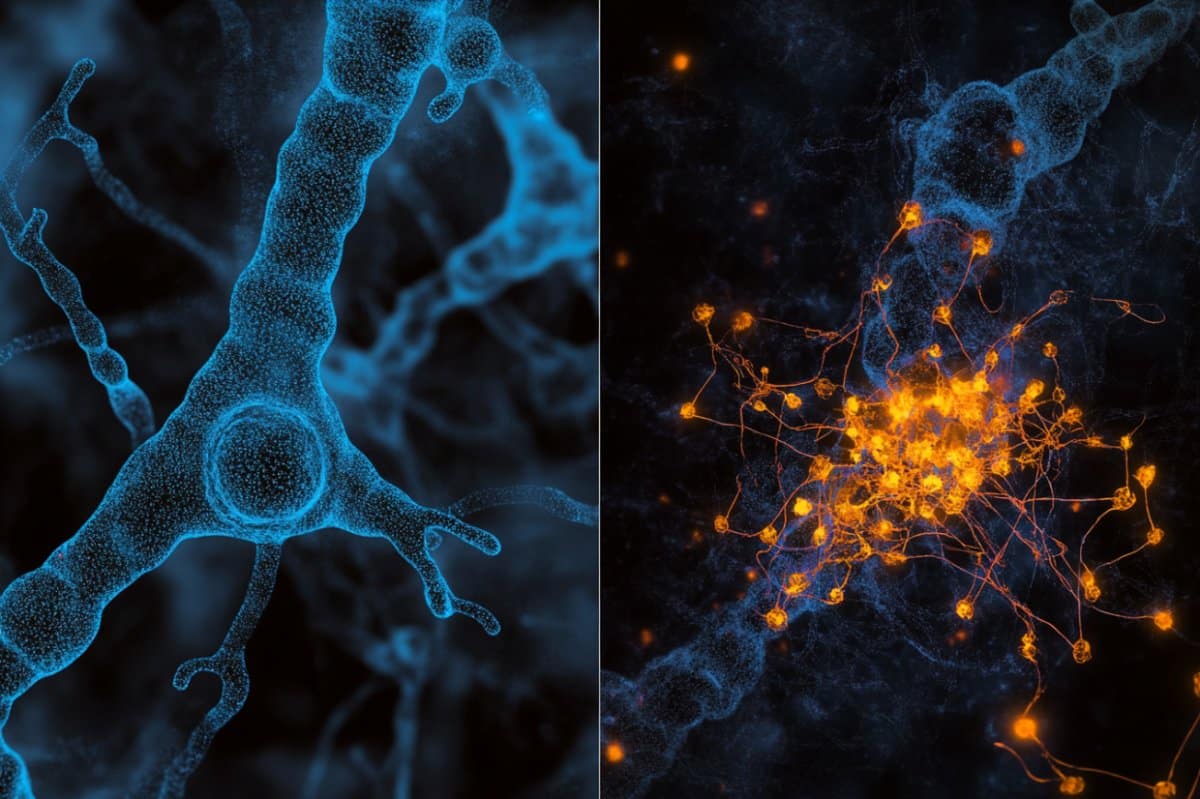
Microscopy on tissue swollen to 16 times its normal size can help unravel neural structures




Valve founder Gabe Newell’s neural chip company Starfish Neuroscience announced it’s developing a custom chip designed for next-generation, minimally invasive brain-computer interfaces—and it may be coming sooner than you think.
The company announced in a blog update that it’s creating a custom, ultra-low power neural chip in collaboration with R&D leader imec.
Starfish says the chip is intended for future wireless, battery-free brain implants capable of reading and stimulating neural activity in multiple areas simultaneously—a key requirement for treating complex neurological disorders involving circuit-level dysfunction. That’s the ‘read and write’ functions we’ve heard Newell speak about in previous talks on the subject.
Gabe Newell, co-founder of Valve, sat down with IGN for a chat about the company, the promise of VR, and Newell’s most bleeding edge project as of late, brain-computer interfaces (BCI).
Whenever I used to think about brain-computer interfaces (BCI), I typically imagined a world where the Internet was served up directly to my mind through cyborg-style neural implants—or basically how it’s portrayed in Ghost in the Shell. In that world, you can read, write, and speak to others without needing to lift a finger or open your mouth. It sounds fantastical, but the more I learn about BCI, the more I’ve come to realize that this wish list of functions is really only the tip of the iceberg. And when AR and VR converge with the consumer-ready BCI of the future, the world will be much stranger than fiction.
Be it Elon Musk’s latest company Neuralink —which is creating “minimally invasive” neural implants to suit a wide range of potential future applications, or Facebook directly funding research on decoding speech from the human brain—BCI seems to be taking an important step forward in its maturity. And while these well-funded companies can only push the technology forward for its use as a medical devices today thanks to regulatory hoops governing implants and their relative safety, eventually the technology will get to a point when it’s both safe and cheap enough to land into the brainpan’s of neurotypical consumers.
