It looks like “food from air”
Time: 3–5 min (Eng/Rus)
It looks like “food from air”
Time: 3–5 min (Eng/Rus)
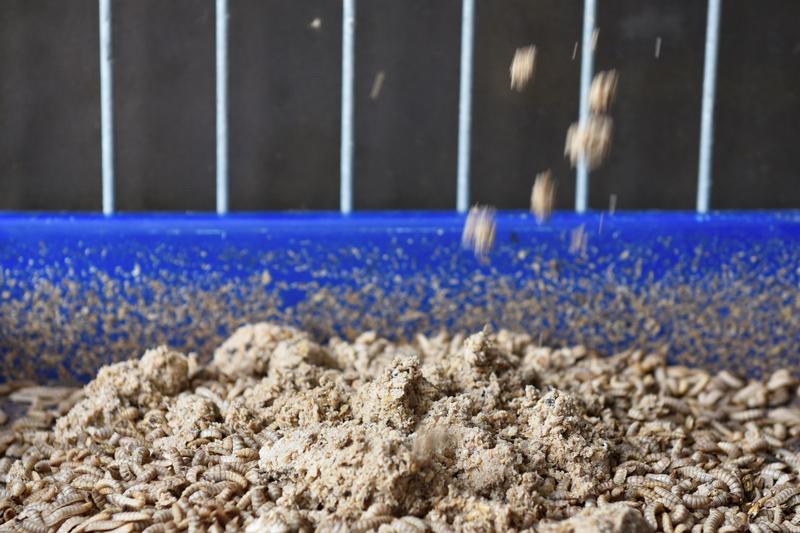

Working in conjunction with Singapore’s Agency for Science, Technology and Research, Insectta’s technology uses a proprietary and environmentally friendly process to extract lucrative substances such as chitosan, melanin and probiotics from the larvae, it said.
SINGAPORE (Reuters) — In a quiet, mainly residential district of Singapore, trays of writhing black soldier fly larvae munch their way through hundreds of kilograms of food waste a day.
The protein-rich maggots can be sold for pet food or fertiliser, but at Insectta — a startup that says it is Singapore’s first urban insect farm — they are bred to extract biomaterials that can be used in pharmaceuticals and electronics.
“What these black soldier flies enable us to do is transform this food waste, which is a negative-value product, into a positive-value product,” said Chua Kai-Ning, Insectta’s co-founder and chief marketing officer.
“Ahsan Noor Khan, a PhD student and first author of the study, said: “We’re now looking to investigate how we could use low-cost existing systems, such as Wi-Fi routers, to detect emotions of a large number of people gathered, for instance in an office or work environment.” Among other things, this could be useful for HR departments to assess how new policies introduced in a meeting are being received, regardless of what the recipients might say. Outside of an office, police could use this technology to look for emotional changes in a crowd that might lead to violence.”
Research from the UK and an update from Elon Musk on human trials at his brain interface company show software is now eating the mind.
The report said the wildlife farms were part of a project the Chinese government has been promoting for 20 years.
Daszak said: “They take exotic animals, like civets, porcupines, pangolins, raccoon dogs and bamboo rats, and they breed them in captivity,” NPR cited. He added that the project was a means to “alleviate rural populations out of poverty,”
In the next two weeks, the WHO is expected to reveal the team’s investigative findings. However, Daszak provided NPR with a “highlight” of what the team determined.

What a beautiful idea.
A woman from the Netherlands has come up with an innovative alternative design for a face mask. Marianne de Groot-Pons, a graphic designer living and working in Utrecht, has created 100% biodegradable masks made out of rice paper and embedded with flower seeds. Once you’ve gotten enough wear out of it, you simply plant the mask and wait for the flowers to grow.
What a lovely take on an object which has become a daily essential in our lives.
This content is imported from Instagram. You may be able to find the same content in another format, or you may be able to find more information, at their web site.
Dr James Desmond, DVM, Co-Founder, Liberia Chimpanzee Rescue & Protection (LCRP), discussing his work at LCRP, as well as his zoonotic disease surveillance work with EcoHealth.
Liberia Chimpanzee Rescue & Protection (LCRP — https://www.liberiachimpanzeerescue.org/) is the first and only chimpanzee sanctuary and conservation center in Liberia rescuing chimpanzees who are victims of the illegal bush meat and pet trades. The organization has over 40 orphaned chimpanzees, nearly all under the age of five, currently under their care.
Dr. James Desmond is the co-founder Liberia Chimpanzee Rescue & Protection. He is a wildlife veterinarian and a consultant specializing in emerging disease and the illegal wildlife trade. He graduated from Tufts Cummings School of Veterinary Medicine, earning a Doctor of Veterinary Medicine degree and a Masters in Comparative Biomedical Sciences. Alongside his work with Liberia Chimpanzee Rescue & Protection, Dr. Desmond leads research on infectious disease, including identifying novel wildlife reservoirs for the Ebola virus.
Jenny Desmond is a co-founder of Liberia Chimpanzee Rescue & Protection and she leads the team who cares for chimpanzees serving as “mom” to the 40+ orphans, nurturing them and helping them form bonds with the other chimpanzees in the organization’s care to ensure they have fulfilling lives in their sanctuary family, providing love, enrichment, and refuge.
James and Jenny were recently the focus of a TV series, Baby Chimp Rescue, which aired on BBC and AMC.

