After Google ditched Qualcomm chips in its Pixel phones, Android chief Hiroshi Lockheimer brings a message of peace to Qualcomm’s Snapdragon Summit.




Qualcomm kicked off its annual Snapdragon Technology Summit with its new premium smartphone SoC dubbed the Snapdragon Series 8 Gen 1. As expected, the new SoC improves performance and efficiency in every aspect of the chip, but enhancements in AI and image processing are especially important for the next generation of premium smartphones.
The new Series 8 Gen 1 SoC follows the previous Snapdragon 888 generation as Qualcomm’s premium smartphone SoC. And yes, there is a new naming convention with this generation. Rather than continuing to count up until the company runs out of numbers for new products, Qualcomm changed the naming convention to that basic series number (Series, 8, 7, 6, and 4) followed by a generational number, similar to what the company began doing with its Snapdragon 8CX SoCs for PCs. Since this is the first generation of smartphone SoCs to use the new nomenclature, the new family of devices will be “Gen 1”. For now, however, the company only announced the premium chip — the Series 8 Gen 1.
Full Story:
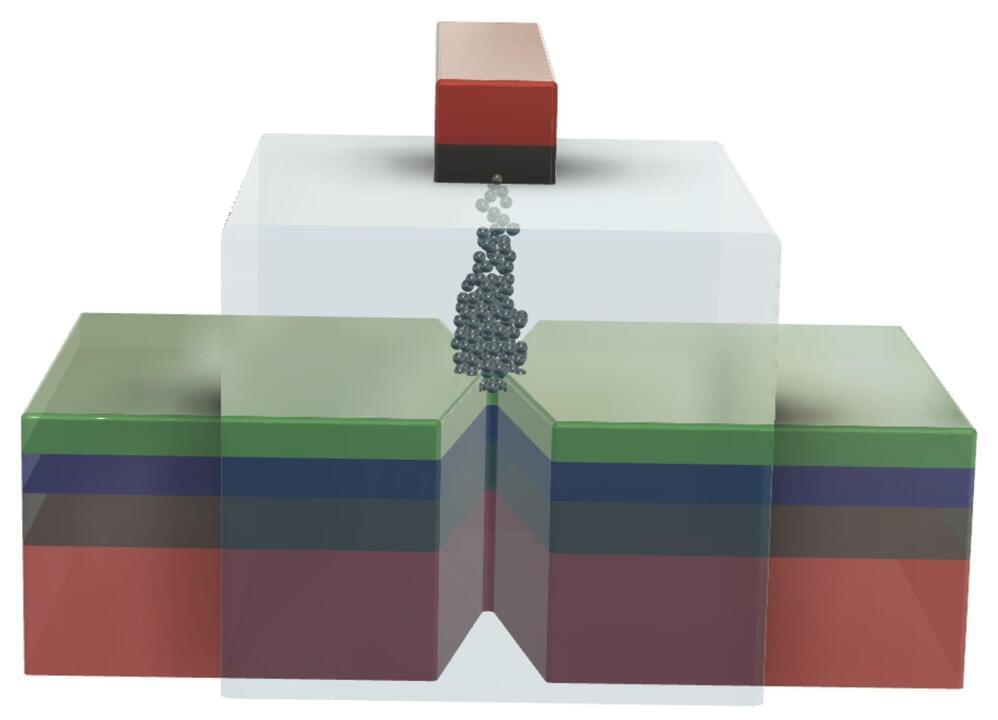

Research has long strived to develop computers to work as energy efficiently as our brains. A study, led by researchers at the University of Gothenburg, has succeeded for the first time in combining a memory function with a calculation function in the same component. The discovery opens the way for more efficient technologies, everything from mobile phones to self-driving cars.
In recent years, computers have been able to tackle advanced cognitive tasks, like language and image recognition or displaying superhuman chess skills, thanks in large part to artificial intelligence (AI). At the same time, the human brain is still unmatched in its ability to perform tasks effectively and energy efficiently.
“Finding new ways of performing calculations that resemble the brain’s energy-efficient processes has been a major goal of research for decades. Cognitive tasks, like image and voice recognition, require significant computer power, and mobile applications, in particular, like mobile phones, drones and satellites, require energy efficient solutions,” says Johan Åkerman, professor of applied spintronics at the University of Gothenburg.
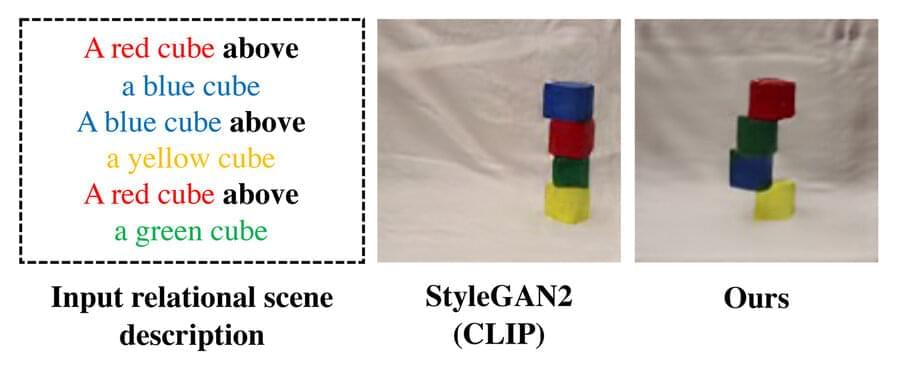
When humans look at a scene, they see objects and the relationships between them. On top of your desk, there might be a laptop that is sitting to the left of a phone, which is in front of a computer monitor.
Many deep learning models struggle to see the world this way because they don’t understand the entangled relationships between individual objects. Without knowledge of these relationships, a robot designed to help someone in a kitchen would have difficulty following a command like “pick up the spatula that is to the left of the stove and place it on top of the cutting board.”
In an effort to solve this problem, MIT researchers have developed a model that understands the underlying relationships between objects in a scene. Their model represents individual relationships one at a time, then combines these representations to describe the overall scene. This enables the model to generate more accurate images from text descriptions, even when the scene includes several objects that are arranged in different relationships with one another.

