Ranjan KC shared a link to the group: Ray Kurzweil.
With the Linpack exaflops milestone achieved by the Frontier supercomputer at Oak Ridge National Laboratory, the United States is turning its attention to the next crop of exascale machines, some 5-10x more performant than Frontier. At least one such system is being planned for the 2025–2030 timeline, and the DOE is soliciting input from the vendor community to inform the design and procurement process.
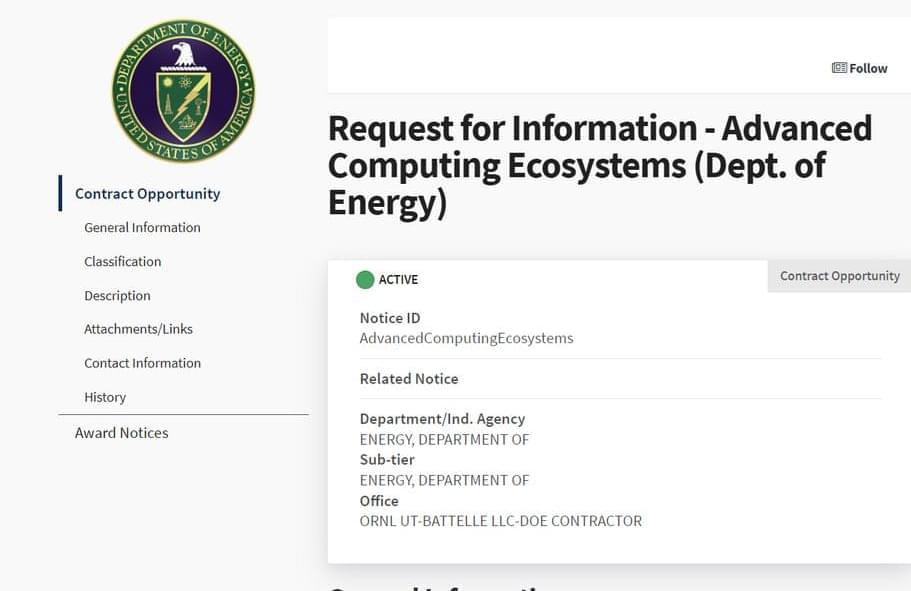
A request for information (RFI) was issued today by the Department of Energy, seeking feedback from computing hardware and software vendors, system integrators, and other entities to assist the DOE National Laboratories in planning for next-gen exascale systems. The RFI says responses will “inform one or more DOE system acquisition RFPs, which will describe requirements for system deliveries in the 2025–2030 timeframe.” This could include the successor to Frontier (aka OLCF-6), the successor to Aurora (aka ALCF-5), the successor to Crossroads (aka ATS-5), the successor to El Capitan (aka ATS-6) as well as a future NERSC system (possibly NERSC-11). Note that of the “predecessor systems,” only Frontier has been installed so far.
Here’s an excerpt from the RFI: