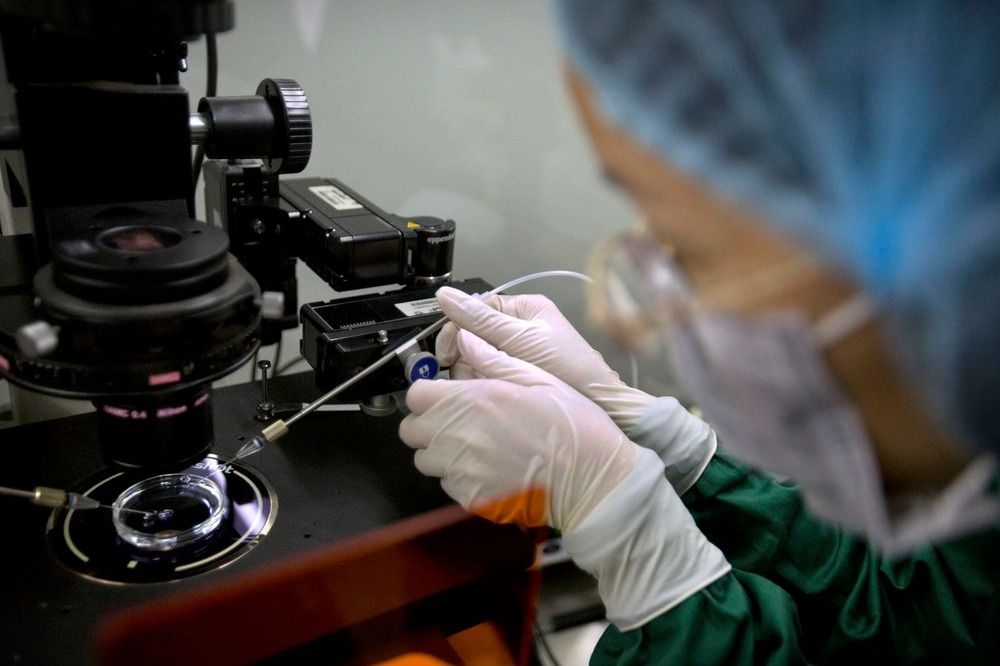
In the wake of CRISPR babies, there is an urgent need to better regulate and debate whether, when and how related research should be done.
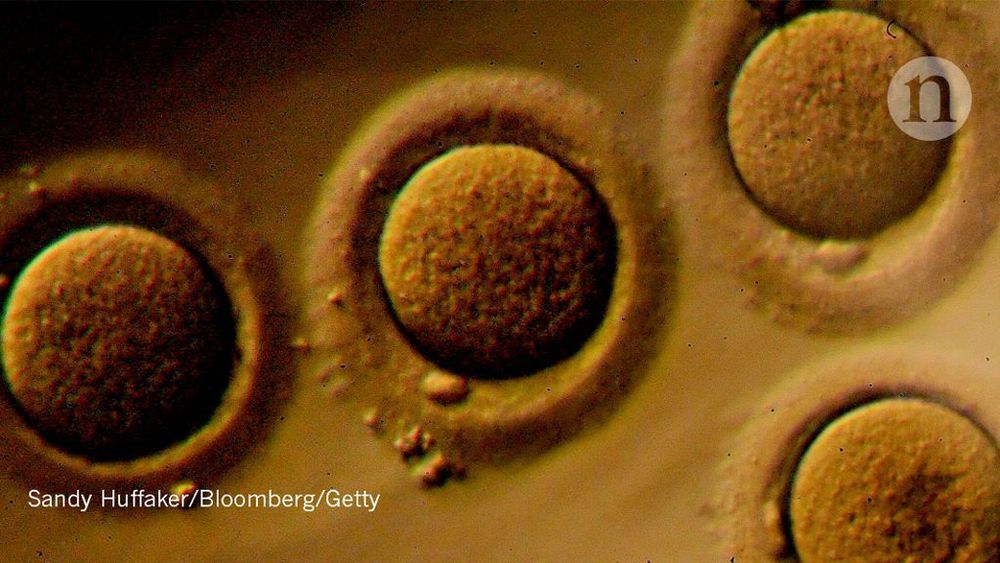
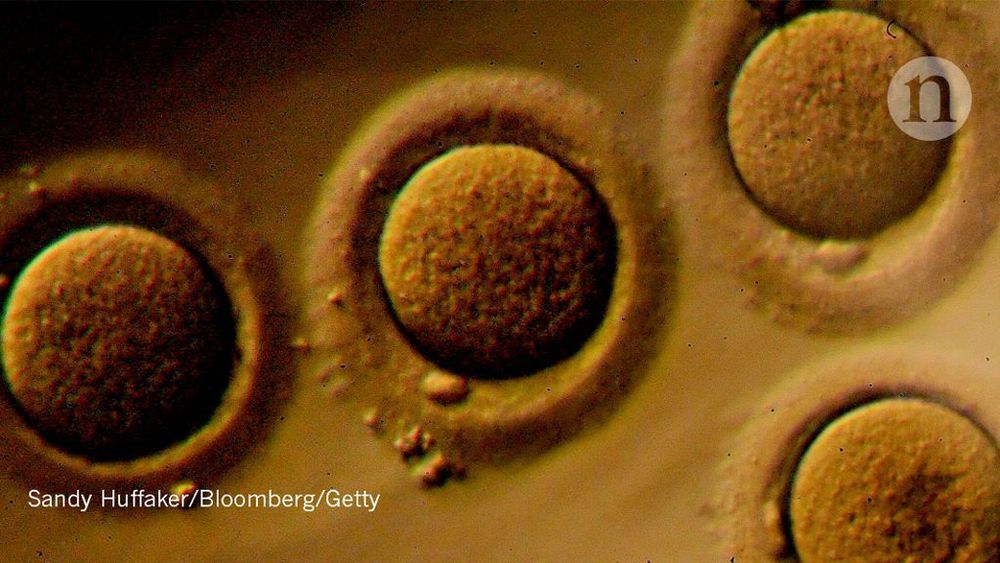

