Uncover the truth behind the human lifespan. From Ancient Rome to modern America, discover the progress we’ve made in extending life expectancy and the flaws in measuring it. Join us as we explore the science of aging, the pursuit of immortality, and the ongoing debate on the limits of human longevity.
Category: science – Page 57
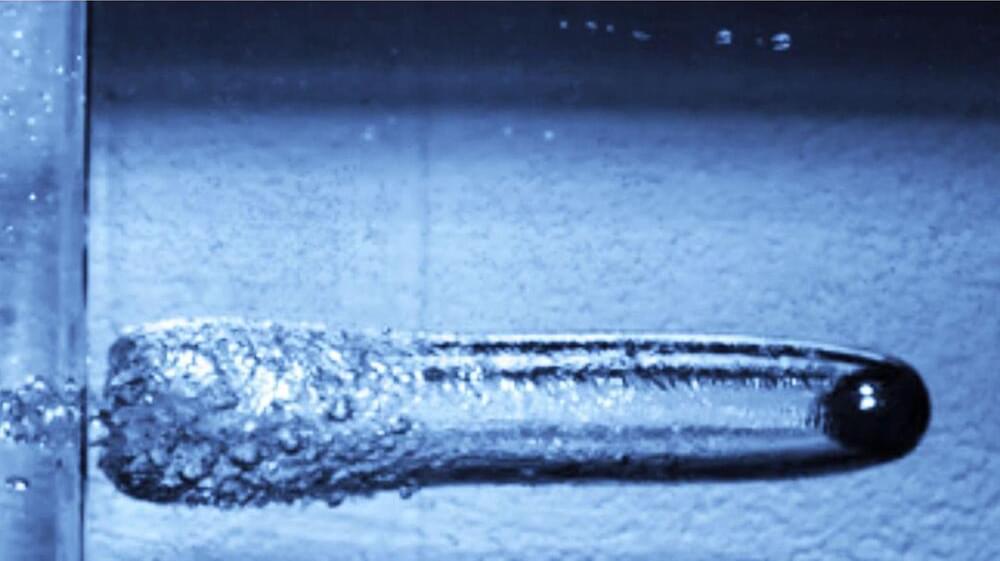

Researchers will shoot a projectile at 9,000 miles an hour for science
The study is being funded by the U.S. Army and Air Force.
Researchers at the Case Western Reserve University in the U.S. are currently working toward an experiment that will record something that has never been captured at such a resolution before; the moment of impact when a projectile traveling at 9,000 miles (14,484 km) an hour hits a wall of water, a press release said.
Research of this nature has been done earlier, but that was nearly eight decades ago. Back in the 1940s, the U.S. military conducted such studies to gauge the impact of shockwaves from underwater explosions on boats and submarines.
The Daily.
Bryan Schmidt, an assistant professor of mechanical and aerospace engineering at Case Western Reserve University, expects that the upcoming experiments will be twice as fast as what has previously been studied, and the recording equipment is far superior now.