Japan’s space agency wants to keep the satellite’s cameras out of military hands.
An unusual geopolitical situation is brewing aboard the International Space Station. Prior to the military coup in Myanmar earlier this year, Japan’s space agency JAXA had been collaborating with the country to build microsatellites that it planned to deploy in partnership with Myanmar’s government.
Now, JAXA has no idea what to do with the pair of 50-kilogram satellites, according to SlashGear. And while Japanese scientists hope to bring the agriculture and fishery-monitoring satellites to life, they’re currently holding them on the ISS instead of deploying them out of fear they might be misused for military purposes — a striking example of real-world geopolitics spilling over into space.
After the military coup in Myanmar, Teppei Kasai, the Asia program director for the group Human Rights Watch noted that it would be relatively straightforward to use the satellites’ Earth-facing cameras for military or surveillance purposes, according to SlashGear.
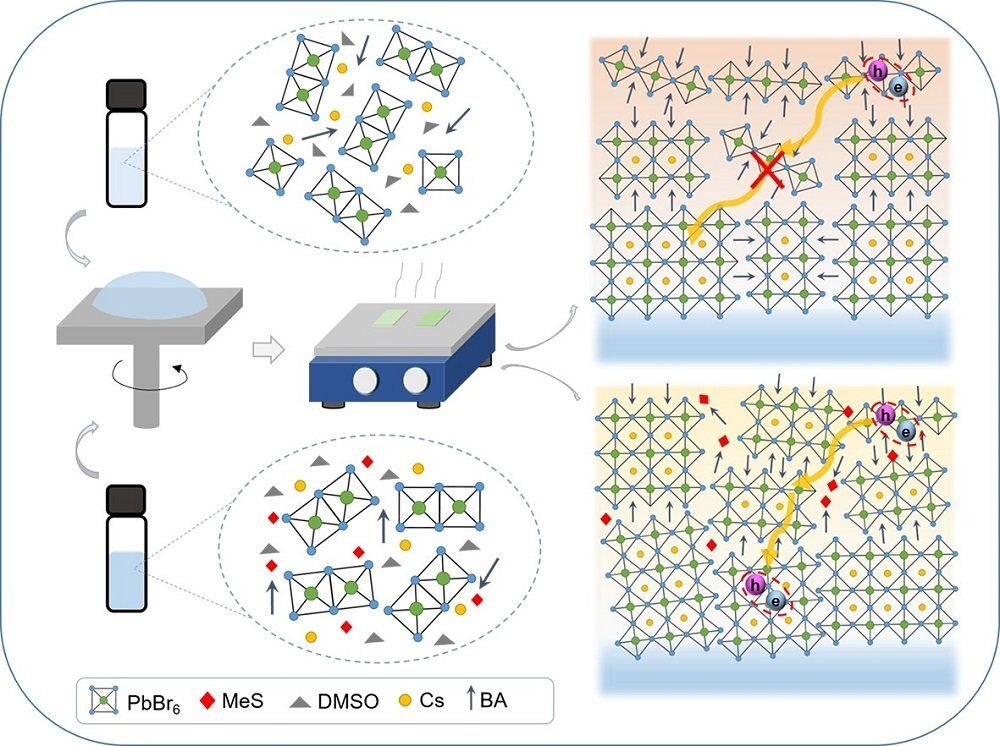
Energy efficient light-emitting diodes (LEDs) have been used in our everyday life for many decades. But the quest for better LEDs, offering both lower costs and brighter colors, has recently drawn scientists to a material called perovskite. A recent joint-research project co-led by the scientist from City University of Hong Kong (CityU) has now developed a 2-D perovskite material for the most efficient LEDs.
From household lighting to mobile phone displays, from pinpoint lighting needed for endoscopy procedures, to light source to grow vegetables in Space, LEDs are everywhere. Yet current high-quality LEDs still need to be processed at high temperatures and using elaborated deposition technologies—which makes their production cost expensive.
Scientists have recently realized that metal halide perovskites —semiconductor materials with the same structure as calcium titanate mineral, but with another elemental composition—are extremely promising candidate for next generation LEDs. These perovskites can be processed into LEDs from solution at room temperature, thus largely reducing their production cost. Yet the electro-luminescence performance of perovskites in LEDs still has a room for improvements.


While these tools will enable our society to reopen (and stay open) by improving detection of the virus, CRISPR will also have an important effect on the way we treat other diseases. In 2021, we will see increased use of CRISPR-Cas enzymes to underpin a new generation of cost-effective, individualised therapies. With CRISPR enzymes, we can cut DNA at precise locations, using specifically designed proteins, and insert or delete pieces of DNA to correct mutations.
As we deepen our understanding of the human genome and genetic disorders, patients with previously intractable diseases, such as sickle-cell disease and cancer, will benefit more widely from CRISPR-based therapies that are rapidly moving from the lab to the clinic. In 2019, sickle-cell patient Victoria Gray, for example, became one of the first patients in the world to receive CRISPR therapy for her genetic disease. She has already seen significant improvements to her health, including reduced pain and less frequent need for blood transfusions.
CRISPR will also allow us to act more boldly in the face of other important, interconnected issues such as food security, environmental sustainability and social inequality. The technology will help us grow more nutritious and robust crops, establish “gene drives” to control the spread of other infectious diseases such as Zika, and develop cleaner energy sources such as algae-based biofuels.