According to reports, Samsung will increase the proportion of Exynos chips used in its own models in 2022 to reduce its dependence on Qualcomm chips. Samsung’s use of Exynos chips in its own models will increase by about 2–3 times next year. At the same time, Samsung has set a sales target of 300 million mobile phones next year.
Industry insiders pointed out that Samsung is vigorously supporting Exynos chips. On the one hand, it will increase the proportion of Exynos chips in its own models. On the other hand, it is open to partners. Recall that the company co-developed the Exynos 1,080 chip with Vivo which the latter used in the Vivo X60 series.
Watch the newest video from Big Think: https://bigth.ink/NewVideo.
Learn skills from the world’s top minds at Big Think+: https://bigthink.com/plus/
Everything we do as living organisms is dependent, in some capacity, on time. The concept is so complex that scientists still argue whether it exists or if it is an illusion. In this video, astrophysicist Michelle Thaller, science educator Bill Nye, author James Gleick, and neuroscientist Dean Buonomano discuss how the human brain perceives of the passage of time, the idea in theoretical physics of time as a fourth dimension, and the theory that space and time are interwoven. Thaller illustrates Einstein’s theory of relativity, Buonomano outlines eternalism, and all the experts touch on issues of perception, definition, and experience. Check Dean Buonomano’s latest book Your Brain Is a Time Machine: The Neuroscience and Physics of Time at https://amzn.to/2GY1n1z.
TRANSCRIPT: MICHELLE THALLER: Is time real or is it an illusion? Well, time is certainly real but the question is what do we mean by the word time? And it may surprise you that physicists don’t have a simple answer for that. JAMES GLEICK: Physicists argue about and physicists actually have symposia on the subject of is there such a thing as time. And it’s also something that has a traditional in philosophy going back about a century. But, I think it’s fair to say that in one sense it’s a ridiculous idea. How can you say time doesn’t exist when we have such a profound experience of it first of all. And second of all we’re talking about it constantly. I mean we couldn’t get, I can’t get through this sentence with out referring to time. I was going to say we couldn’t get through the day without discussing time. So, obviously when a physicist questions the existence of time they are trying to say something specialized, something technical. BILL NYE: Notice that in English we don’t have any other word for time except time. It’s unique. It’s this wild fourth dimension in nature. This is one dimension, this is one dimension, this is one dimension and time is the fourth dimension. And we call it the fourth dimension not just in theoretical physics but in engineering. I worked on four dimensional autopilots so you tell where you want to go and what altitude it is above sea level and then when you want to get there. Like you can’t get there at any time. GLEICK: Einstein or maybe I should say more properly Minkowski, his teacher and contemporary, offers a vision of space-time as a single thing, as a four dimensional block in which the past and the future are just like spatial dimensions. They’re just like north and south in the equations of physics. And so you can construct a view of the world in which the future is already there and you can say, and physicists do say something very much like this, that in the fundamental laws of physics there is no distinction between the past and the future. And so if you’re playing that game you’re essentially saying time as an independent thing doesn’t exist. Time is just another dimension like space. Again, that is in obvious conflict with our intuitions about the world. We go through the day acting as though the past is over and the future has not yet happened and it might happen this way or it might happen that way. We could flip a coin and see. We tend to believe in our gut that the future is not fully determined and therefore is different from the past. DEAN BUONOMANO: If the flow if time, if our subjective sense of the flow of time is an illusion we have this clash between physics and neuroscience because the dominant theory in physics is that we live in the block universe. And I should be clear. There’s no consensus. There’s no 100 percent agreement. But the standard view in physics is that, and this comes in large part from relativity, that we live in an eternalist universe, in a block universe in which the past, present and future is equally real. So, this raises the question of whether we can trust our brain to tell us that time is flowing. NYE: In my opinion time is both subjective and objective. What we do in science and engineering and in life, astronomy, is measure time as carefully as we can because it’s so important to our everyday world. You go to plant crops you want to know when to plant them. You want to know when to harvest them. If you want to have a global positioning system that enables you to determine which side of the street you’re on, from your phone you need to take into account both the traditional passage of time that you might be familiar with watching a clock here on the Earth’s surface, and the passage of time as it’s affected by the… Read the full transcript at https://bigthink.com/videos/does-time-exist

