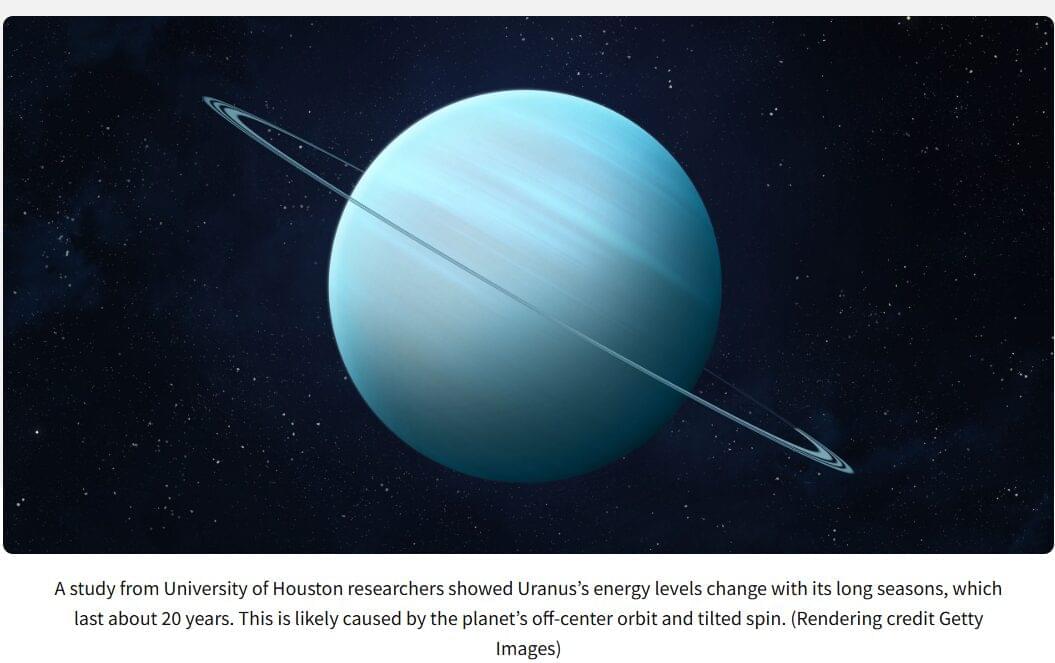
For decades, scientists puzzled over why Uranus seemed colder than expected. Now, an international research team led by the University of Houston has solved the mystery: Uranus emits more heat than it gets from the Sun, meaning it still carries internal warmth from its ancient formation. This revelation rewrites what scientists know about the ice giant’s history, strengthens the case for NASA’s upcoming mission, and offers fresh insight into the forces shaping not only other planets, but also Earth’s future climate.
A new study led by University of Houston researchers, in collaboration with planetary scientists worldwide, suggests Uranus does have its own internal heat — an advance that not only informs NASA’s future missions but also deepens scientists’ understanding of planetary systems, including processes that influence Earth’s climate and atmospheric evolution.
The discovery resolves a long-standing scientific mystery about the giant planet, because observational analyses from Voyager 2 in 1986 didn’t suggest the presence of significant internal heat — contradicting scientists’ understanding of how giant planets form and evolve.