Lumacyte CEO on how real-time insight is driving down manufacturing failures and opening doors for more patients.



A new study published by Mayo Clinic researchers suggests that ovarian cancer cells quickly activate a survival response after PARP inhibitor treatment, and blocking this early response may make this class of drugs work better. The research is published in the journal Science Translational Medicine.
PARP inhibitors are a common treatment for ovarian cancer and can be especially effective in cancers with impaired DNA repair. However, many tumors eventually stop responding, even when the drugs initially show results. The new research identifies a way cancer cells may survive PARP inhibitor treatment early on, and it points to a potential strategy to block that response.
In the study, researchers found that ovarian cancer cells rapidly activate a pro-survival program after exposure to PARP inhibitors. A key driver of this response is FRA1, a transcription factor that helps turn on genes that allow cancer cells to adapt and avoid cell death.


What if we could test spinal cord injury therapies in human tissue without a clinical trial?
It could be possible, as spinal cord organoids derived from human stem cells now replicate real injury responses.
Read more.
Organoids developed from human stem cells modeled spinal cord injuries, providing a powerful in vitro tool to evaluate regenerative therapies for CNS injuries.
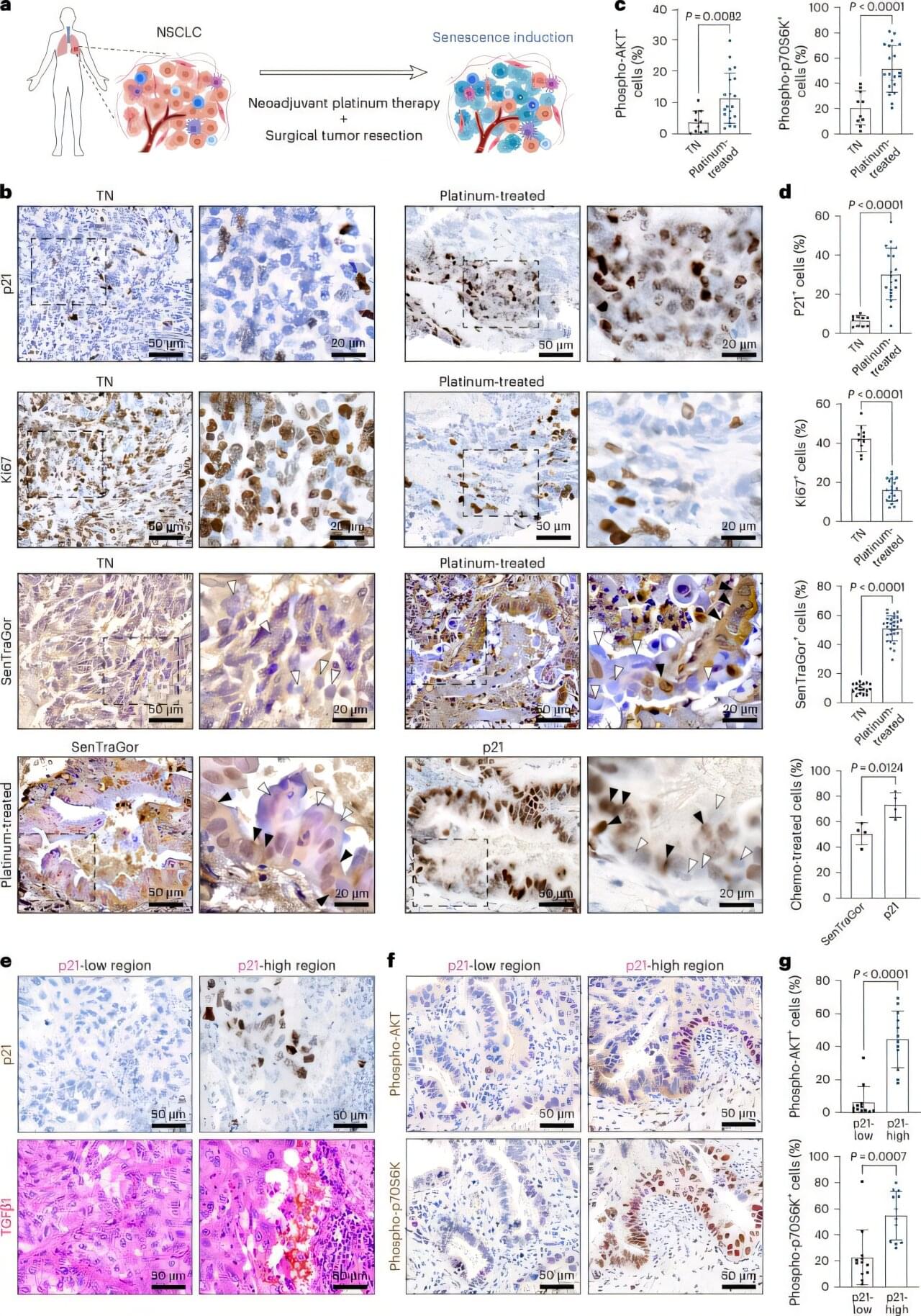
Researchers have identified a biological mechanism that helps explain why some lung and ovarian cancers become resistant to chemotherapy, offering insight into why cancers recur. The study, published in Nature Aging this month, investigated how platinum-based chemotherapies such as cisplatin negatively affect tumor behavior in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) and high-grade serous ovarian cancer (HGSOC). Although these treatments are widely used, their long-term effectiveness is often limited when tumors return or stop responding.
Professor Ljiljana Fruk and Muhamad Hartono from the Department of Chemical Engineering and Biotechnology (CEB) contributed to the international collaboration, led by researchers from the Early Cancer Institute and the Cancer Research UK Cambridge Institute. Their involvement follows her Bionano Engineering group’s recent development of a urine test for early lung cancer detection.

In a study published today, Friday, February 13, 2026, in the journal Nature Aging, researchers show that blood-based biomarkers can support accurate dementia diagnosis across diverse populations when integrated with cognitive and neuroimaging measures. Blood-based biomarkers are emerging as one of the most promising advances for the global diagnosis of dementia, including Alzheimer’s disease and frontotemporal lobar degeneration. These tests offer a more accessible, scalable, and cost-effective alternative to traditional diagnostic tools such as brain imaging or cerebrospinal fluid analysis.
However, most blood-based biomarkers have been developed and validated primarily in relatively homogeneous populations. Genetic background, overall physical health, and environmental and social exposures can substantially influence biomarker levels, raising concerns about how well these tests perform across diverse populations worldwide.
