Tech firm is building ‘humanoid park’ in US to try out robots, which could ‘spring out’ of its vans



The organization of this paper is as follows. In Section 2 we introduce the formalism used to estimate the number of lunar craters containing ore-bearing asteroid remnants. In Section 2.1, we use the formalism to estimate the number of PGM ore-bearing craters, and in Section 2.2, we use it to obtain the number of water-bearing craters, before concluding in Section 3.

If we chose to shovel matter along a straight line through the observable Universe, what is the average mass of matter per unit area that our shovel will collect? To answer this question, I did a simple calculation before my morning jog at sunrise today.
The answer depends on how far the shovel goes. Projecting all the matter out to the farthest galaxy, MoM-z14, discovered last month by the Webb telescope at a cosmic redshift 14.44 or equivalently 280 million years after the Big Bang, the answer is about 0.5 grams per square centimeter, of order the mass per unit area of a thumb. This establishes the cosmic rule-of-thumb: the observable universe yields on average as much mass per unit area as a thumb.
This mass budget includes mostly dark matter whose nature is unknown. Ordinary matter accounts for only 16% of the total budget or 0.08 grams per square centimeter out to MoM-z14, of order the surface mass density of a fingernail.

Scientists know the stomach talks to the brain, but two new studies from Rutgers Health researchers suggest the conversation is really a tug-of-war, with one side urging another bite, the other signaling “enough.”
Together, the papers in Nature Metabolism and Nature Communications trace the first complementary wiring diagram of hunger and satiety in ways that could refine today’s blockbuster weight-loss drugs and blunt their side effects.
One study, led by Zhiping Pang of Robert Wood Johnson Medical School’s Center for NeuroMetabolism, pinpointed a slender bundle of neurons that runs from the hypothalamus to the brainstem.

The bottom line is that no matter what the zero-point energy is, it’s the background of the universe on top of which all of physics takes place. Just as you can’t go lower than the ground floor of a building with no basement, you can’t get lower than the ground state of the universe — so there’s nothing for you to extract, and there’s no way to leverage that into useful applications of energy.
So, unfortunately, any work you do in the universe will have to be done the old-fashioned way.
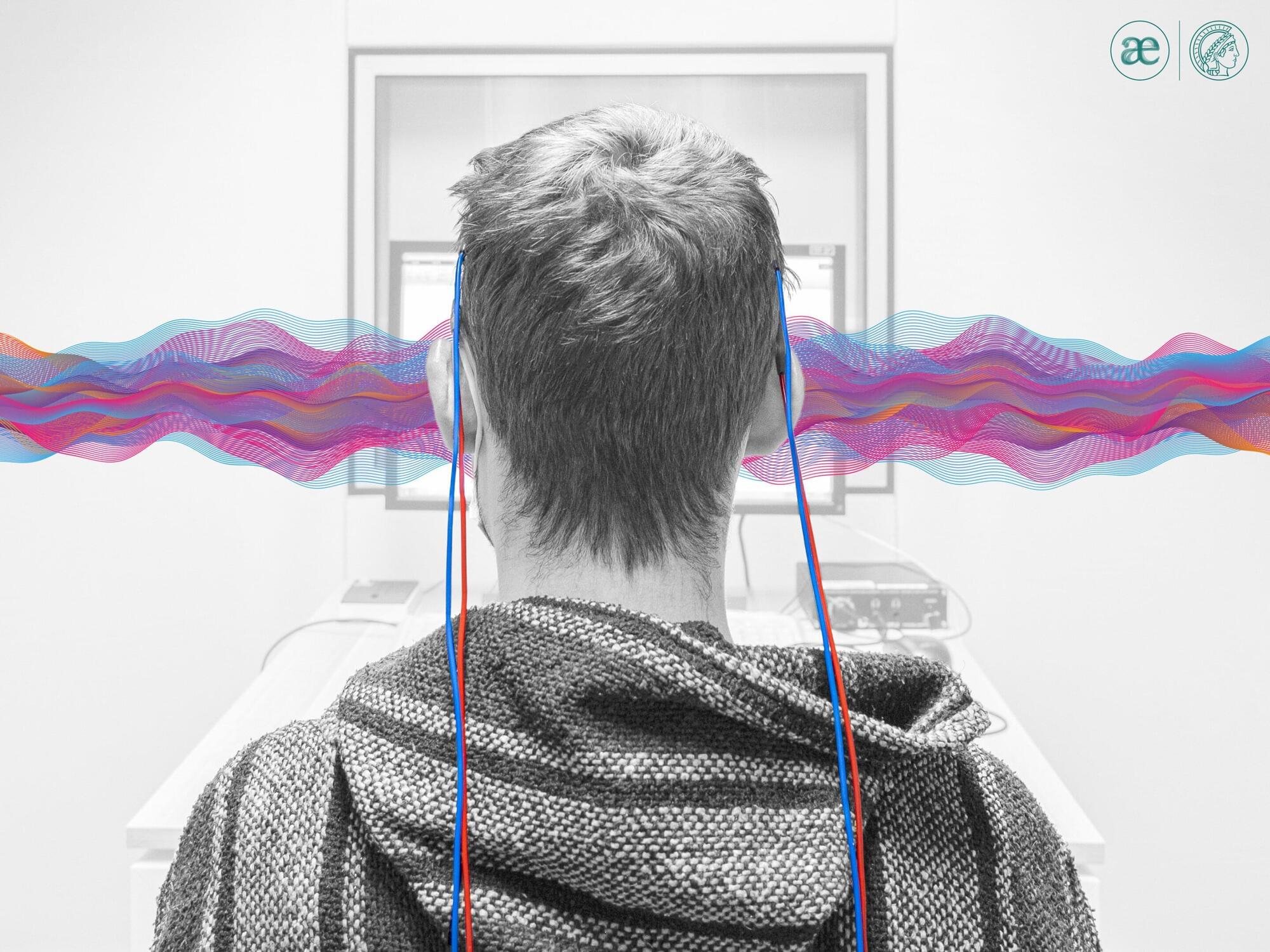

