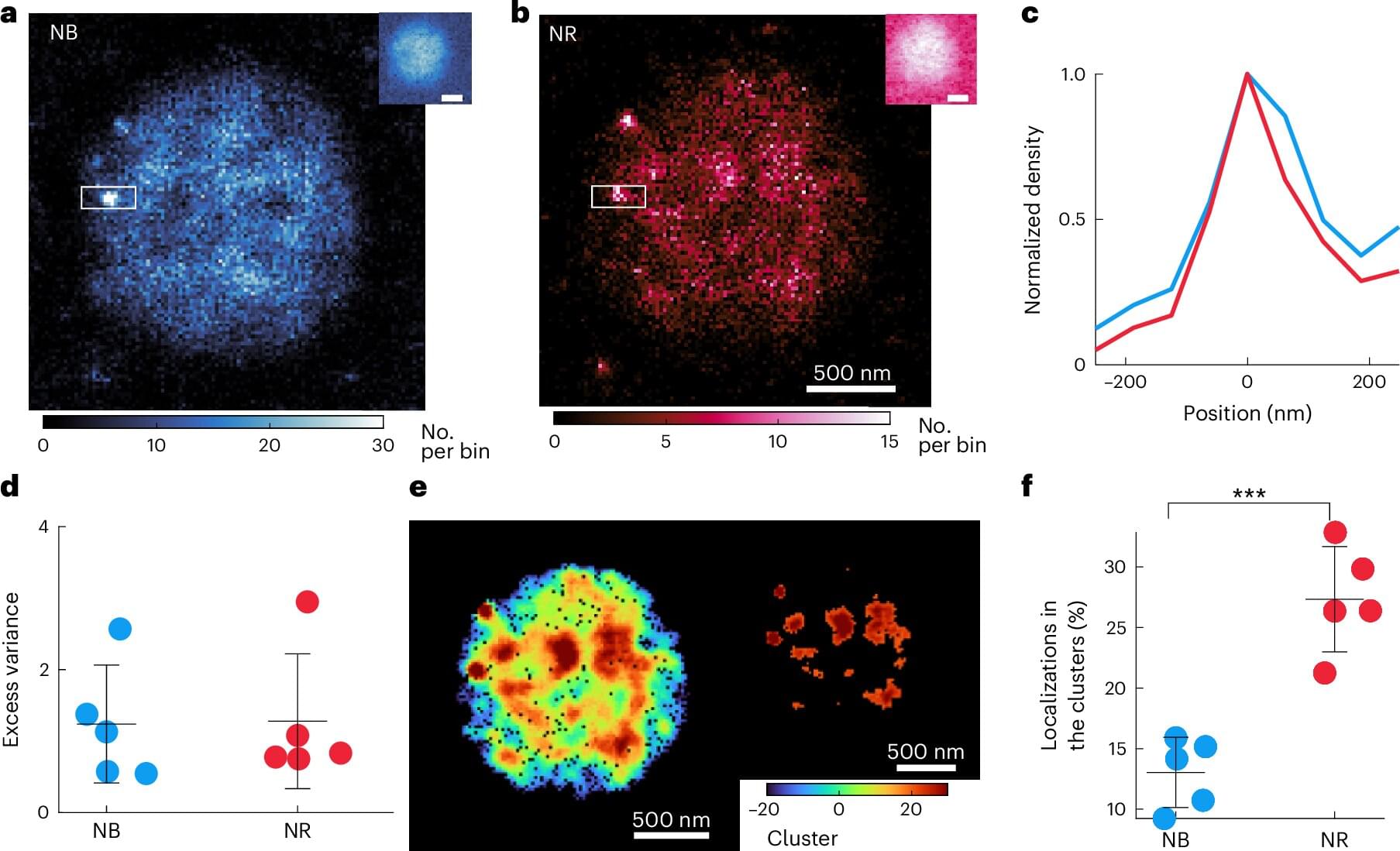
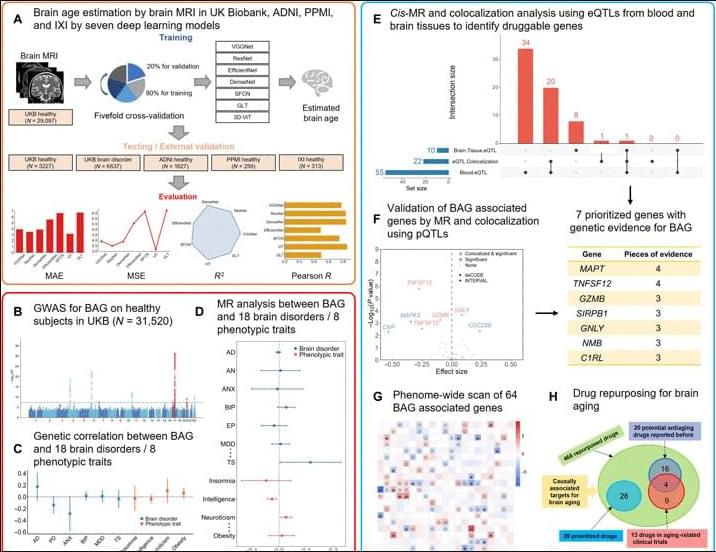
Moreover, among the 37 druggable genes supported by at least two pieces of genetic evidence, we have identified 28 drugs targeting MPL, CA4, TUBB, and RRM1, although neither in clinical trials nor reported previously have the potential to be repurposed for slowing down brain aging. Specifically, four drugs, namely, avatrombopag, eltrombopag, lusutrombopag, and romiplostim, which are typically used for thrombocytopenia, act as agonists for MPL. As mentioned above, MPL is a thrombopoietin receptor and has been linked to platelet count and brain morphology in the GWAS catalog. Notably, platelet signaling and aggregation pathway is enriched using the 64 MR genes. It is worth noting that platelet count decreases during aging and is lower in men compared to women (84). A recent study of platelets has also revealed that platelets rejuvenate the aging brain (85). Schroer et al. (86) found that circulating platelet-derived factors could potentially serve as therapeutic targets to attenuate neuroinflammation and improve cognition in aging mice (86). Park et al. (87) reported that longevity factor klotho induces multiple platelet factors in plasma, enhancing cognition in the young brain and decreasing cognitive deficits in the aging brain (87). Leiter et al. (88) found that platelet-derived platelet factor 4, highly abundant chemokine in platelets, ameliorates hippocampal neurogenesis, and restores cognitive function in aged mice. These findings suggest that the aforementioned drugs may enhance the expression of MPL, leading to increased platelet count and potentially contributing to a delay in brain aging. It is important to note that determining the significant tissue(s) for gene prioritization can be challenging. Although brain tissues may be more biologically relevant for brain aging, circulating proteins have the capability to modulate brain aging as well (89, 90). Six drugs (cladribine, clofarabine, gallium nitrate, gemcitabine, hydroxyurea, and tezacitabine) are inhibitors of RRM1, whereas 12 drugs (brentuximab vedotin, cabazitaxel, crolibulin, indibulin, ixabepilone, paclitaxel, plinabulin, podofilox, trastuzumab emtansine, vinblastine, vinflunine, and vinorelbine) are inhibitors of TUBB. Most of these drugs targeting RRM1 and TUBB are antineoplastic agents used in cancer treatment. In addition, six drugs (acetazolamide, brinzolamide, chlorothiazide, methazolamide, topiramate, and trichlormethiazide) are inhibitors of CA4 and most of them are used for hypertension.
There are a few limitations to this study: (i) The accurate estimation of brain age is hindered by the lack of ground-truth brain biological age and discrepancies between brain biological age and chronological age in supposedly healthy individuals. The estimated brain age derived from MRI data includes inherent biases (91). Although our model has shown better generalization performance compared to other models, there is always an expectation for a more accurate brain age estimation model that can deliver more robust outcomes for clinical applicants (3, 91). (ii) Potential data bias may affect the findings of this comprehensive study. For instance, the brain age estimation model and GWAS summary statistics primarily relied on cohorts of European white individuals, potentially overlooking druggable