Imagine a future where an online dating app doesn’t just match you to potential partners who meet your preferences for age, height and fondness for pinot noir, but to those with whom you’re genetically compatible. Not so much people you’re likely to have physical chemistry with – apps that make dubious claims to do that on the basis of a cheek swab already exist – but those with whom you won’t pass on a devastating genetic disease to your children.
It’s not sexy stuff; certainly not first-date conversation. Most people only discover that they’re among the four per cent who carry the same recessive genetic mutation for a rare condition, such as cystic fibrosis or Tay-Sachs, as their partner when their baby is born with it – or dies from it.
True, couples could find out their genes don’t mix after they’ve decided to have a baby and before they start trying – but how heartbreaking would that be, once they’re already in love? Far simpler never to meet in the first place, and simply to pick from the other 96 per cent with whom they can mate with abandon.
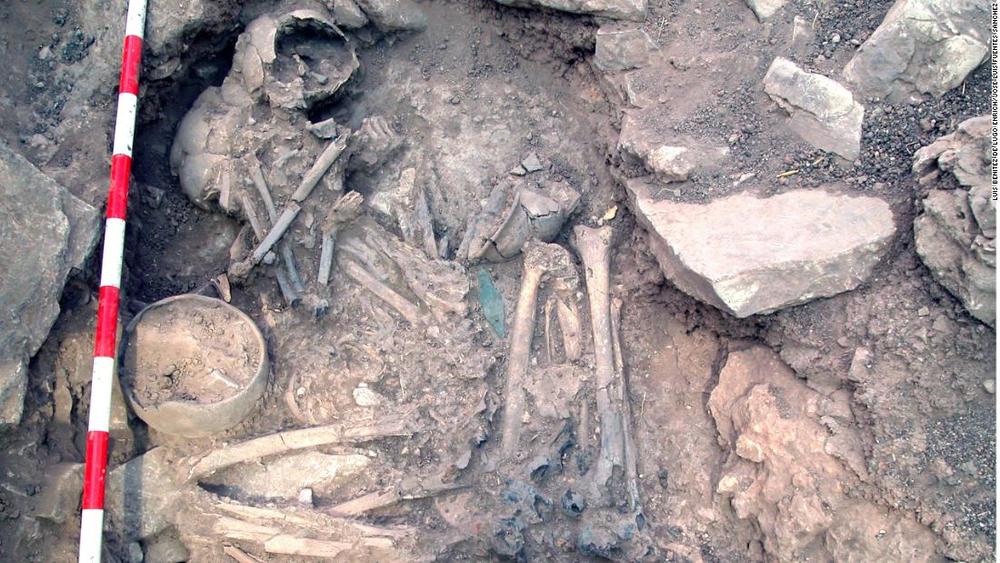


“The modern people of Basque Country, in northern Spain, are genetically similar to the Iberian Iron Age people with ancestry from the Russian steppe. While people around them mixed with different groups and changed, the Basques held on to their heritage.”
Ancient DNA is uncovering the secrets of the unique populations of what are now Portugal and Spain. Two studies published this week include unexpected findings from the DNA of people who lived thousands of years ago on the Iberian Peninsula.
The rugged peninsula is positioned between North Africa, Europe and the Mediterranean on the westernmost edge of the continent, so the DNA of its ancient population shows how it was affected by migration over time.
Iberia was also relatively warm during the last Ice Age, between 18,000 and 24,000 years ago, presenting a more welcoming climate for animals and people who retreated from the rest of Europe.

With the announcement today that Mammoth Biosciences has received the exclusive license from the University of California, Berkeley to the new CRISPR protein Cas14, the company now has the last piece of its diagnostics toolkit in place.
Cas14 is a newly discovered protein from the lab of Jennifer Doudna, a pioneer in gene-editing research and a member of the first research team to identify and unlock the power of CRISPR technology.
Doudna and Mammoth Biosciences co-founder Lucas Harrington were part of the team of researchers to identify the new Cas14 protein, which can identify single-stranded DNA. The journal Science published their findings in October 2018.
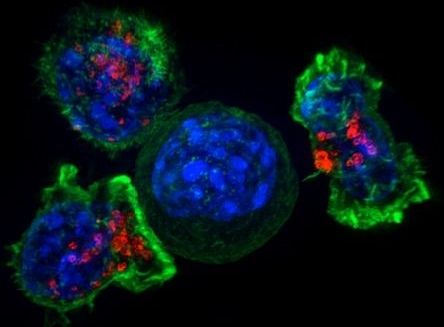
Chinese doctors have reported success with a new type of immunotherapy for multiple myeloma, a blood cancer: 33 out of 35 patients in a clinical trial had clinical remission within two months.
The researchers used a type of T cell called “chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T.” In a phase I clinical trial in China, the patient’s own T cells were collected, genetically reprogrammed in a lab, and injected back into the patient. The reprogramming involved inserting an artificially designed gene into the T-cell genome, which helped the genetically reprogrammed cells find and destroy cancer cells throughout the body.
