Sep 27, 2015
Time Travel Could Become Reality Sooner Than You Think
Posted by Shailesh Prasad in categories: particle physics, quantum physics, space, time travel
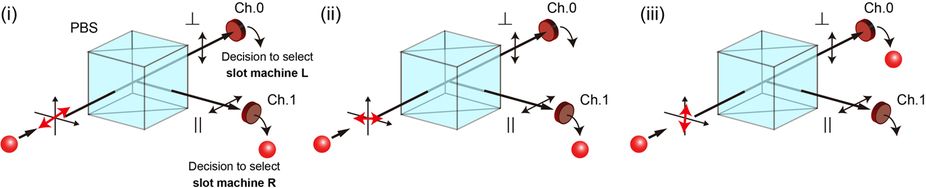
According to scientists photons can travel through time. They already have simulated directing quantum light particles to the past for the first time in the history. University of Queensland scientists learned that a simulation of two wormhole-travelling photons might interrelate; signifying hopping through time is conceivable at smallest scales. Their study might help to comprehend how time-travel could be conceivable in the quantum realm. PhD student Martin Ringbauer spoke to The Speaker: “For the first, ‘photon one’ would travel through a wormhole into the past and interact with its older version. In the second, ‘photon two’ travels through normal space-time but interacts with a photon that is stuck in a time-travelling loop through a wormhole, known as a closed timelike curve (CTC).”
Tim Ralph, UQ Physics Professor, said: “We used single photons to do this, but the time-travel was simulated by using a second photon to play the part of the past incarnation of the time travelling photon.”
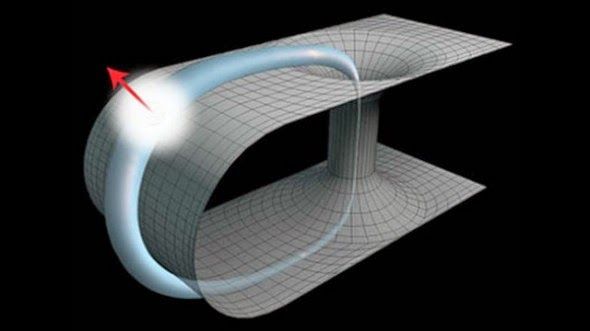


 The dimensionless aspect, since it has no dimensions, is outside of space and time. This is the key aspect to existence: an aspect outside of space and time perpetually interacting dialectically with an aspect inside space and time. All of the weird and wonderful phenomena of the universe are the products of this ultimate dichotomy.
The dimensionless aspect, since it has no dimensions, is outside of space and time. This is the key aspect to existence: an aspect outside of space and time perpetually interacting dialectically with an aspect inside space and time. All of the weird and wonderful phenomena of the universe are the products of this ultimate dichotomy.