targets that would be effective in individuals of non-European ancestry. Validation using genomic and clinical data from more diverse populations could help remedy this limitation. (iii) Validation on independent discovery and replication cohorts would enhance the reliability of the identified genes as drug targets for the prevention of brain aging. Although we maximized statistical power using the UKB data as a large discovery cohort, the absence of a discovery-replication design is unavoidable. As large-scale datasets containing both MRI and genome-wide genotypes were not widely available, we used a combination of GWAS for BAG, MR with xQTL, colocalization analysis, MR-PheWAS, and the existing literature to carefully identify genetic targets that are supported by evidence for their involvement in brain aging. With the availability of more comprehensive proteomics platforms and the inclusion of more diverse non-European ancestry populations in studies, it is likely to replicate and validate our results. (iv) Brain aging is a complex process involving numerous potential causes, such as aging of cerebral blood vessels (92), atrophy of the cerebral cortex (93), etc. These causes may overlap and interweave, undergoing considerable changes during brain aging (48). Although our study demonstrates the utility of systematically analyzing GWAS alongside extensive brain imaging information and xQTL analysis to enrich the identification of drug targets, there remains a need for machine learning or statistical methods to address the various risk factors associated with brain aging. Fine-grained analysis is a must to comprehend the individualized causes and trajectories of brain aging, enabling the identification of effective drug targets and the use of precision medications for the purpose of slowing down or even preventing brain aging. There is also an increasing need for comprehensive studies spanning different tissues and organs to evaluate tissue-or organ-specific effects of targets, enabling the systematic prevention or treatment of human aging. (v) This study did not explore adverse effects of the rediscovered antiaging drugs. This is particularly important because healthy aging individuals should be encouraged to consider the potential risks associated with taking medications or supplements for slowing down aging as these interventions may have unintended negative consequences for both individuals and society. Alternatively, it is worthwhile to explore nonpharmacological interventions/digital therapies that can help preserve mental and physical fitness in people during aging.
In summary, we present a systematic study for identify genetically supported targets and drugs for brain aging with deep learning-based brain age estimation, GWAS for BAG, analysis of the relation between BAG and brain disorders, prioritization of targets using MR and colorization analysis for BAG with xQTL data, drug repurposing for these targets of BAG, and PheWAS. Our results offer the potential to mitigate the risk associated with drug discovery by identifying genetically supported targets and repurposing approved drugs to attenuate brain aging. We anticipate that our findings will serve as a valuable resource for prioritizing drug development efforts for BAG, shedding light on the understanding of human brain aging and potentially extending the health span in humans.