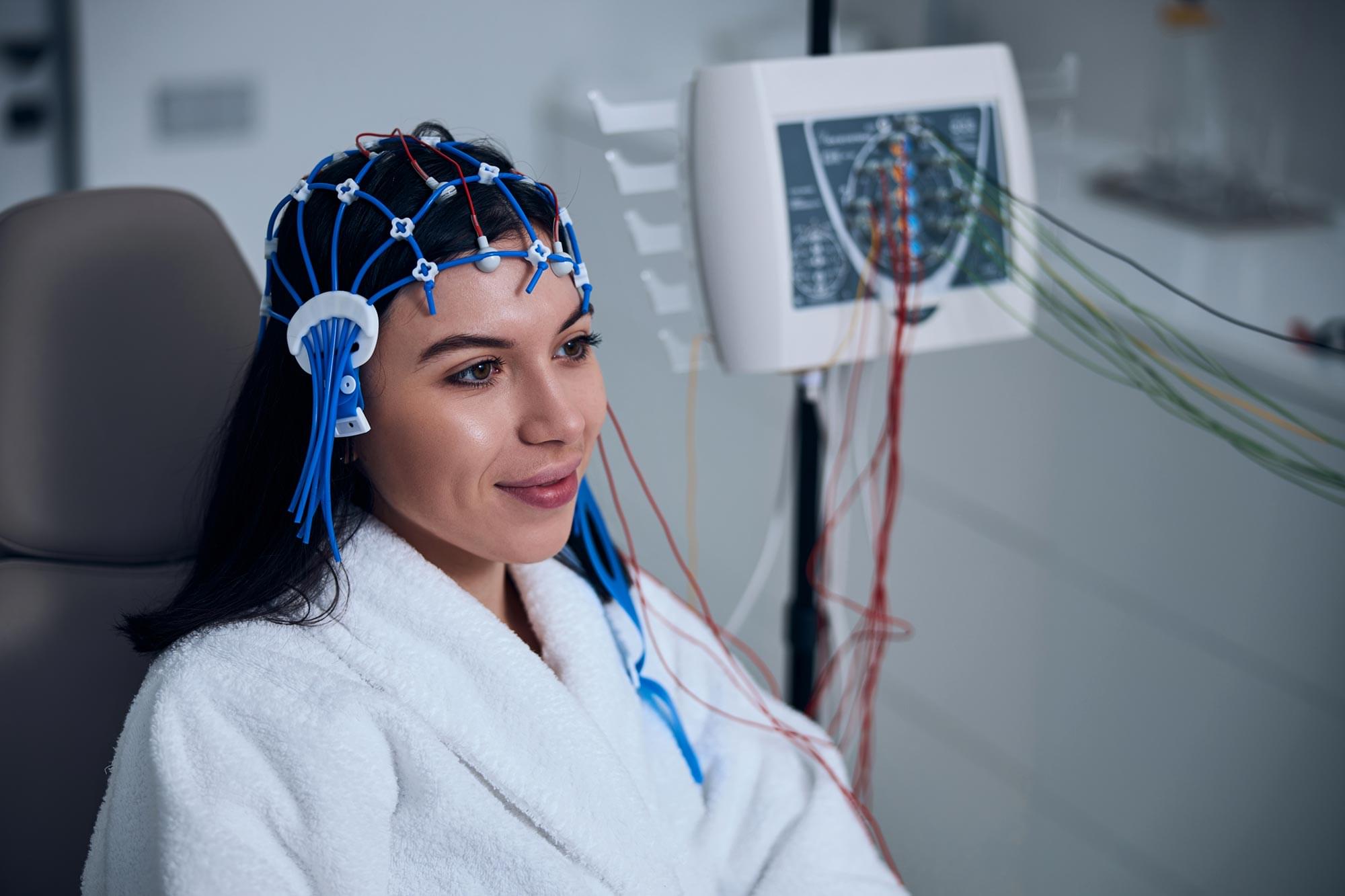
A brain cap and smart algorithms may one day help paralyzed patients turn thought into movement—no surgery required.


