The findings could help predict which glioblastoma patients are most likely to benefit from immunotherapy. Read more.
An abstract is unavailable.

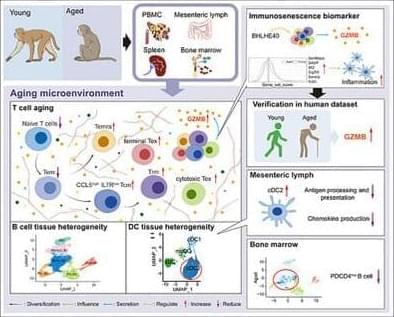
For the first time, researchers have directly visualized how newly formed cellular organelles leave the endoplasmic reticulum (ER) and transition onto microtubule tracks inside living cells. This new finding reveals that the ER plays an active and dynamic role in steering intracellular traffic rather than serving as a passive factory. The study is published in the journal ACS Nano.
For the study led by Director Cho Minhaeng at the Center for Molecular Spectroscopy and Dynamics within the Institute for Basic Science and Professor Hong Seok-Cheol at Korea University, the research team captured in real time the moment an autophagosome—an organelle responsible for cellular recycling—moves from the ER onto a neighboring microtubule. This long-sought observation provides direct experimental evidence for how intracellular transport is coordinated at nanoscopic contact sites within the crowded environment of living cells.
