Will today’s wars over oil be over water in the future? For years this question has been at the heart of a scientific debate on the causes of these wars and how they should be studied.
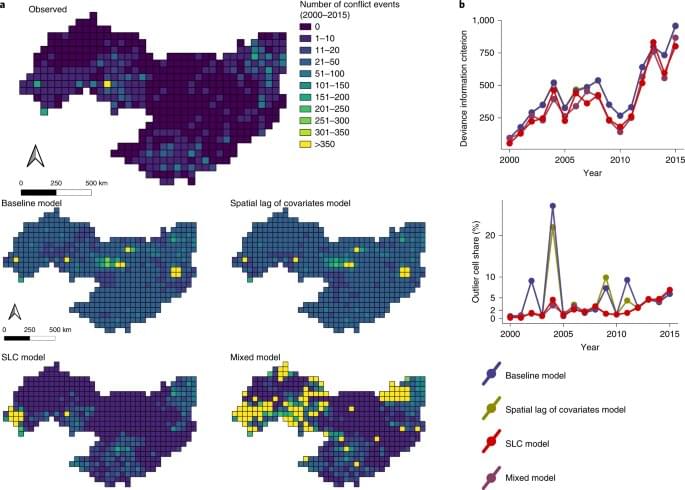
A study published in the prestigious Nature Sustainability by a group of researchers from the Politecnico di Milano has investigated the phenomenon, also in light of “new” types of conflict in which paramilitary groups seem to capitalize on environmental stress.
In order to define the relationship between water and conflict, speaking only of water availability —or lack thereof—is not enough: in fact, conflicts tend to be associated with specific and complex socio-hydrological conditions, which in turn deal with the socio-economic value of water as a form of livelihood, especially in agriculture, and with the effects that human use of water has on the accessibility of this resource.