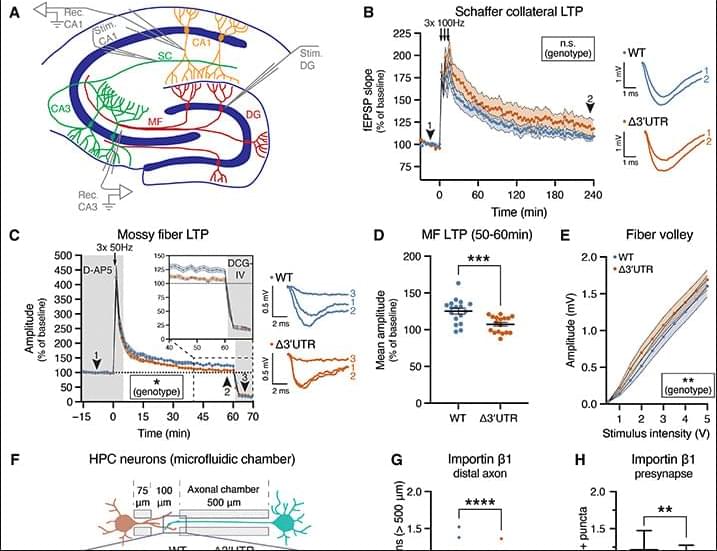
Scientists have mapped out an importin-based pathway that enables neurons to maintain synaptic plasticity and spatial memory despite their unusually elongated shape.
Read more in ScienceSignaling.
Axonal localization of importin β1 is required for presynaptic functions that support spatial memory tasks.
In a recent paper, SFI Professor David Wolpert, SFI Fractal Faculty member Carlo Rovelli, and physicist Jordan Scharnhorst examine a longstanding, paradoxical thought experiment in statistical physics and cosmology known as the “Boltzmann brain” hypothesis—the possibility that our memories, perceptions, and observations could arise from random fluctuations in entropy rather than reflecting the universe’s actual past. The work is published in the journal Entropy.
The paradox arises from a tension at the heart of statistical physics. One of the central pillars of our understanding of the time-asymmetric second law of thermodynamics is Boltzmann’s H theorem, a fundamental concept in statistical mechanics. However, paradoxically, the H theorem is itself symmetric in time.
That time-symmetry implies that it is, formally speaking, far more likely for the structures of our memories, perceptions, and observations to arise from random fluctuations in the universe’s entropy than to represent genuine records of our actual external universe in the past. In other words, statistical physics seems to force us to conclude that our memories might be spurious—elaborate illusions produced by chance that tell us nothing about what we think they do. This is the Boltzmann brain hypothesis.
Navigating the world is no mean feat, especially when the world pushes back. For instance, airflow hitting a fly on its right side can, after a turn, become a headwind. To stay on course, the fly’s brain must interpret sensations that constantly shift with each turn of its body.
Indeed, transforming changing sensory inputs into a more stable, map-like understanding of the world is intimately connected to an animal’s ability to survive and navigate within its environment. How do flies make it look so easy?
Now, a study published in Cell shows that the fly brain uses a surprisingly economical strategy. Earlier work had demonstrated that flies calculate their direction of travel by combining four neural signals, each encoding motion along a different axis. The new research finds that when it comes to wind direction, the brain doesn’t need four neuronal populations, but only two. This is because each population can handle two opposite directions in the wind system.