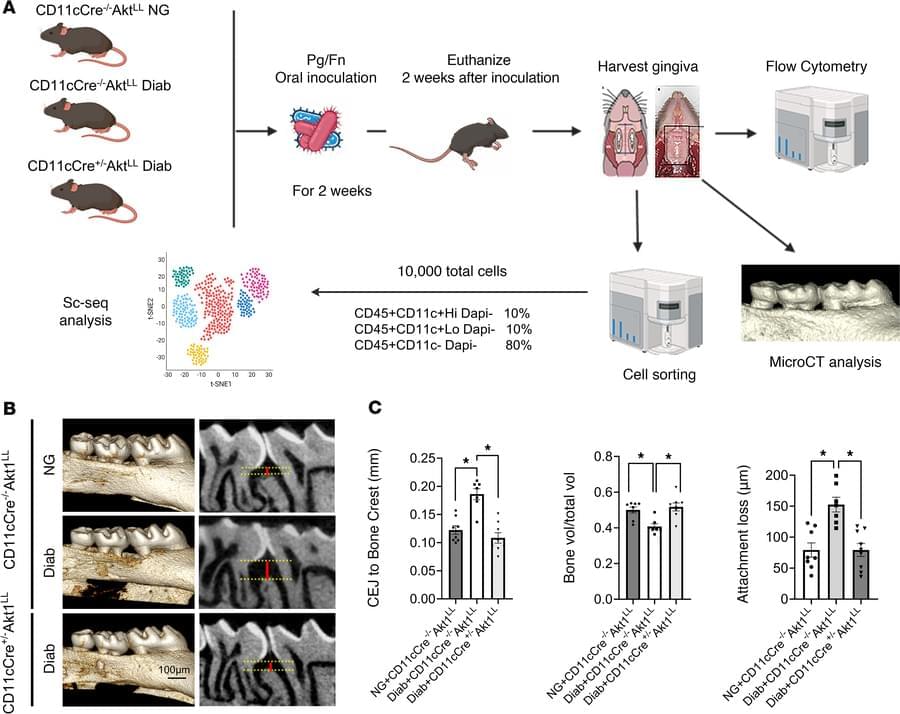
Dana T. Graves & team identify the CD137L/CD137 axis as a pivotal mediator of diabetes-induced inflammatory tissue destruction, in which dendritic cell produced CD137L activates γδ T-cells through CD137, leading to a dysregulated host response and worsening damage from bacterial challenge:
The figure shows microCT images of 3D reconstruction of the molar teeth from mouse models of periodontitis injected with control, CD137L-agonist, CD137L-antagonist antibodies.
1Hospital of Stomatology, Guanghua School of Stomatology and.
2Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Stomatology, Sun Yat-sen University, Guangzhou, Guangdong, China.
3Department of Periodontics, School of Dental Medicine, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, USA.
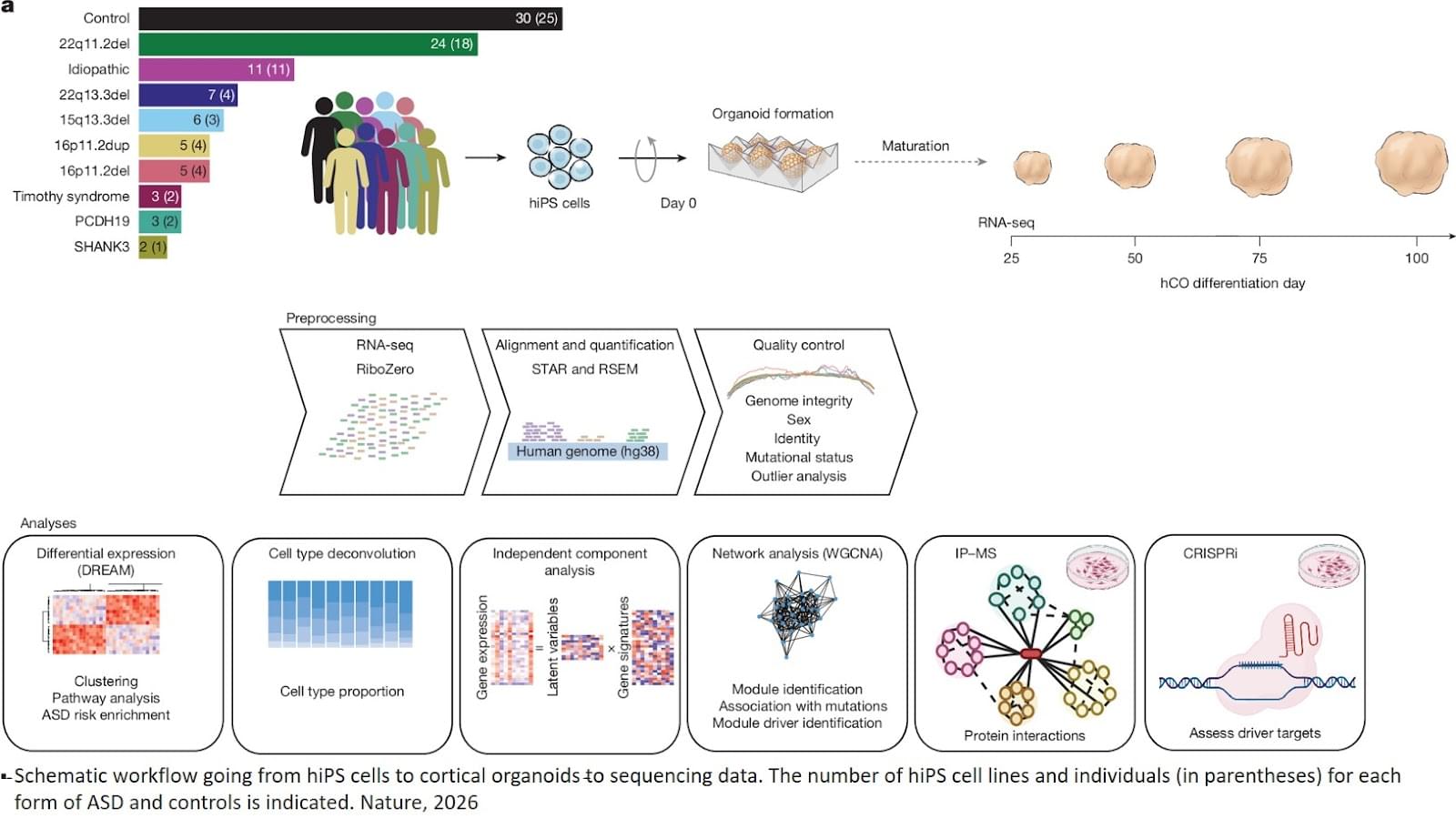
The new study, published in the journal Nature, provides new insights by demonstrating that while different mutations affect the developing brain in initially distinct ways, they increasingly impact overlapping molecular pathways as development progresses.
Researchers monitored the gene expression of the organoids over 100 days as they developed, which allowed researchers to observe how genetic changes affect brain during the critical early development windows.
Early in development, each genetic form showed distinct molecular signatures. However, as the organoids matured, these different mutations increasingly affected similar biological processes, particularly those involved in neuronal maturation and synapse formation.
