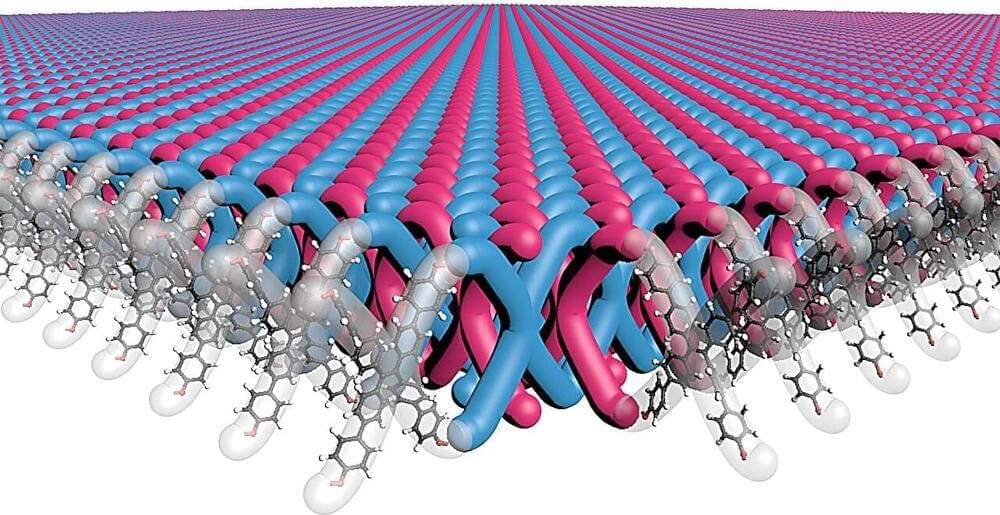
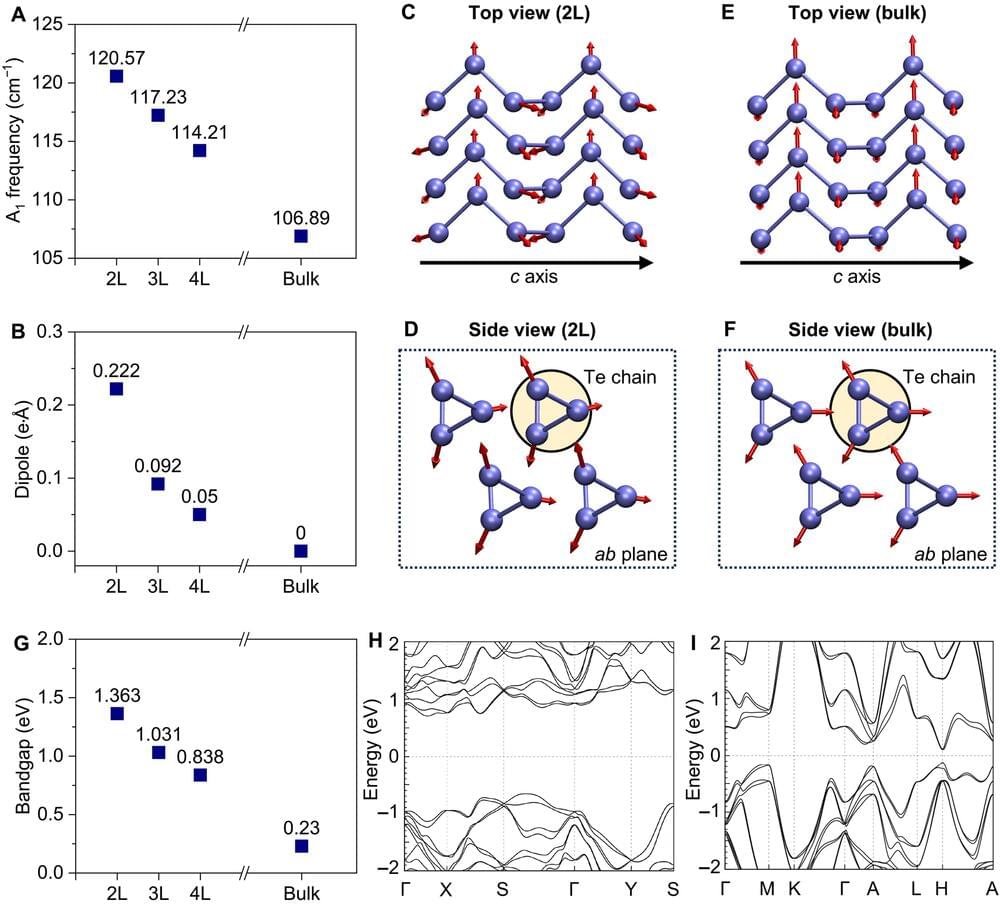
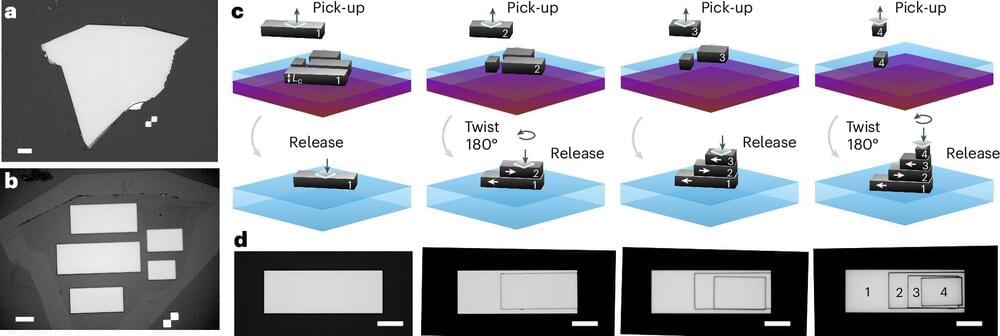
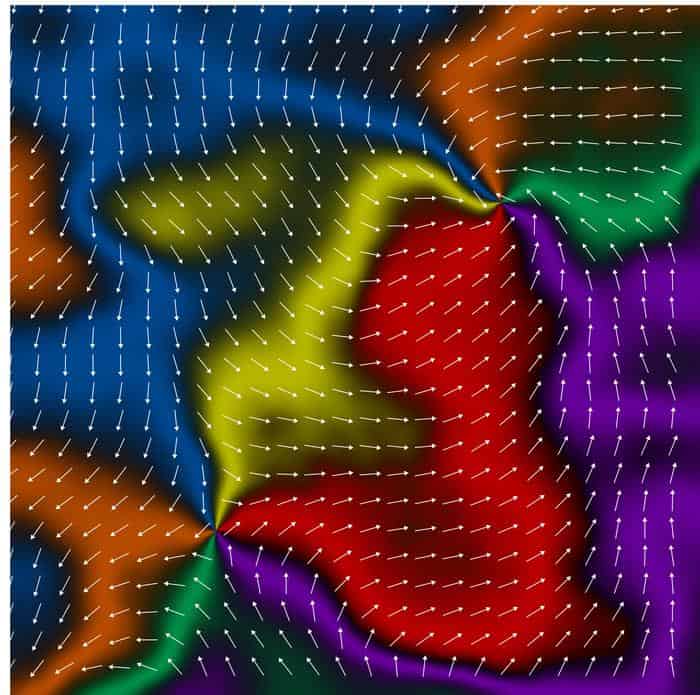
In a remarkable feat of chemistry, a Northwestern University-led research team has developed the first two-dimensional (2D) mechanically interlocked material.
Resembling the interlocking links in chainmail, the nanoscale material exhibits exceptional flexibility and strength. With further work, it holds promise for use in high-performance, light-weight body armor and other uses that demand lightweight, flexible and tough materials.
Publishing on Jan. 17 in the journal Science, the study marks several firsts for the field. Not only is it the first 2D mechanically interlocked polymer, but the novel material also contains 100 trillion mechanical bonds per 1 square centimeter—the highest density of mechanical bonds ever achieved.