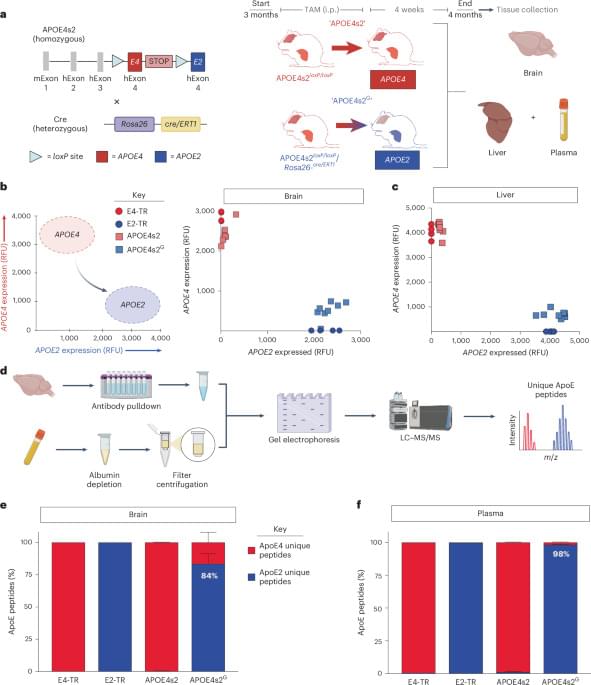
APOE allele switching improves Alzheimer’s in mice.
Type of apolipoprotein E (APOE) allele carried by individuals is a major risk factor in Alzheimer’s disease (AD). For example, compared to individuals carrying two copies of the APOE ε4 allele, ε2 homozygotes have an approximate 99% reduction in late-onset Alzheimer’s disease (AD) risk.
The authors in this study developed a knock-in mouse model that allows for an inducible ‘switch’ between risk and protective alleles (APOE4s2). These mice synthesize E4 at baseline and E2 after tamoxifen administration.
A whole-body allelic switch resulted in a metabolic profile resembling E2/E2 humans and drives AD-relevant alterations in the lipidome and single-cell transcriptome, particularly in astrocytes.
E4 to E2 switching improved cognition, decreased amyloid pathology, lowered gliosis and reduced plaque-associated apolipoprotein E.
Thus, APOE replacement may be a viable strategy for future gene editing approaches to simultaneously reduce multiple AD-associated pathologies. sciencenewshighlights ScienceMission https://sciencemission.com/APOE4-to-APOE2-allelic-switching
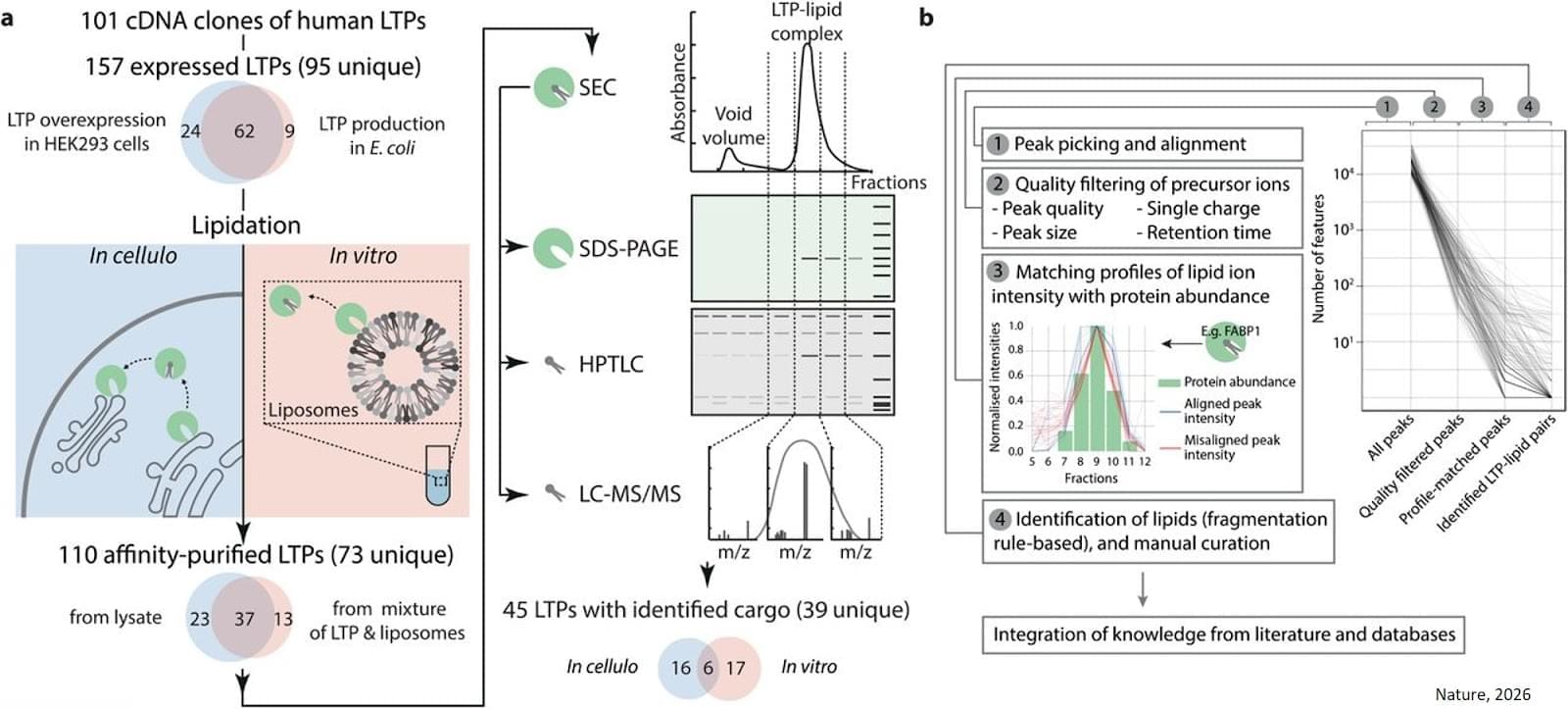
In addition to providing energy, lipids are also essential building blocks of our cell membranes. However, despite their importance, they remain poorly understood. A research team has revealed for the first time the secrets of their transport within cells. Each lipid uses a limited number of proteins to move from its place of production to its place of action. The team has also compiled an inventory of the proteins involved in the transport of hundreds of lipids.
These findings, published in the journal Nature, provide a better picture of the functioning of our cells, as well as of many genetic and metabolic disorders, such as diabetes and Alzheimer’s disease.
Biologists brought together more than a hundred transfer proteins with hundreds of different lipids. The aim was to obtain the most comprehensive list possible of the ‘pairs’ formed between each protein and the lipids it can carry.
To do this, two experimental methods were combined. The first, carried out in a test tube, provides a highly controlled environment, while the second, which more closely corresponds to the inside of a cell, allows researchers to verify how these bonds are formed under near-real conditions. This is a world first on such a scale and at such a level of complexity. “The ‘‘couples’’ identified show that transfer proteins are not “buses” capable of transporting most lipids, but private chauffeurs with specific characteristics,” explains the senior author.
Scientists have been able to determine, using advanced mathematical models, how three transfer proteins recognise, among all lipids, those that they actually transport. ScienceMission sciencenewshighlights.
