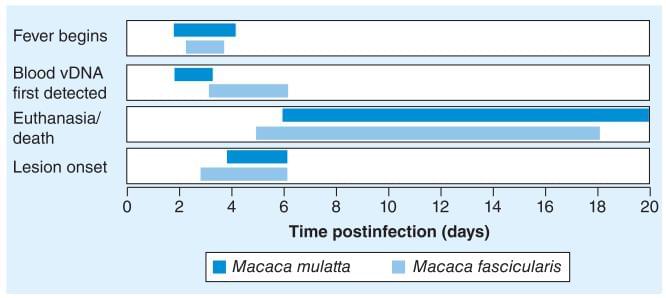
MPXV was first discovered during a nonfatal outbreak at an animal facility in Copenhagen, Denmark, in 1958. The facility received a continual supply of Asian monkeys (mostly M. fascicularis) and rhesus macaques (Macaca mulatta), which were used for polio vaccine research. The first outbreak occurred 2 months after the monkeys had been received and the second outbreak occurred 4 months after the initial outbreak. The outbreaks occurred in M. fascicularis that had arrived from Singapore. Upon arrival, monkeys were treated with antibiotics and appeared in satisfactory health.
Monkeypox virus (MPXV) was discovered in 1958 during an outbreak in an animal facility in Copenhagen, Denmark. Since its discovery, MPXV has revealed a propensity to infect and induce disease in a large number of animals within the mammalia class from pan-geographical locations. This finding has impeded the elucidation of the natural host, although the strongest candidates are African squirrels and/or other rodents. Experimentally, MPXV can infect animals via a variety of multiple different inoculation routes; however, the natural route of transmission is unknown and is likely to be somewhat species specific. In this review we have attempted to compile and discuss all published articles that describe experimental or natural infections with MPXV, dating from the initial discovery of the virus through to the year 2012. We further discuss the comparative disease courses and pathologies of the host species.
Keywords: aerosol, animals, infection, intrabronchial, intradermal, intramuscular, intranasal, intratracheal, intravenous, outbreak, primates, subcutaneous.
Orthopoxviruses (OPVs) have host specificities ranging from narrow (e.g., ectromelia and variola [VARV]) to broad (e.g., cowpox and vaccinia [VACV]). Monkeypox virus (MPXV) has a broad host-range and is capable of infecting many species from across the globe. In nature, the major environs of MPXV are restricted to the Congo Basin (CB) and West Africa (WA). The MPXV virion is a brick-shaped enveloped virus of 200–250 nm, characterized by surface tubules and a dumbbell-shaped core. Humans and highly susceptible nonhuman primates (NHPs) infected with MPXV have near identical clinical manifestations compared to humans infected with VARV. For humans, the only obvious difference in clinical signs is the absence of lymphadenopathy in smallpox patients [1,2].