The new vehicle is being developed by the Automotive Parts Manufacturers’ Association (APMA), expected to debut in 2023.


With new major spending packages investing billions of dollars in electric vehicles in the U.S., some analysts have raised concerns over how green the electric vehicle industry actually is, focusing particularly on indirect emissions caused within the supply chains of the vehicle components and the fuels used to power electricity that charges the vehicles.
But a recent study from the Yale School of the Environment published in Nature Communications found that the total indirect emissions from electric vehicles pale in comparison to the indirect emissions from fossil fuel-powered vehicles. This is in addition to the direct emissions from combusting fossil fuels —either at the tailpipe for conventional vehicles or at the power plant smokestack for electricity generation—showing electric vehicles have a clear advantage emissions-wise over conventional vehicles.
“The surprising element was how much lower the emissions of electric vehicles were,” says postdoctoral associate Stephanie Weber. “The supply chain for combustion vehicles is just so dirty that electric vehicles can’t surpass them, even when you factor in indirect emissions.”
Researchers at the Italian Institute of Technology (IIT) have recently been exploring a fascinating idea, that of creating humanoid robots that can fly. To efficiently control the movements of flying robots, objects or vehicles, however, researchers require systems that can reliably estimate the intensity of the thrust produced by propellers, which allow them to move through the air.
As thrust forces are difficult to measure directly, they are usually estimated based on data collected by onboard sensors. The team at IIT recently introduced a new framework that can estimate thrust intensities of flying multibody systems that are not equipped with thrust-measuring sensors. This framework, presented in a paper published in IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters, could ultimately help them to realize their envisioned flying humanoid robot.
“Our early ideas of making a flying humanoid robot came up around 2016,” Daniele Pucci, head of the Artificial and Mechanical Intelligence lab that carried out the study, told TechXplore. “The main purpose was to conceive robots that could operate in disaster-like scenarios, where there are survivors to rescue inside partially destroyed buildings, and these buildings are difficult to reach because of potential floods and fire around them.”

This summer Tesla finally decided to jump into the housing market, to provide products for the upcoming homes being built by a home builder called E-home. With the technological advances that Tesla has shown. It will be interesting to see what products Tesla will provide for these homes.
This could be an innovation that might shake at the housing markets and an agreement was made between Tesla and the real estate developer. Tesla would supply Powerwalls electric, Vehicle chargers, and Solar panels to all set E-home Inc, which is a subsidiary of international incorporated.
When interviewed, the corporation stated that the Tesla products will be installed in 20 new single-family homes, which will be at the north park community in porter Texas. Also, E-home is having to build 100 single-family homes by the end of 2021 within Texas.
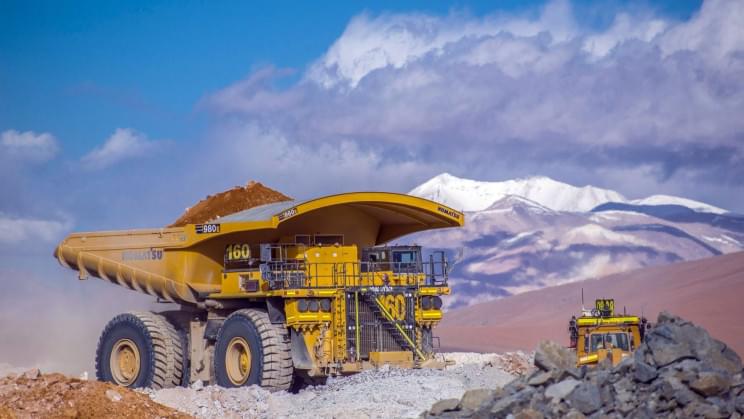

