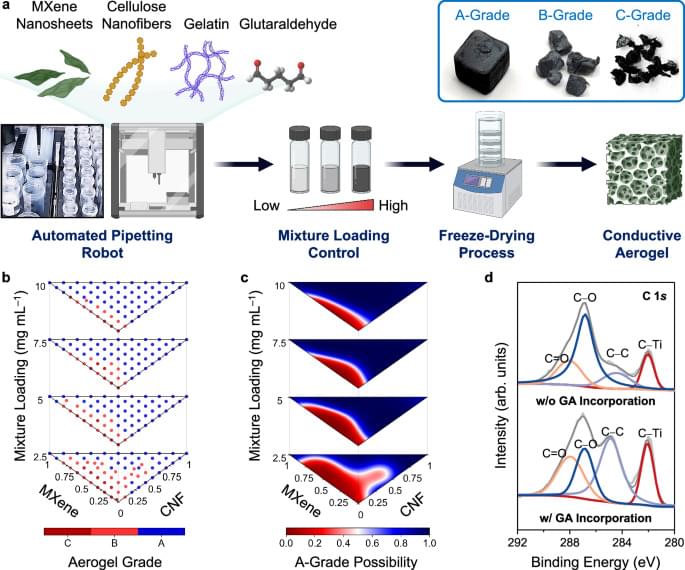
Conductive aerogels have gained significant research interests due to their ultralight characteristics, adjustable mechanical properties, and outstanding electrical performance1,2,3,4,5,6. These attributes make them desirable for a range of applications, spanning from pressure sensors7,8,9,10 to electromagnetic interference shielding11,12,13, thermal insulation14,15,16, and wearable heaters17,18,19. Conventional methods for the fabrication of conductive aerogels involve the preparation of aqueous mixtures of various building blocks, followed by a freeze-drying process20,21,22,23. Key building blocks include conductive nanomaterials like carbon nanotubes, graphene, Ti3C2Tx MXene nanosheets24,25,26,27,28,29,30, functional fillers like cellulose nanofibers (CNFs), silk nanofibrils, and chitosan29,31,32,33,34, polymeric binders like gelatin25,26, and crosslinking agents that include glutaraldehyde (GA) and metal ions30,35,36,37. By adjusting the proportions of these building blocks, one can fine-tune the end properties of the conductive aerogels, such as electrical conductivities and compression resilience38,39,40,41. However, the correlations between compositions, structures, and properties within conductive aerogels are complex and remain largely unexplored42,43,44,45,46,47. Therefore, to produce a conductive aerogel with user-designated mechanical and electrical properties, labor-intensive and iterative optimization experiments are often required to identify the optimal set of fabrication parameters. Creating a predictive model that can automatically recommend the ideal parameter set for a conductive aerogel with programmable properties would greatly expedite the development process48.
Machine learning (ML) is a subset of artificial intelligence (AI) that builds models for predictions or recommendations49,50,51. AI/ML methodologies serve as an effective toolbox to unravel intricate correlations within the parameter space with multiple degrees of freedom (DOFs)50,52,53. The AI/ML adoption in materials science research has surged, particularly in the fields with available simulation programs and high-throughput analytical tools that generate vast amounts of data in shared and open databases54, including gene editing55,56, battery electrolyte optimization57,58, and catalyst discovery59,60. However, building a prediction model for conductive aerogels encounters significant challenges, primarily due to the lack of high-quality data points. One major root cause is the lack of standardized fabrication protocols for conductive aerogels, and different research laboratories adopt various building blocks35,40,46. Additionally, recent studies on conductive aerogels focus on optimizing a single property, such as electrical conductivity or compressive strength, and the complex correlations between these attributes are often neglected to understand37,42,61,62,63,64. Moreover, as the fabrication of conductive aerogels is labor-intensive and time-consuming, the acquisition rate of training data points is highly limited, posing difficulties in constructing an accurate prediction model capable of predicting multiple characteristics.
Herein, we developed an integrated platform that combines the capabilities of collaborative robots with AI/ML predictions to accelerate the design of conductive aerogels with programmable mechanical and electrical properties (see Supplementary Fig. 1 for the robot–human teaming workflow). Based on specific property requirements, the robots/ML-integrated platform was able to automatically suggest a tailored parameter set for the fabrication of conductive aerogels, without the need for conducting iterative optimization experiments. To produce various conductive aerogels, four building blocks were selected, including MXene nanosheets, CNFs, gelatin, and GA crosslinker (see Supplementary Note 1 and Supplementary Fig. 2 for the selection rationale and model expansion strategy). Initially, an automated pipetting robot (i.e., OT-2 robot) was operated to prepare 264 mixtures with varying MXene/CNF/gelatin ratios and mixture loadings (i.e.