The researchers identified a network of genes involved in regulating gene expression and chromatin remodeling, which is the process by which DNA is packaged and made accessible for reading. This network appears to play a central role in this convergence. Using CRISPR technology to individually reduce the activity of these regulatory genes in neural cells, the team confirmed that many of them control downstream pathways were previously linked to autism.
Notably, the study found few consistent molecular changes in organoids derived from individuals with idiopathic autism, likely reflecting the highly complex genetic architecture of autism that doesn’t involve major mutations. This finding underscores the need for much larger studies to understand the more common, polygenic forms of autism. ScienceMission sciencenewshighlights.
The researchers have created a comprehensive map showing how eight different genetic mutations associated with autism spectrum disorder affect early brain development, providing new insights into the ways diverse genetic causes may lead to shared features and symptoms of the disorder.
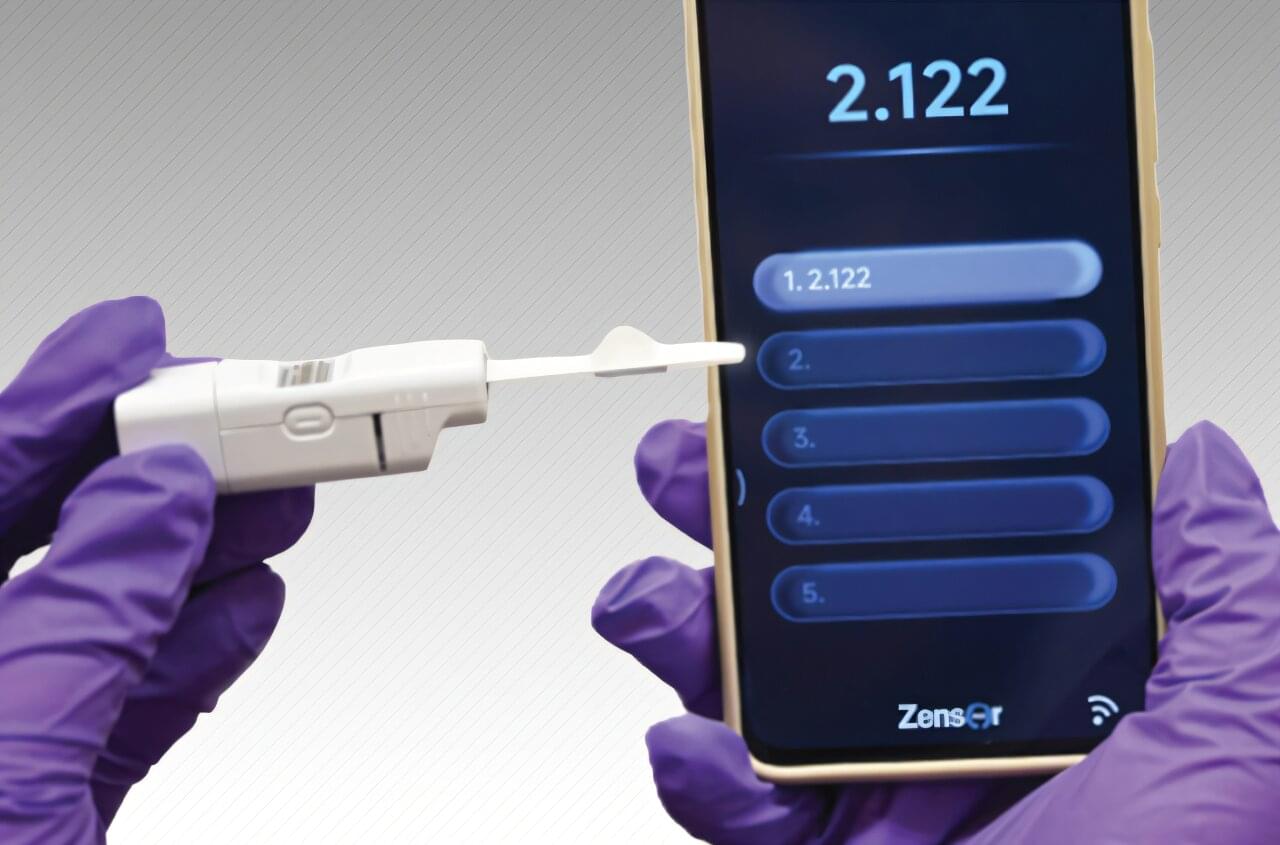
A wearable biosensor developed by Washington State University researchers could improve wireless glucose monitoring for people with diabetes, making it more cost-effective, accurate, and less invasive than current models. The WSU researchers have developed a wearable and user-friendly sensor that uses microneedles and sensors to measure sugar in the fluid around cells, providing an alternative to continuous glucose monitoring systems. Reporting in the journal The Analyst, the researchers were able to accurately detect sugar levels and wirelessly transmit the information to a smartphone in real time.
“We were able to amplify the signal through our new single-atom catalyst and make sensors that are smaller, smarter, and more sensitive,” said Annie Du, research professor in WSU’s College of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences and co-corresponding author on the work. “This is the future and provides a foundation for being able to detect other disease biomarkers in the body.”
Measuring glucose levels is important for diabetes, helping to keep patients healthy and preventing complications. Continuous glucose monitors on the market require the use of small needles to insert the monitor, and people can get skin irritation or rashes from the chemical processes that are done under the skin. Furthermore, they’re not always sensitive enough.

This case report describes mogamulizumab-associated Kaposi sarcoma in 2 patients with primary cutaneous T-cell lymphomas.
📄Read the full report.
Corresponding Author: Emilie Holder, MD, Service de Dermatologie, Hospices Civils de Lyon, Hôpital Lyon Sud, F-69495 Oullins-Pierre-Bénite, France ([email protected]).
Published Online: February 11, 2026. doi:10.1001/jamadermatol.2025.
Conflict of Interest Disclosures: Dr Dalle reported grants from Bristol Myers Squibb, Merck Sharp & Dohme, Pierre Fabre, and Regeneron, and his spouse is an employee of Sanofi outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported.