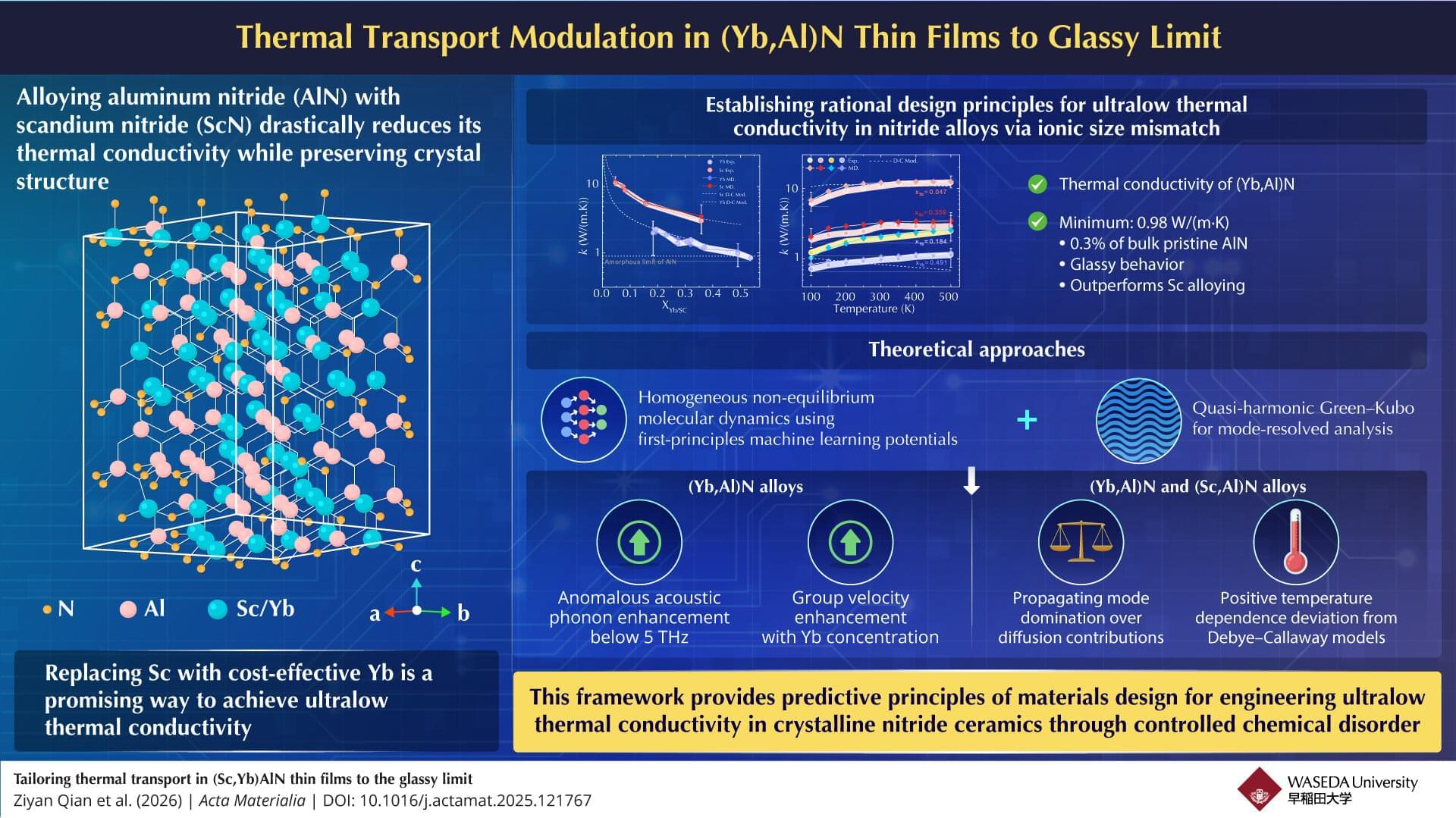
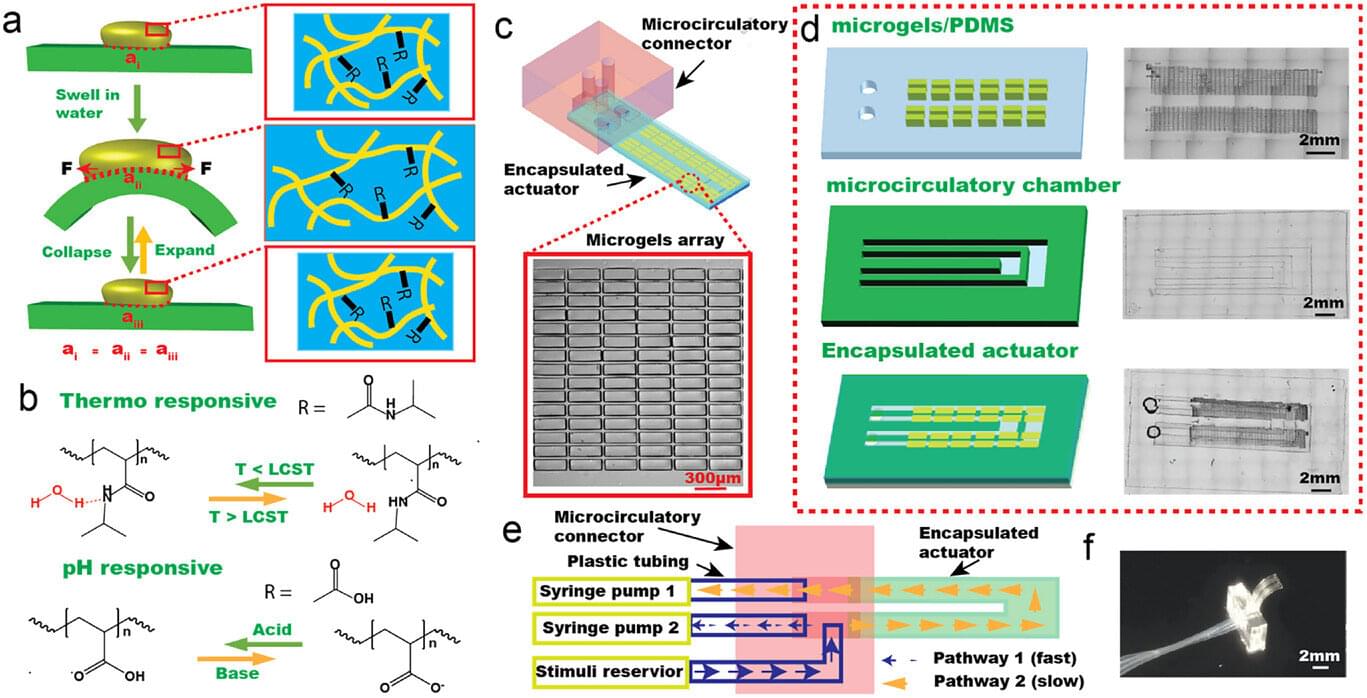
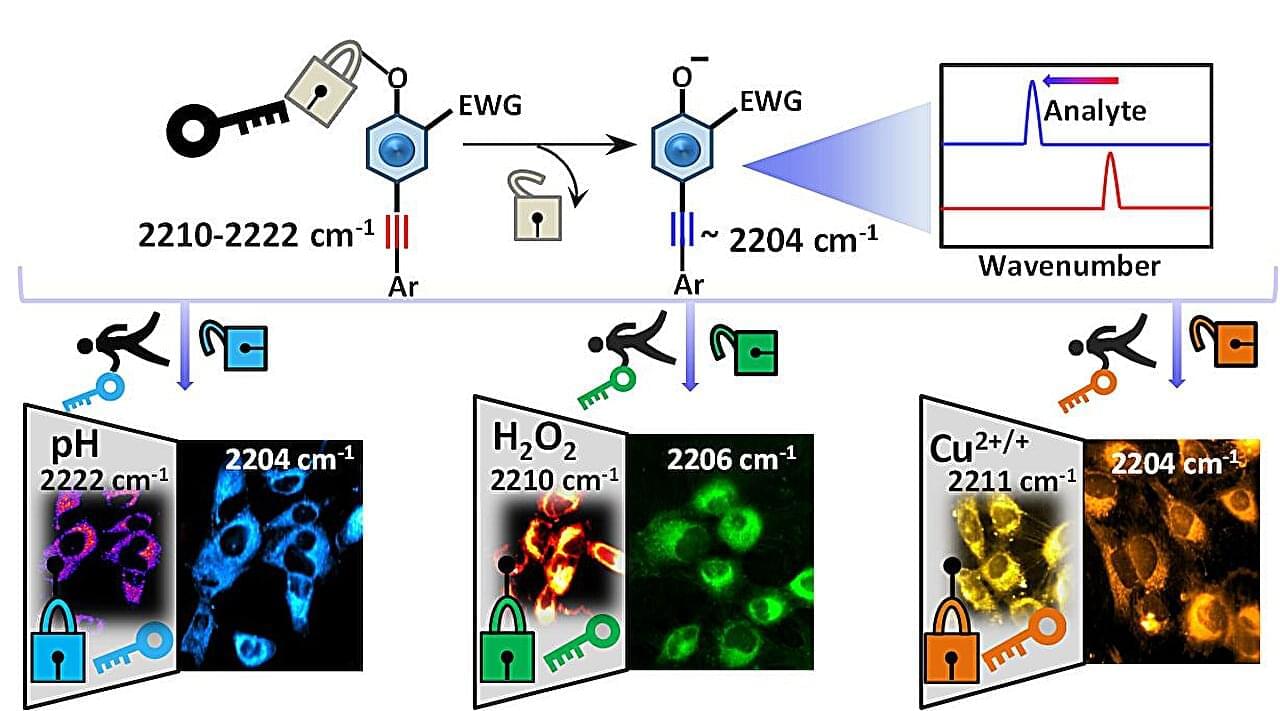
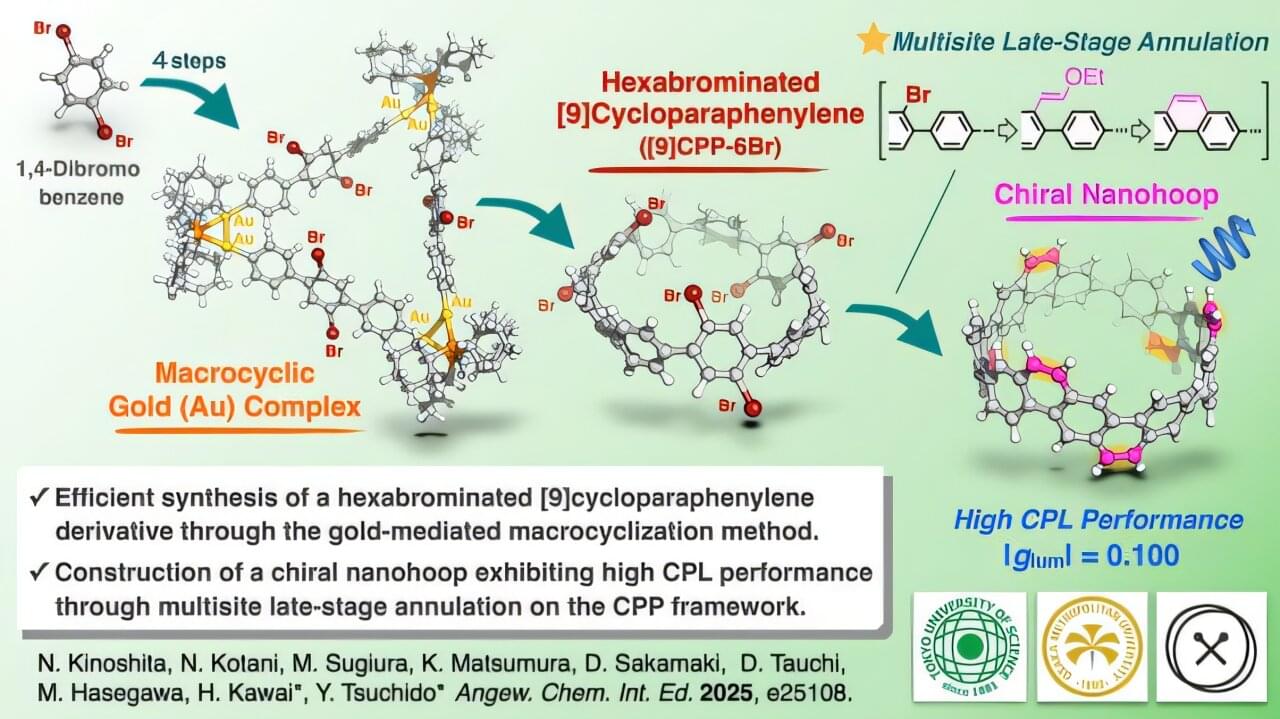
A major challenge in thermal-management and thermal-insulation technologies, across multiple industries, is the lack of materials that simultaneously offer low thermal conductivity, mechanical robustness, and scalable fabrication routes.
Discovering materials that exhibit completely insulating thermal behavior—or, conversely, extraordinarily high thermal conductivity—has long been a dream for researchers in materials physics. Traditionally, amorphous materials are known to possess very low thermal conductivity.
This naturally leads to an important question: Can a crystalline material be engineered to achieve thermal conductivity close to that of an amorphous solid? Such a material would preserve the structural stability of a crystal while achieving exceptionally low thermal conductivity.