Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.

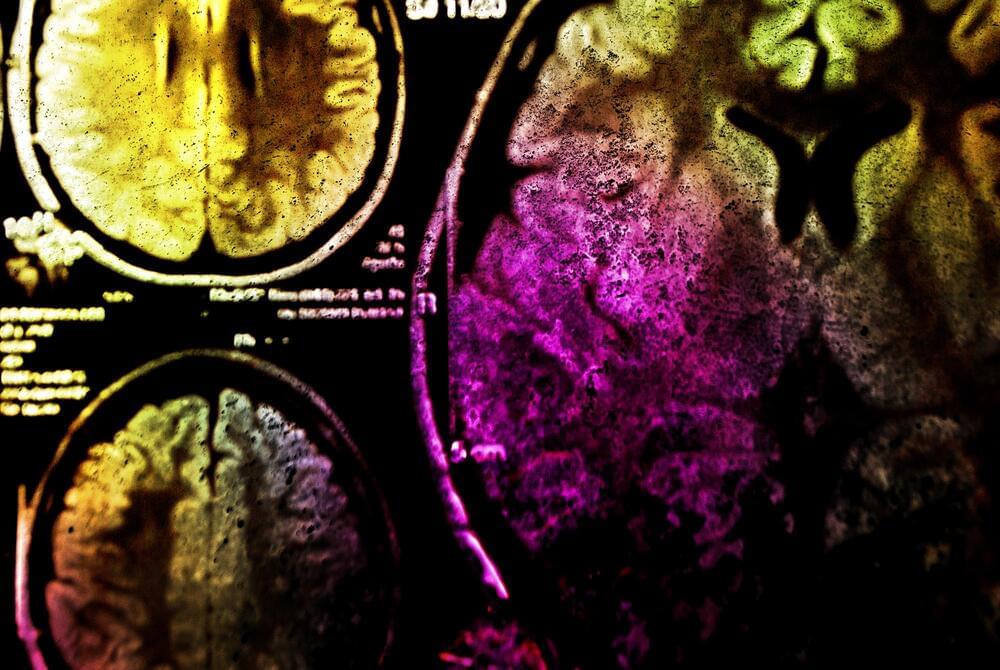
Light-activated “photoimmunotherapy” kills brain cancer, reduces relapse
Scientists at the Institute of Cancer Research in London have developed a new light-activated “photoimmunotherapy” that could help treat brain cancer. The key is a compound that glows under light to guide surgeons to the tumor, while near-infrared light activates a cancer-killing mechanism.
The new study builds on a common technique called Fluorescence Guided Surgery (FGS), which involves introducing a fluorescent agent to the body which glows under exposure to light. This is paired with a synthetic molecule that binds to a specific protein, such as those expressed by cancer cells. The end result is tumors that glow under certain lighting conditions or imaging, guiding surgeons to remove the affected cells more precisely.
For the new study, the researchers gave the technique an extra ability – killing the cancer as well. They added a new molecule that binds to a protein called EGFR, which is often mutated in cases of the brain cancer glioblastoma. After the fluorescence has helped surgeons remove the bulk of the tumor, they can shine near-infrared light on the site, which switches the compound into a tumor-killing mode by releasing reactive oxygen species. The idea is to kill off any remaining cells that could – and often do – stage an aggressive comeback after surgery.

Speeding Up Molecule Design With a New Technique That Can Delete Single Atoms
University of ChicagoFounded in 1,890, the University of Chicago (UChicago, U of C, or Chicago) is a private research university in Chicago, Illinois. Located on a 217-acre campus in Chicago’s Hyde Park neighborhood, near Lake Michigan, the school holds top-ten positions in various national and international rankings. UChicago is also well known for its professional schools: Pritzker School of Medicine, Booth School of Business, Law School, School of Social Service Administration, Harris School of Public Policy Studies, Divinity School and the Graham School of Continuing Liberal and Professional Studies, and Pritzker School of Molecular Engineering.


