Leukemia starts when mutations in blood-forming cells disrupt the balance between growth and differentiation. Patients with entirely different genetic changes show strikingly similar patterns of gene activity and can respond to the same drugs. What invisible thread could make so many mutations behave the same way?
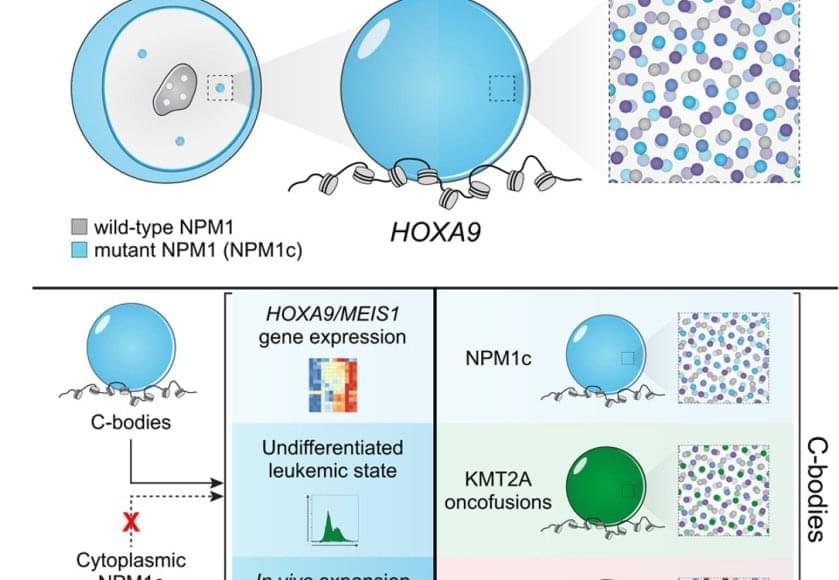
The authors looked into high-resolution microscope and saw something no one expected: leukemia cell nuclei shimmered with a dozen bright dots – tiny beacons missing from healthy cells.
Those dots weren’t random. They contained large amounts of mutant leukemia proteins and drew in many normal cell proteins to coordinate activation of the leukemia program. The dots were new nuclear compartments formed by phase separation, the same physical principle that describes why oil droplets form in water. The team named this new compartment, “coordinating bodies,” or C-bodies.
Inside the nucleus, these C-bodies act like miniature control rooms, pulling together the molecules that keep leukemia genes switched on. Like drops of oil collecting on the surface of soup, they appear when the cell’s molecular ingredients reach just the right balance.
Even more surprising, cells carrying entirely different leukemia mutations formed droplets with the same behavior. Although their chemistry differs, the resulting nuclear condensates perform the same function, using the same physical playbook.
A new quantitative assay confirmed it. These droplets are biophysically indistinguishable – like soups made from different ingredients that still simmer into the same consistency. No matter which mutation started the process, each leukemia formed the same kind of C-body.
The team confirmed the finding across human cell lines, mouse models and patient samples. When they tweaked the proteins so they could no longer form these droplets – or dissolved them with drugs, the leukemia cells stopped dividing and began to mature into healthy blood cells.