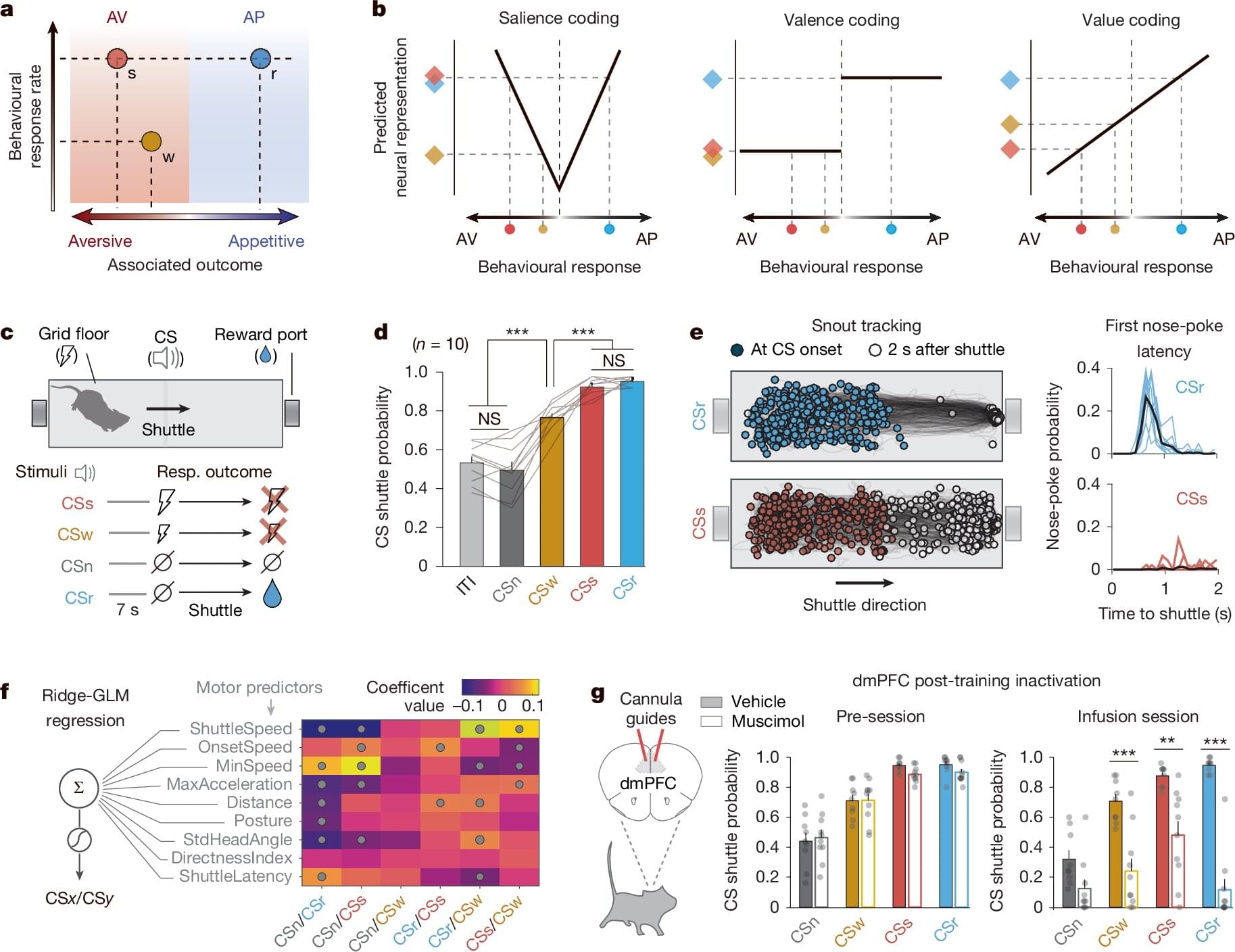
The sound of a fire alarm tells us to get out quickly to not get hurt, while the sight of a gas station sign can signal a chance to refuel. In everyday life, we learn to link cues we sense with what they mean, helping us avoid danger or find what we need. But how does the brain sort and prioritize all these cues and their significance to quickly guide our reactions to what we see, hear, feel and sense?
Following new research in mice, scientists hope to be closer to answering this question.
“A sensory cue, like the sound of an alarm, can be more or less attention-grabbing, feel positive or negative, and feel more or less important or motivating for us to act, depending on what outcome we associate with it. These aspects help define the significance we assign to environmental stimuli and are key to driving behavior and decision-making. But how the brain organizes this information to guide appropriate behaviors remains unclear,” explains Assistant Professor Daniel Jercog from the Department of Neuroscience at the University of Copenhagen.
Vaccines may do far more than prevent infections.
The way that some inoculations train your immune system could also reduce the risk of cancer, stroke, or heart attacks, and possibly guard against dementia.