Autophagy is an essential cellular process in which damaged proteins and aged organelles are enclosed by double-membrane structures and delivered for degradation and recycling. The importance of autophagy was recognized by the 2016 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine awarded to Yoshinori Ohsumi. Although scientists have long proposed that autophagosomes are transferred from the ER to microtubules at specialized contact sites, direct real-time experimental evidence of this cellular “handoff” had remained out of reach—until now.
In a bid to treat blindness, Life Biosciences will try out potent cellular reprogramming technology on volunteers.
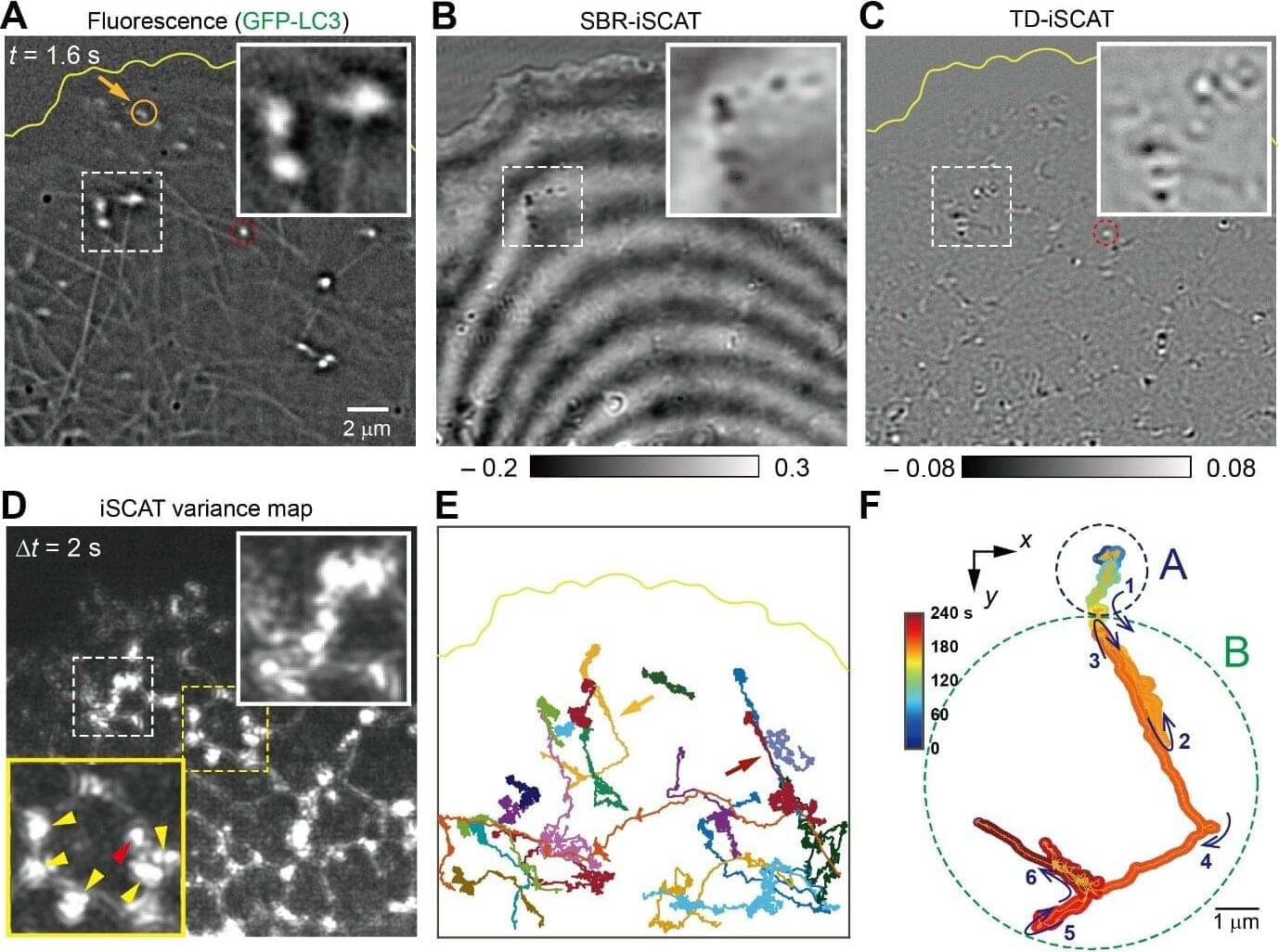
Scientists at Oregon State University have developed a new nanomaterial that triggers a pair of chemical reactions inside cancer cells, killing the cells via oxidative stress while leaving healthy tissues alone. The study led by Oleh and Olena Taratula and Chao Wang of the OSU College of Pharmacy appears in Advanced Functional Materials.
The findings advance the field of chemodynamic therapy (CDT), an emerging treatment approach based on the distinctive biochemical environment found in cancer cells. Compared to healthy tissues, malignant tumors are more acidic and have elevated concentrations of hydrogen peroxide, the scientists explain.