‘Disruptive’ science has declined — and no one knows why
Why the slide?
It is important to understand the reasons for the drastic changes, Walsh says. The trend might stem in part from changes in the scientific enterprise. For example, there are now many more researchers than in the 1940s, which has created a more competitive environment and raised the stakes to publish research and seek patents. That, in turn, has changed the incentives for how researchers go about their work. Large research teams, for example, have become more common, and Wang and his colleagues have found3 that big teams are more likely to produce incremental than disruptive science.
Finding an explanation for the decline won’t be easy, Walsh says. Although the proportion of disruptive research dropped significantly between 1945 and 2010, the number of highly disruptive studies has remained about the same. The rate of decline is also puzzling: CD indices fell steeply from 1945 to 1970, then more gradually from the late 1990s to 2010. “Whatever explanation you have for disruptiveness dropping off, you need to also make sense of it levelling off” in the 2000s, he says.
Dr. Stuart Minchin, Ph.D. — Sustainable Pacific Development Through Science, Knowledge & Innovation
Is the Director General of the Pacific Community (SPC — https://www.spc.int/about-us/director-general) which is the largest intergovernmental organization in the Pacific and serves as a science and technology for development organization owned by the 26 Member countries and territories in the Pacific region.
SPC’s 650 member staff deliver services and scientific advice to the Pacific across the domains of Oceans, Islands and People, and has deep expertise in food security, water resources, fisheries, disasters, energy, maritime, health, statistics, education, human rights, social development and natural resources.
Dr. Minchin previously served as the Chief of the Environmental Geoscience Division of Geoscience Australia, and has an extensive background in the management and modelling of environmental data and the online delivery of data, modelling and reporting tools for improved natural resource management. He has a long track record of conceiving, developing and delivering transformational and innovative projects in the Environmental and Natural Resource Management domains.
Dr. Minchin has represented Australia in key international forums and was Australia’s Principal Delegate to both the UN Global Geospatial Information Management Group of Experts (UNGGIM) and the Intergovernmental Group on Earth Observations (GEO).
Dr. Minchin has previously been responsible for the Environmental Observation and Landscape Science (EOLS) research program in CSIRO and prior to that was a Principal Scientist with the Victorian Department of Sustainability and Environment.
Dr. Minchin has a PhD in Aquatic/Environmental Chemistry, from Monash University, where he also did his undergraduate work in Chemistry achieving a BSc (Hons). He also holds a BSc (Aquatic Science), Aquatic Chemistry and Aquatic Biology from Deakin University.

Where Are All The Scientific Breakthroughs? Forget AI, Nuclear Fusion And mRNA Vaccines, Advances In Science And Tech Have Slowed, Major Study Says
Despite surges in fields like AI, medicine and nuclear energy, major advances in science and technology are slowing and are fewer and farther between than decades ago, according to a study published in Nature.
The researchers analyzed some 45 million scientific papers and 3.9 million patents between 1945 and 2010, examining networks of citations to assess whether breakthroughs reinforced the status quo or disrupted existing knowledge and more dramatically pushed science and technology off into new directions.
Across all major scientific and technological fields, these big disruptions—the discovery of the double helix structure of DNA, which rendered earlier research obsolete, is a good example of such research—have become less common since 1945, the researchers found.
Scientists crashed a Boeing 727 on purpose for science in a real-world experiment
A Boeing 727 that spent much of its lifetime ferrying passengers across the world was deliberately crashed into a Mexican desert by a filing crew as part of a big science experiment.


2022 Highlights in Science And Technology
This year has seen remarkable developments in artificial intelligence, an inflection point for quantum computing, progress in aging research, a number of exciting discoveries in astronomy, a potentially revolutionary new material, and many more breakthroughs.
These were our top 20 most viewed blogs of 2022, in reverse order. See you in 2023!
The Future of Data Science and AI: Careers in Data Science
Join the Pan Asian Alumni Network (PAAN) and the Alumni Club of New York City for a series of virtual panels featuring diverse perspectives from the UChicago alumni community exploring career pathways, philosophical questions and trends determining the future of data science and artificial intelligence.
The first program in our series, Careers in Data Science, brings together UChicago alumni across different industries to discuss their career pathways, highlight key industry trends, and share advice for anyone looking to break into these fields.
The Biggest Discoveries in Computer Science in 2022
As computer scientists tackle a greater range of problems, their work has grown increasingly interdisciplinary. This year, many of the most significant computer science results also involved other scientists and mathematicians. Perhaps the most practical involved the cryptographic questions underlying the security of the internet, which tend to be complicated mathematical problems. One such problem — the product of two elliptic curves and their relation to an abelian surface — ended up bringing down a promising new cryptography scheme that was thought to be strong enough to withstand an attack from a quantum computer. And a different set of mathematical relationships, in the form of one-way functions, will tell cryptographers if truly secure codes are even possible.
Computer science, and quantum computing in particular, also heavily overlaps with physics. In one of the biggest developments in theoretical computer science this year, researchers posted a proof of the NLTS conjecture, which (among other things) states that a ghostly connection between particles known as quantum entanglement is not as delicate as physicists once imagined. This has implications not just for our understanding of the physical world, but also for the myriad cryptographic possibilities that entanglement makes possible.