New evidence shows that the shingles vaccine is linked to slower aging, with benefits that can last for several years after vaccination.
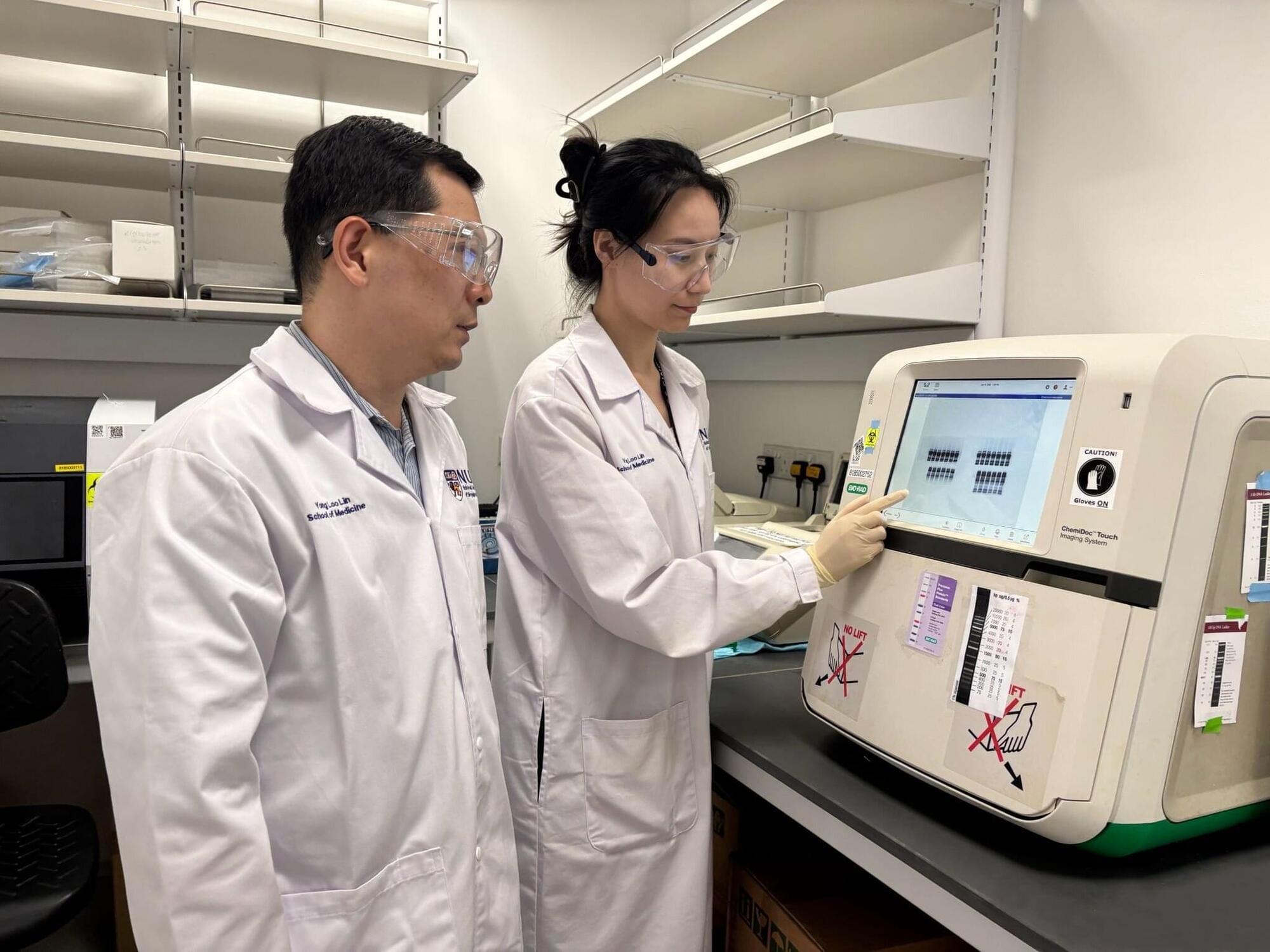

Researchers at the Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine, National University of Singapore (NUS Medicine), have found that a key protein can help to regenerate neural stem cells, which may improve aging-associated decline in neuronal production of an aging brain.