Conventional CDT works by using the tumor microenvironment to trigger the chemical production of hydroxyl radicals—molecules, made up of oxygen and hydrogen—with an unpaired electron. These reactive oxygen species are able to damage cells through oxidation by stealing electrons from molecules like lipids, proteins, and DNA.

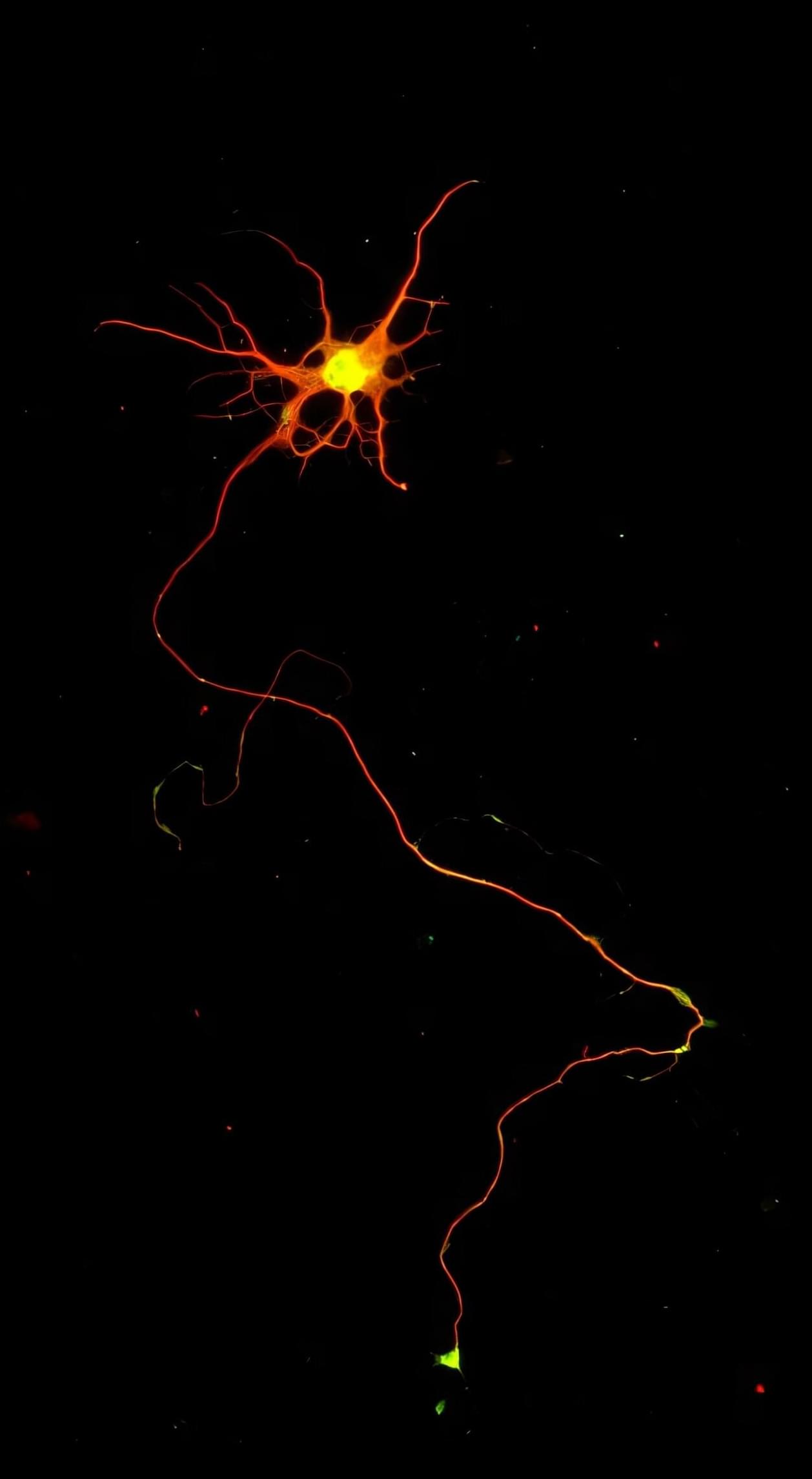
Researchers have developed a way to grow a highly specialized subset of brain nerve cells that are involved in motor neuron disease and damaged in spinal injuries. Their study, published today in eLife, presents fundamental findings on the directed differentiation of a rare population of special brain progenitors—also known as adult or parent stem cells—into corticospinal-like neurons. The editors note that the work provides compelling data demonstrating the success of this new approach.
The findings set the stage for further research into whether these molecularly directed neurons can form functional connections in the body, and to explore their potential use in human diseases where corticospinal neurons are compromised.
New in practicalRO.