Our brain is adept at synchronizing with rhythmic sounds, whether it’s the beat of a song or the steady patter of rain. This ability helps us recognize and process sounds more effectively.
A research team led by the Max Planck Institute for Empirical Aesthetics (MPIEA) in Frankfurt am Main has shown that stimulation with weak electrical currents, known as transcranial alternating current stimulation (tACS), can influence this ability. The new study is published in the journal PLOS Biology.
The study builds on previous work showing that tACS can either enhance or suppress brain rhythms depending on how it’s timed with incoming sound. In order to investigate the interaction between electrical stimulation and brain rhythms, 50 participants took part in three experiments where they listened to noisy sounds and were asked to identify short, barely perceptible pauses. The researchers then transmitted electrical rhythms to the participants’ brains via electrodes placed on their scalps several times to see how this influenced their brain activity.
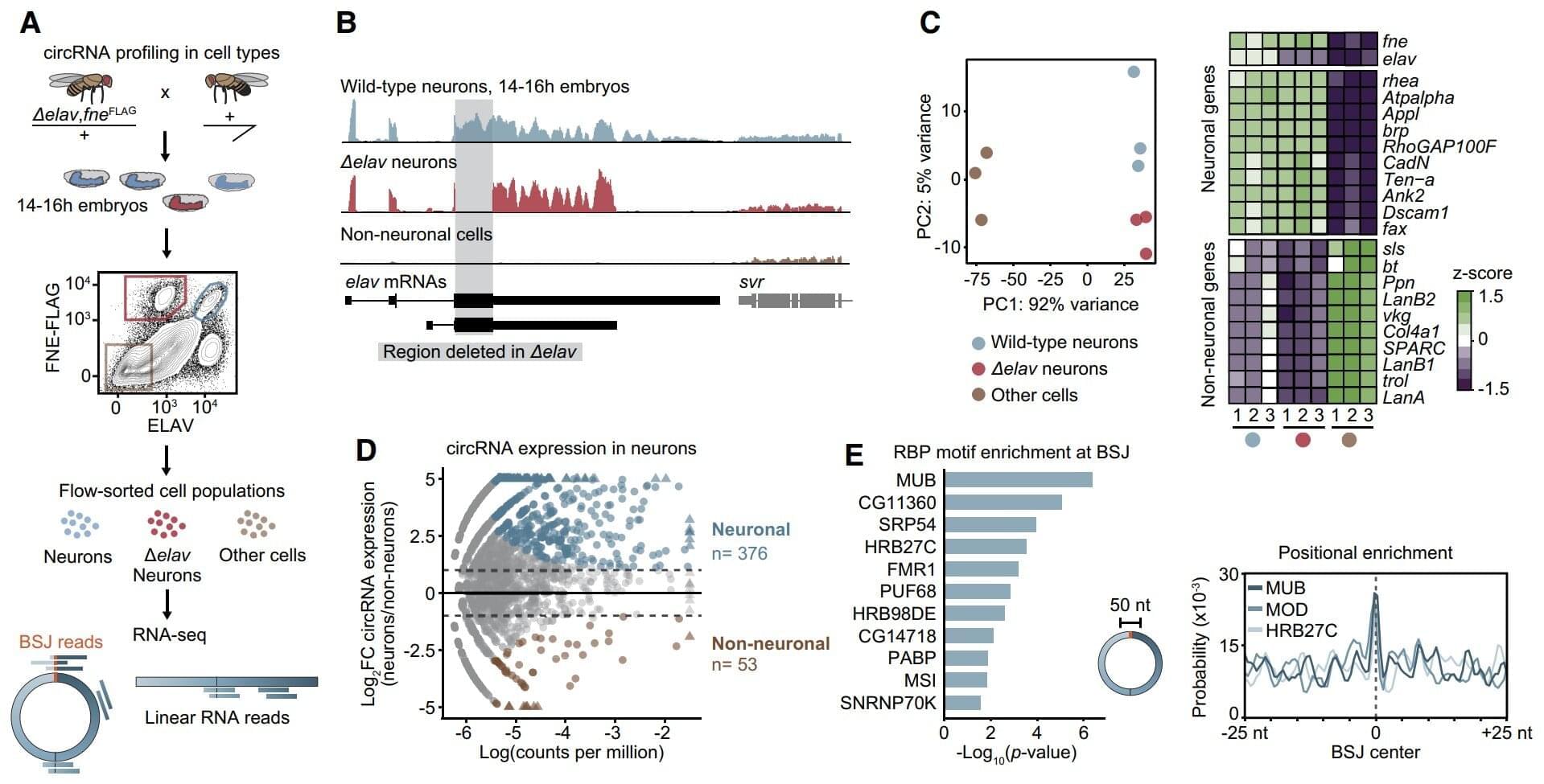
Deep within our nerve cells, a molecule is at work that has no beginning and no end. Instead of a straight chain, as is common for most RNA strands, it forms a closed loop. Known as circular RNAs (circRNAs), these molecules are crucial for development, thought, and synaptic function, yet their high prevalence in neurons has long been a scientific mystery. How does the brain produce so many of them?
Now, Max Planck researchers from Freiburg have discovered a crucial mechanism that explains the remarkable abundance of circRNAs in the nervous system. Published in Genes & Development, the study reveals that the protein ELAV acts as a global master switch for the production of these molecules.
CircRNAs are found across all life forms. They are expressed in specific patterns during different developmental stages and in different cells—especially abundant in cells of the nervous system. While their roles are not as well-studied as normal, linear RNAs, circRNAs are known to be important in brain development, cognition, and even in conditions like neurodegeneration and addiction.
Among the billions of neurons in the brain, fewer than 500 are responsible for suppressing binge drinking, according to new research by Gilles E. Martin, Ph.D., associate professor of neurobiology.
Published in Nature Neuroscience, these findings provide insights into binge-drinking behavior and alcohol dependency that may lead to new therapeutic targets.
“It’s really hard to comprehend how only a few neurons can have such a profound effect on behavior,” said Dr. Martin, a member of the Brudnick Neuropsychiatric Research Institute at UMass Chan. “This is exciting because we are starting to understand how only a handful of cells are involved in very specific behaviors. Truly, this study is about finding a needle in a haystack.”