Humans Can Learn to ‘Echolocate’ in Just 10 Weeks, Experiment Shows
Echolocation is a skill we usually associate with animals such as bats and whales, but some blind humans also use the echoes of their own sounds to detect obstacles and their outlines. Some use the tapping of a cane or the snapping of their fingers to make the necessary noise, while others use their mouths to make a clicking sound.
Despite how useful this skill can be, very few blind people are currently taught how to do it. Expert echolocators have been trying to spread t… See more.
With enough training, most humans can learn how to echolocate, using their tongue to make clicking sounds and interpreting the echoes that come back, reflected from the surrounding environment.
In as few as 10 weeks, researchers have been able to teach participants how to navigate obstacles and recognize the size and orientation of objects using the rebounding calls of their clicks.
The experiment, the results of which were published in 2021, involved 12 participants who’d been diagnosed as legally blind during their childhood, and 14 sighted people.

Is 150 years really the limit of human life span?
While most of us can expect to live to around 80, some people defy expectations and live to be over 100.
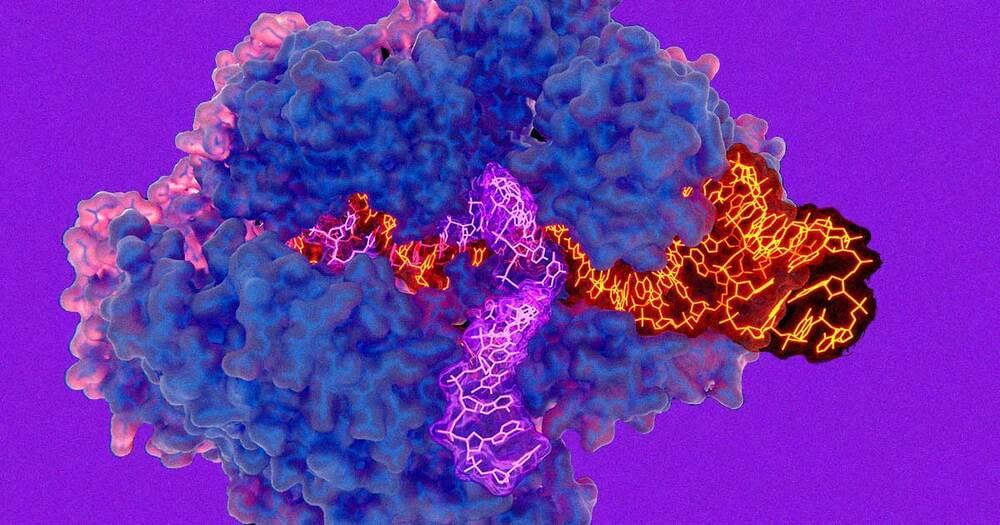
Patients Treated With CRISPR Still “Cured” Three Years Later
A long-running human trial has shown that CRISPR gene editing could prove to be a highly effective way of treating serious conditions.
The trial, which was kicked off in 2019 by an international team of scientists, found that a new gene-editing therapy called exagamglogene autotemcel, or ex-cel for short, was able to essentially “cure” patients with transfusion-dependent beta thalassemia (TDT) or severe sickle cell disease (SCD), two blood disorders that are conventionally treated using blood transfusions.
It’s a promising new use of the technology. Around 100,000 Americans are affected by TDT, while SCD affects an estimated 300 to 3,000. And in a broader sense, the results suggest that tinkering with genetic code could come to be a practical, widespread new area of medicine.
Dead star’s cannibalism of its planetary system is most far-reaching ever witnessed
The violent death throes of a nearby star so thoroughly disrupted its planetary system that the dead star left behind—known as a white dwarf—is sucking in debris from both the system’s inner and outer reaches, UCLA astronomers and colleagues report today.
This is the first case of cosmic cannibalism in which astronomers have observed a white dwarf consuming both rocky-metallic material, likely from a nearby asteroid, and icy material, presumed to be from a body similar to those found in the Kuiper belt at the fringe of our own solar system.
“We have never seen both of these kinds of objects accreting onto a white dwarf at the same time,” said lead researcher Ted Johnson, a physics and astronomy major at UCLA who graduated last week. “By studying these white dwarfs, we hope to gain a better understanding of planetary systems that are still intact.”