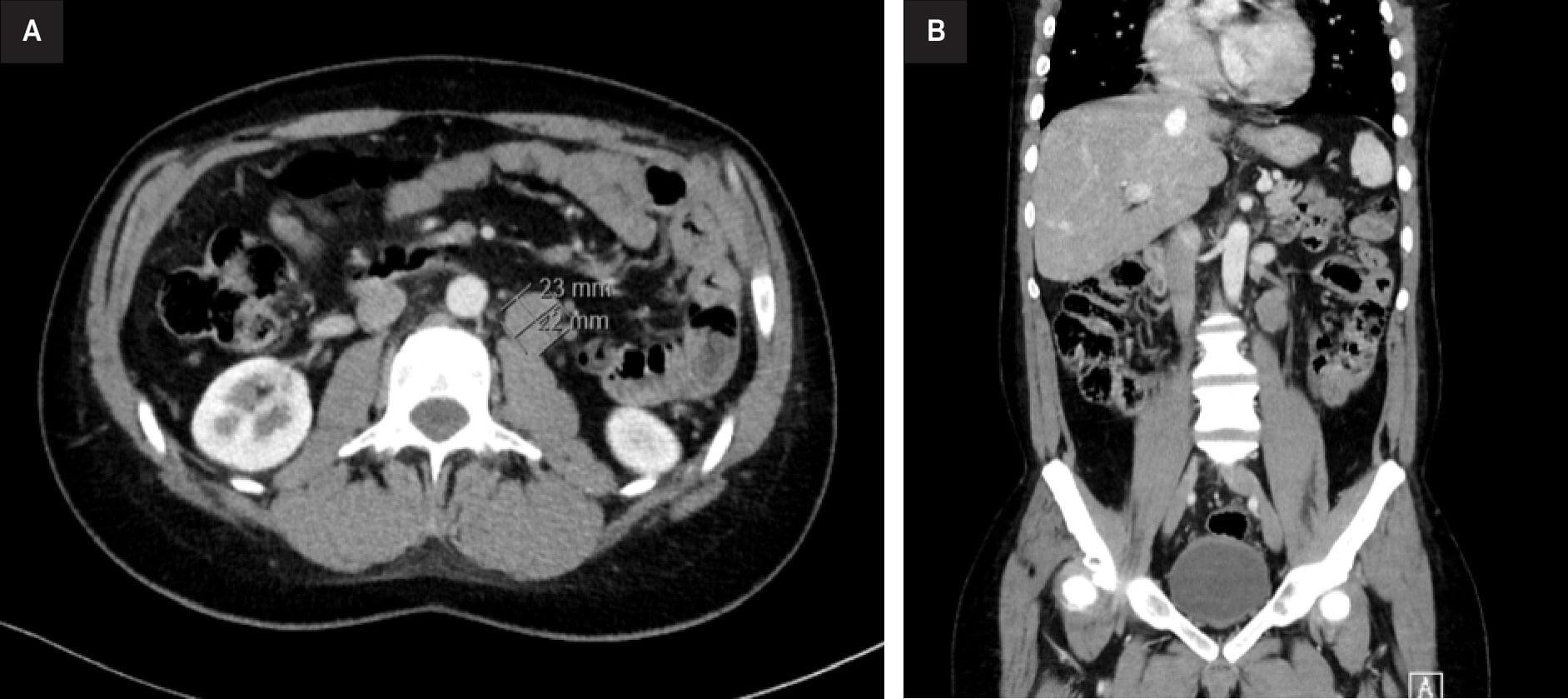
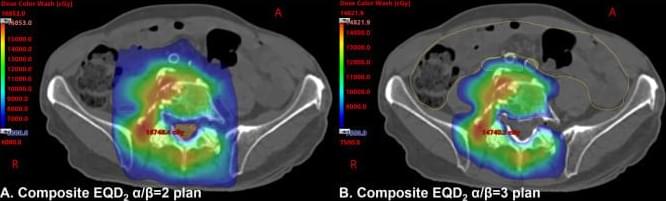
We sought to develop a systematic spine reirradiation planning protocol prioritizing patient safety and maximizing tumor dose delivery. Patients were presented at a Multidisciplinary Spine Oncology Tumor Board to confirm suspicion for recurrent or progressive malignancy and were evaluated in the clinic by the Department of Radiation Oncology and Neurosurgery. Suitable patients proceeded to computed tomography (CT)/magnetic resonance imaging scan simulation. A dedicated physics pathway was activated with the fusion of the magnetic resonance imaging scan and planned CT scan, verified independently by 2 physicists.