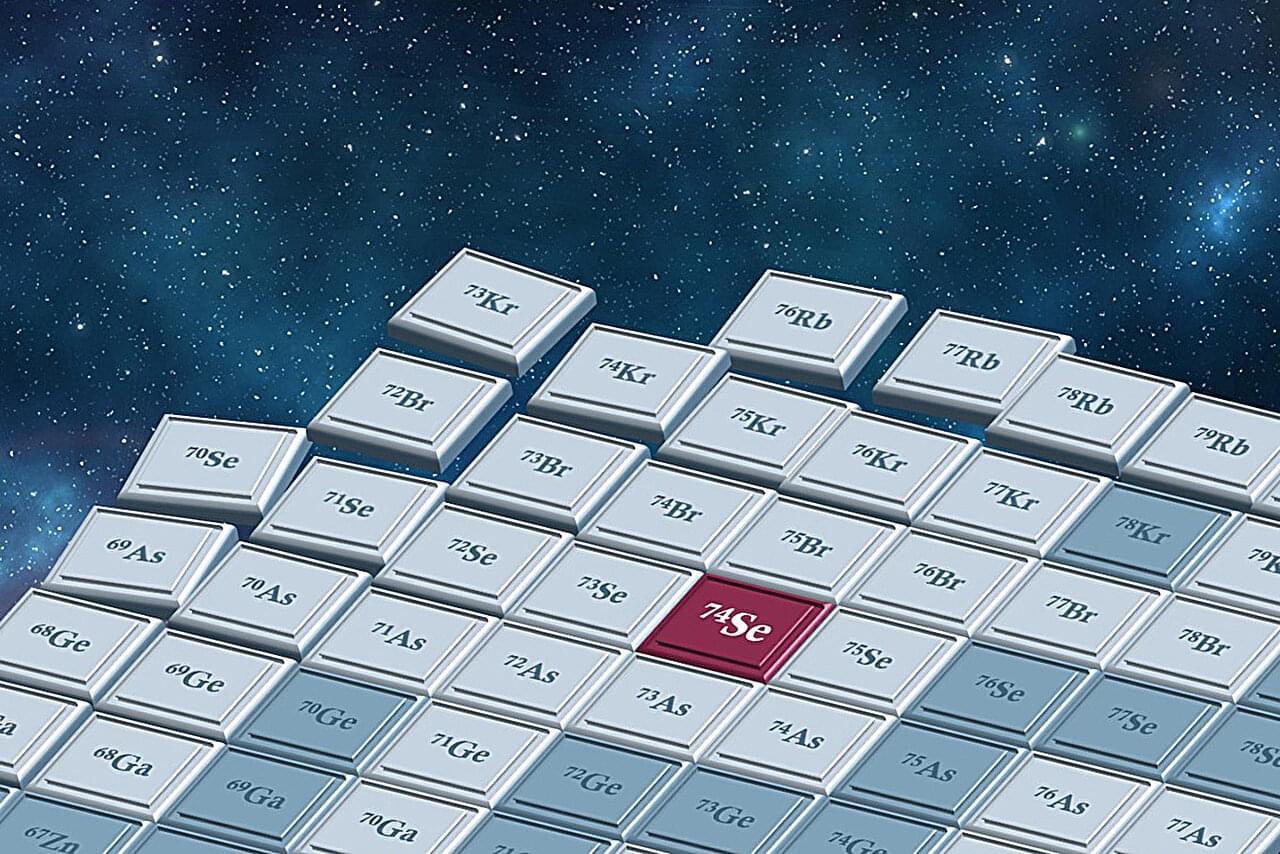
Researchers have reported new experimental results addressing the origin of rare proton-rich isotopes heavier than iron, called p-nuclei. Led by Artemis Tsantiri, then-graduate student at the Facility for Rare Isotope Beams (FRIB) and current postdoctoral fellow at the University of Regina in Canada, the study presents the first rare isotope beam measurement of proton capture on arsenic-73 to produce selenium-74, providing new constraints on how the lightest p-nucleus is formed and destroyed in the cosmos.
The team published the results in Physical Review Letters in a paper titled “Constraining the Synthesis of the Lightest Nucleus 74 Se”. The work involved more than 45 participants from 20 institutions in the United States, Canada, and Europe.
A central question in nuclear astrophysics concerns how and where chemical elements are formed. The slow and rapid neutron-capture processes account for many intermediate-mass and heavy nuclei beyond iron through repeated neutron captures followed by radioactive decays until stable isotopes are reached.