And it’s a hybrid mix of hydrogen and electric power.
Global mining company Anglo American is experimenting with hydrogen to power the giant mining trucks.
Mining trucks consume 35.3 gallons (134 liters) of diesel per hour with their enormous weight of around 220 metric tonnes and therefore emitting vast amounts of carbon dioxide into the atmosphere.
In order to reduce the mining industry’s carbon footprint, Anglo American is focused on mining trucks.
The company is collaborating with several partners, such as Engie, NPROXX, First Mode, Williams Advanced Engineering, Ballard, ABB, Nel, and Plug Power, to develop a hybrid mining vehicle, fueled with hydrogen and electricity.
The truck will be hybrid, with a hydrogen fuel cell providing roughly half of the power and the other half by a battery pack.
The truck can also harvest regenerative energy created when driving downhill and braking, which is stored in the battery and extends the range of the vehicle.
But could it actually work?
Lighter-than-air spacecraft might one day help explore the clouds of Venus and investigate signs of ancient life on the planet.
Proposed in 2014 by Northrop Grumman, the Venus Atmospheric Maneuverability Platform (VAMP) project would deploy crewed inflatable aircraft from space to skim Venus’ upper atmosphere.
Now, a press release from West Virginia University reveals that engineers are developing software to allow spacecraft similar to these to navigate Venus’ atmosphere autonomously.
Could we send humans to Venus? The statement, brought to our attention by Universe Today says the main goal of the new project is to “propose a software solution that will allow hybrid aerobots to explore the atmosphere of Venus.” The researchers claim that their software would optimize flight paths while accounting for strong winds and sunlight intensity, allowing it to plan the crafts flights for the longest periods possible.
Full Story:
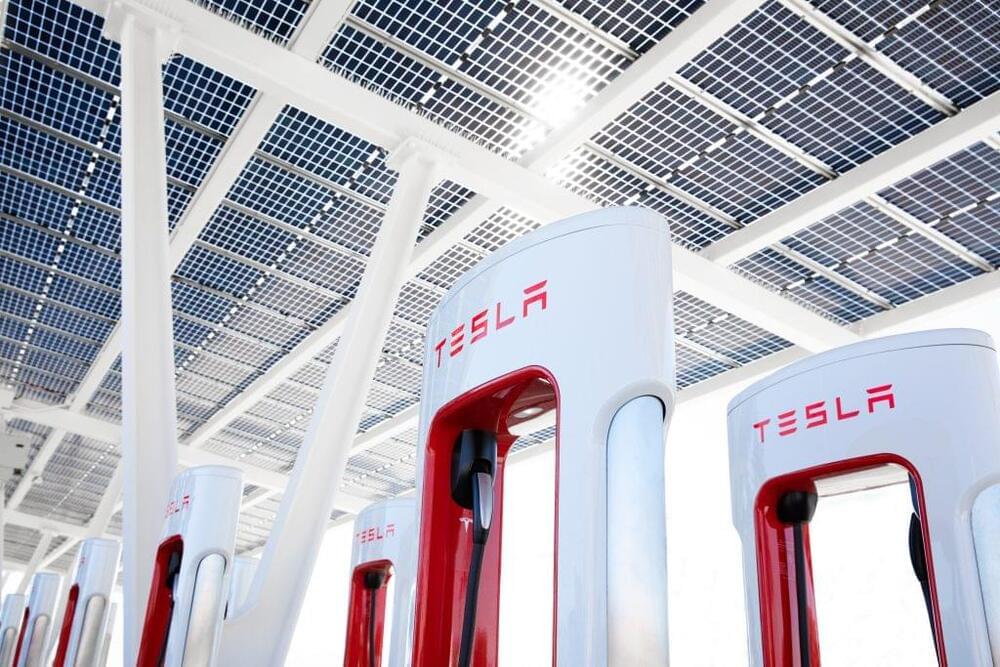

Tesla has launched Free Holiday Supercharging during off-peak hours for the Holiday Season. From December 23 to December 26, Tesla will offer free Supercharging in various locations across the U.S. when charging before 10 AM or after 7 PM.
Tesla will offer the free off-peak Supercharging in eleven states across the U.S.: California, Nevada, Utah, Arizona, New Mexico, Colorado, Texas, Oklahoma, Florida, and Pennsylvania. All four of Tesla’s vehicles will be eligible for the free Supercharging promotion. 75 Supercharging stations will be online for free Supercharging during the off-peak times.
“Avoid the rush this holiday season and charge for free during off-peak hours at Superchargers along select travel routes in the United States,” Tesla wrote on their website. Charging during off-peak hours is usually a less expensive experience, to begin with, because it puts less stress on the grid. However, the Holidays are a high travel time. Despite Tesla’s expansive Supercharger network with over 25,000 locations globally, things will still get pretty congested, especially as AAA estimates that 109.5 million travelers will hit the road to celebrate the Holidays with family this year.
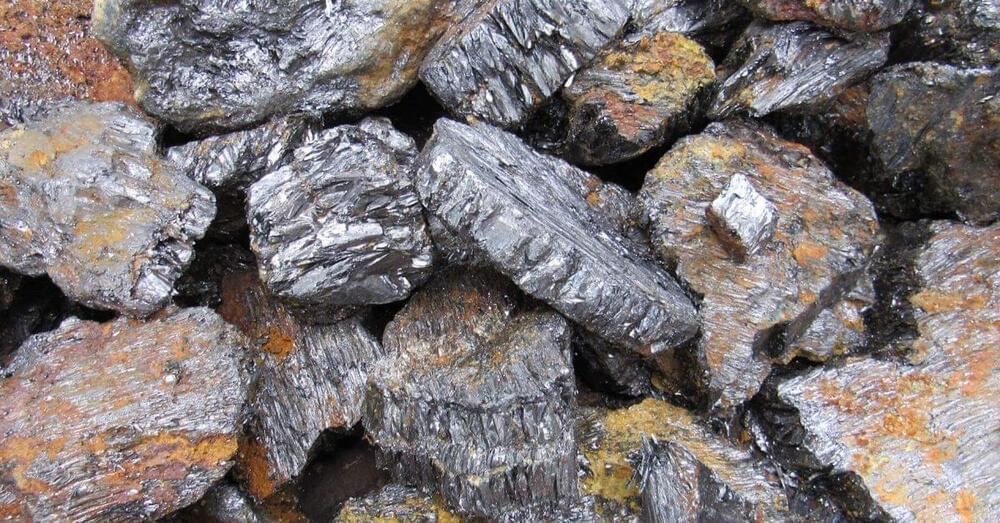



As the electric car revolution ramps up, so does the need for critical minerals used in batteries, such as graphite. According to Benchmark Mineral Intelligence, there will be a global graphite deficit starting in 2022, and demand from the battery sector is expected to rise 30% annually until 2030. The US has no manufacturing plants that can supply automotive-grade graphite at scale. Meanwhile, China controls 84% of the global supply. Electrek spoke with Don Baxter, CEO of Ceylon Graphite, about how graphite is used in EVs, the supply chain issue, and how EV battery manufacturers can successfully source the vital mineral.
Electrek: How is graphite used in battery electric vehicles?
Don Baxter: Processed graphite comprises 95% of the anode (negative electrode) of lithium-ion batteries that power EVs, whereas the cathode (positive electrode) is made up of various materials such as nickel and cobalt.