Although there’s really no telling when you or I will be able to pop into an office for an outpatient implant procedure (much like how corrective laser eye surgery is done today), we know at least that this particular future will undoubtedly come alongside significant advances in augmented and virtual reality. But before we consider where that future might lead us, let’s take a look at where things are today.
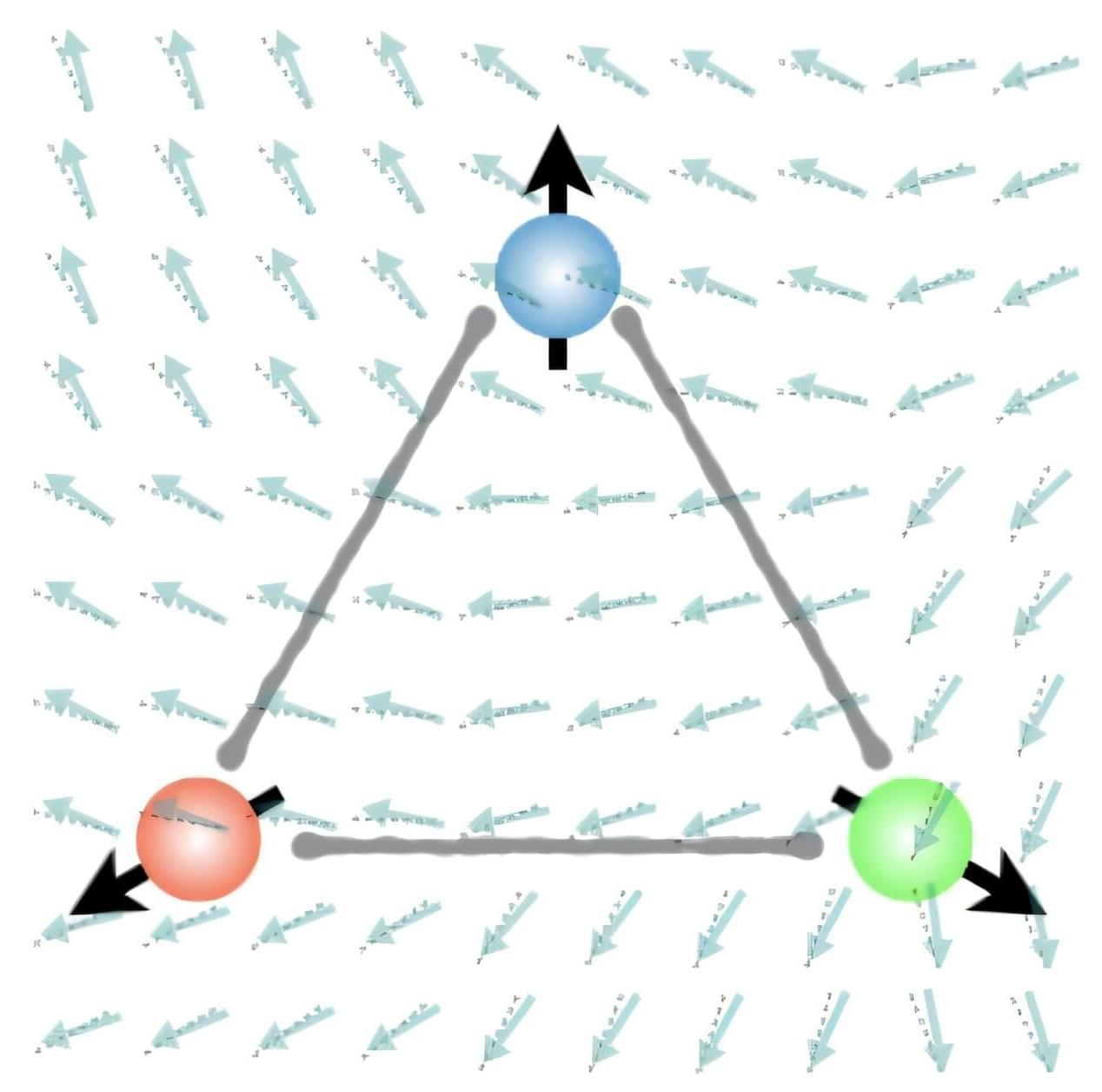
What if the magnon Hall effect, which processes information using magnons (spin waves) capable of current-free information transfer with magnets, could overcome its current limitation of being possible only on a 2D plane? If magnons could be utilized in 3D space, they would enable flexible design, including 3D circuits, and be applicable in various fields such as next-generation neuromorphic (brain-mimicking) computing structures, similar to human brain information processing.
KAIST and an international joint research team have, for the first time, predicted a 3D magnon Hall effect, demonstrating that magnons can move freely and complexly in 3D space, transcending the conventional concept of magnons. The work is published in the journal Physical Review Letters.
Professor Se Kwon Kim of the Department of Physics, in collaboration with Dr. Ricardo Zarzuela of the University of Mainz, Germany, has revealed that the interaction between magnons (spin waves) and solitons (spin vortices) within complex magnetic structures (topologically textured frustrated magnets) is not simple, but complex in a way that enables novel functionalities.