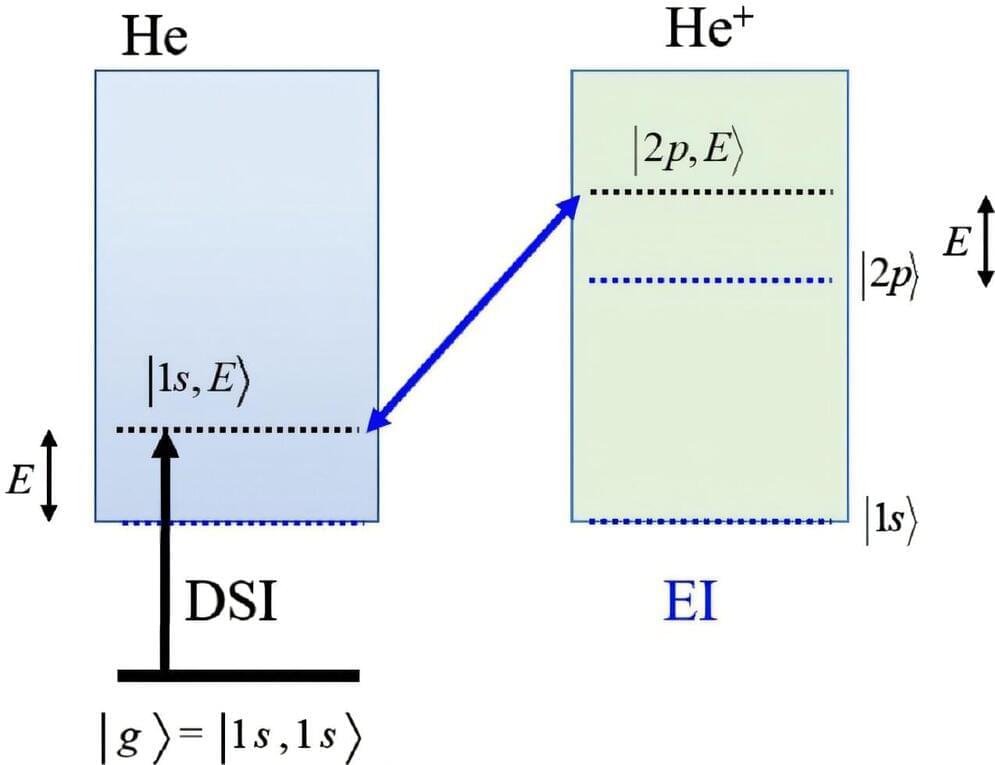
Quantum theory describes events that take place on extremely short time scales. In the past, such events were regarded as ‘momentary’ or ‘instantaneous’: An electron orbits the nucleus of an atom—in the next moment it is suddenly ripped out by a flash of light. Two particles collide—in the next moment they are suddenly ‘quantum entangled.’
How fast is quantum entanglement? Scientists investigate it at the attosecond scale
Posted in particle physics, quantum physics