Published in Science Advances, the study identified a transcription factor in the brain, cyclin D-binding myb-like transcription factor 1 (DMTF1), as a critical driver of neural stem cell function during the aging process. Transcription factors are proteins that regulate genes to ensure that they are expressed correctly in the intended cells.
The study, led by Assistant Professor Ong Sek Tong Derrick and first author Dr. Liang Yajing, both from the Department of Physiology and the Healthy Longevity Translational Research Program at NUS Medicine, sought to identify biological factors that influence the degeneration of neural stem cell function often associated with aging, and guide the development of therapeutic approaches to mitigate the adverse effects of neurological aging.
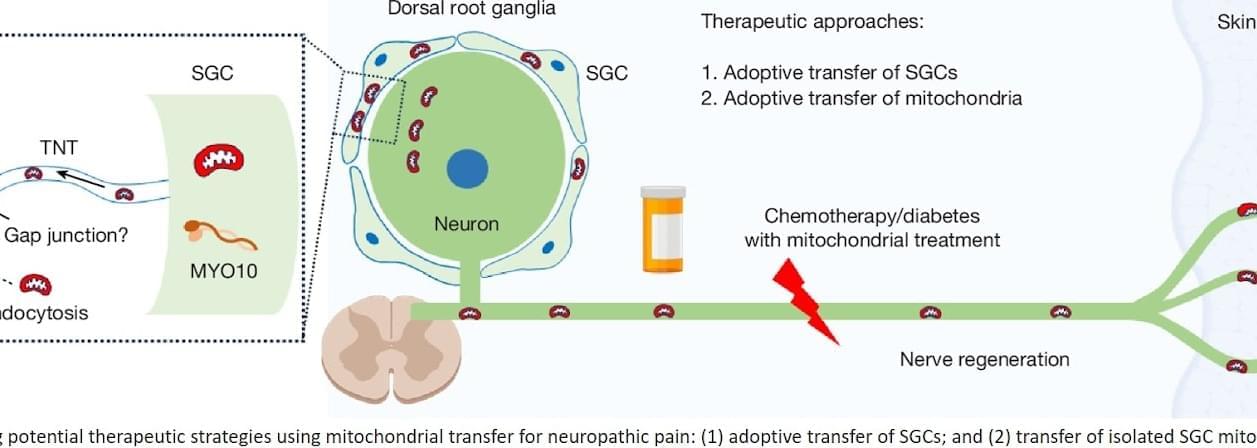
For millions living with nerve pain, even a light touch can feel unbearable. Scientists have long suspected that damaged nerve cells falter because their energy factories known as mitochondria don’t function properly.
Now research published in Nature suggests a way forward: supplying healthy mitochondria to struggling nerve cells.
Using human tissue and mouse models, researchers found that replenishing mitochondria significantly reduced pain tied to diabetic neuropathy and chemotherapy-induced nerve damage. In some cases, the relief lasted up to 48 hours.
Instead of masking symptoms, the approach could fix what the team sees as the root problem — restoring the energy flow that keeps nerve cells healthy and resilient.
“By giving damaged nerves fresh mitochondria — or helping them make more of their own — we can reduce inflammation and support healing,” said the study’s senior author. “This approach has the potential to ease pain in a completely new way.
The work highlights a previously undocumented role for satellite glial cells, which appear to deliver mitochondria to sensory neurons through tiny channels called tunnelling nanotubes.
When this mitochondrial handoff is disrupted, nerve fibers begin to degenerate — triggering pain, tingling and numbness, often in the hands and feet, the distal ends of the nerve fibers.